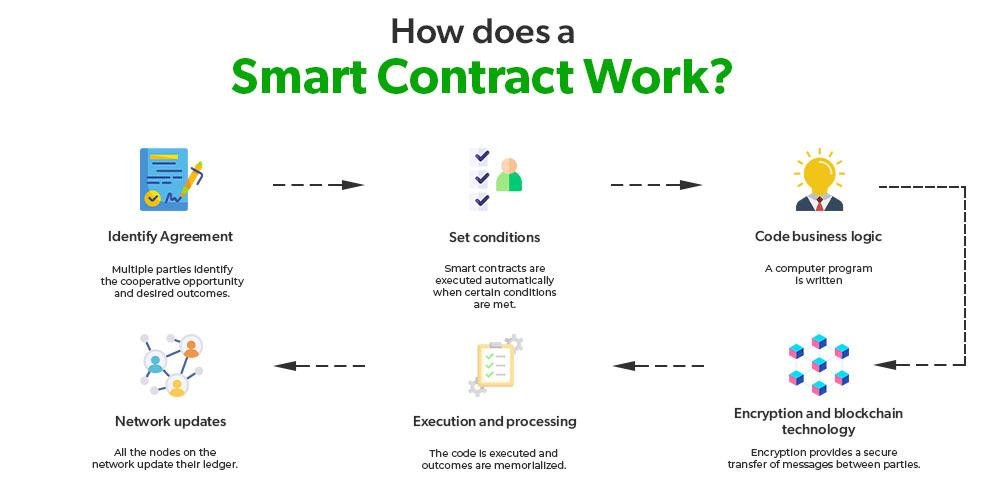
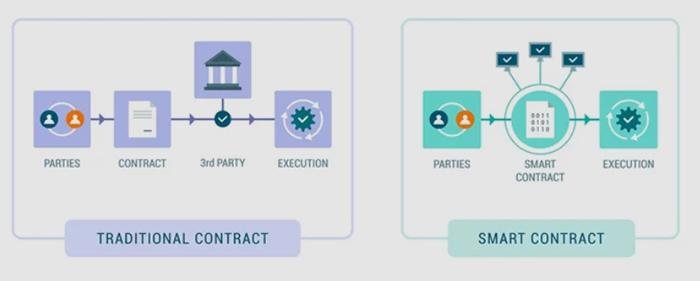
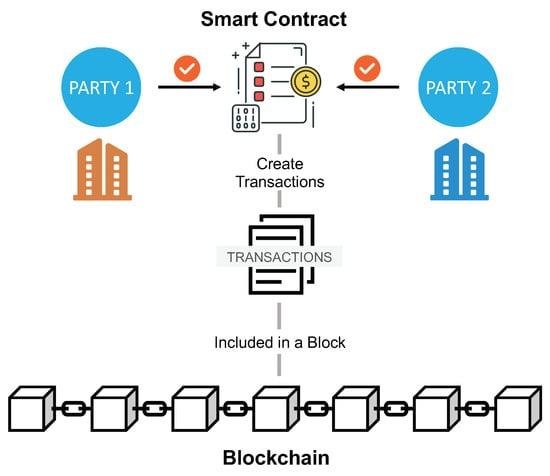
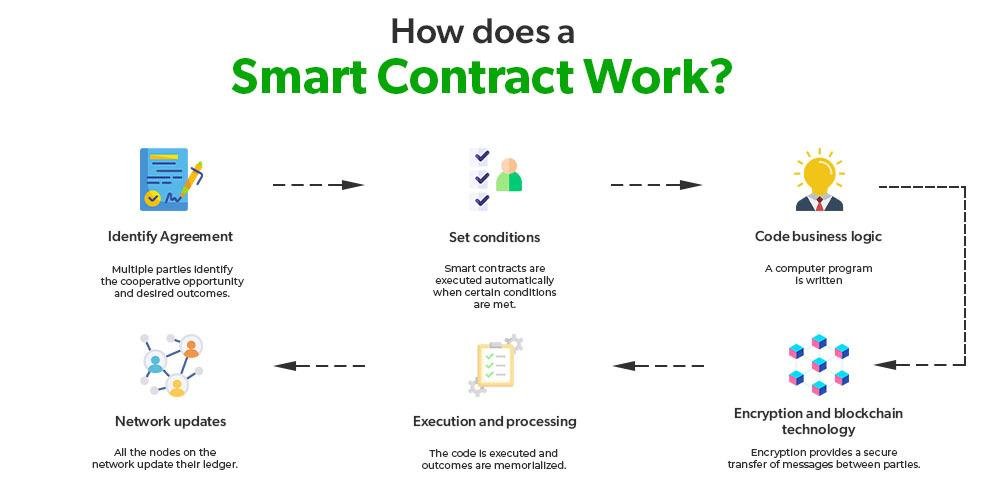
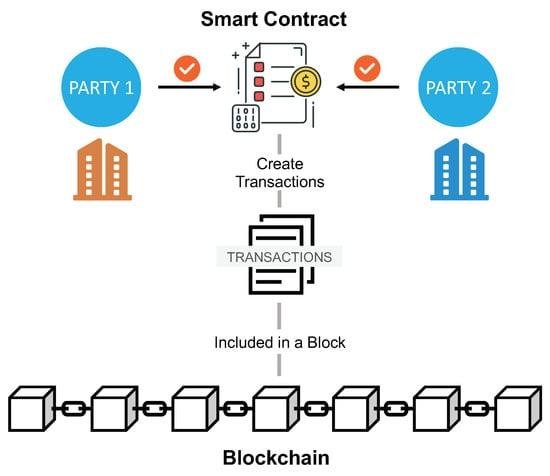
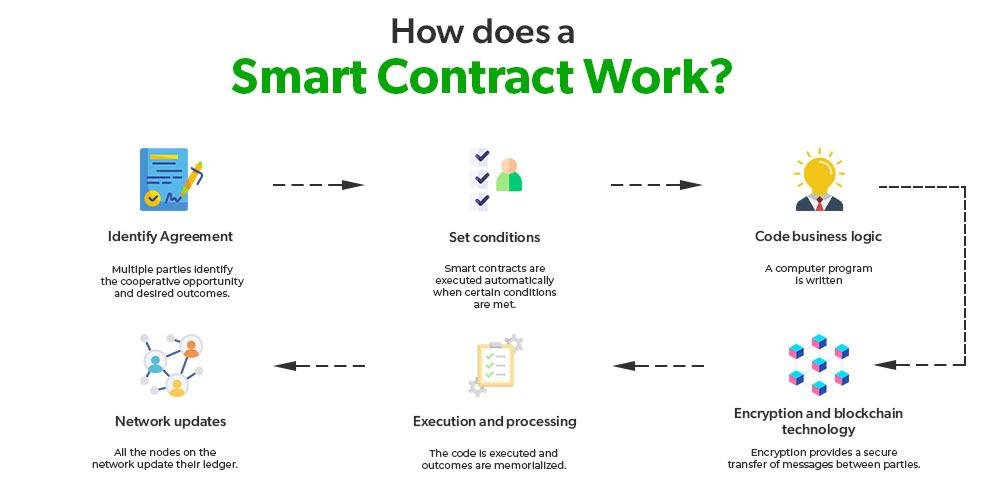
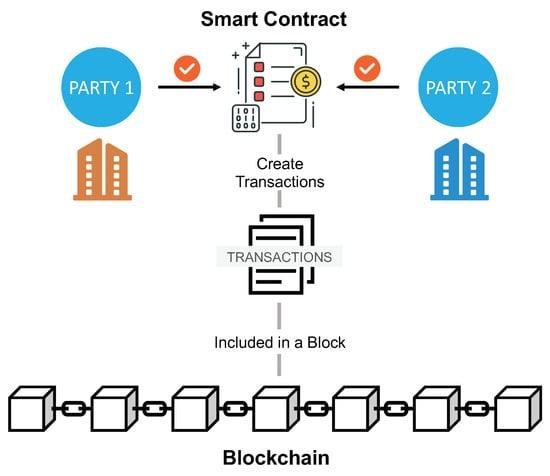
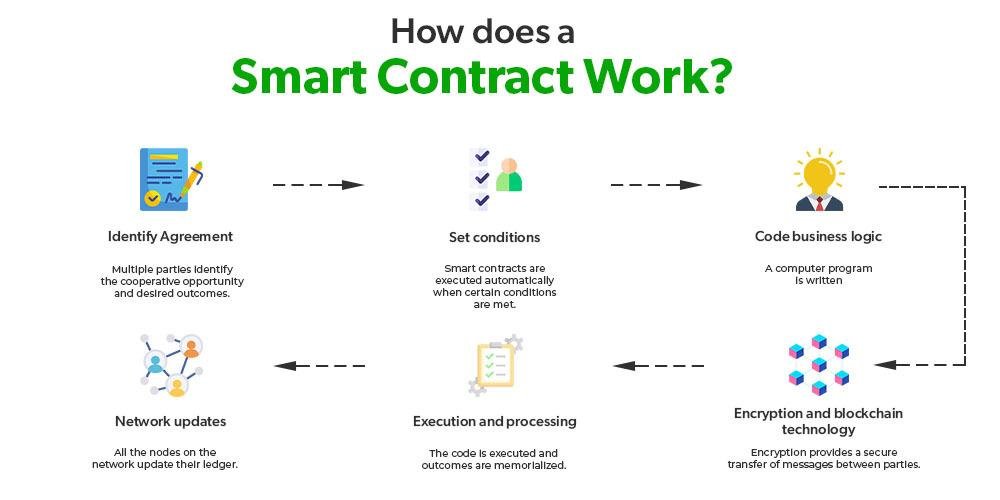
Challenges in Implementing AI Solutions in Legal Practices

Table of Contents
Introduction
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into legal practices presents a myriad of challenges that can hinder its effective implementation. These challenges encompass a range of factors, including ethical considerations, data privacy concerns, resistance to change within traditional legal frameworks, and the need for substantial investment in technology and training. Additionally, the complexity of legal language and the variability of legal systems across jurisdictions complicate the development of AI solutions that can be universally applied. As legal professionals navigate these obstacles, they must also address issues related to accountability, bias in AI algorithms, and the potential impact on employment within the legal sector. Understanding and overcoming these challenges is crucial for harnessing the full potential of AI in enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility in legal practices.
Data Privacy Concerns
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into legal practices has the potential to revolutionize the industry, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in various processes. However, one of the most pressing challenges that legal professionals face in this transition is the issue of data privacy. As AI systems often rely on vast amounts of data to function effectively, the handling, storage, and processing of sensitive legal information raise significant concerns regarding compliance with data protection regulations and the ethical implications of data usage.
To begin with, the legal sector is inherently data-intensive, dealing with confidential client information, sensitive case details, and proprietary legal strategies. The introduction of AI solutions necessitates the collection and analysis of this data, which can inadvertently expose law firms to risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized access. As a result, legal practitioners must navigate a complex landscape of data privacy laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and various state-level regulations in the United States. These regulations impose stringent requirements on how personal data is collected, processed, and stored, compelling law firms to ensure that their AI systems are compliant. Failure to adhere to these regulations can lead to severe penalties, reputational damage, and loss of client trust.
Moreover, the challenge of data privacy is compounded by the fact that AI systems often operate as “black boxes,” making it difficult for legal professionals to understand how data is being used and processed. This lack of transparency can create apprehension among clients who may be concerned about how their information is being handled. Legal practitioners must therefore establish clear protocols and guidelines for data usage within AI systems, ensuring that clients are informed about how their data will be utilized and the measures in place to protect their privacy. This not only fosters trust but also aligns with ethical obligations to maintain client confidentiality.
In addition to regulatory compliance and transparency, the issue of data quality cannot be overlooked. AI systems require high-quality, relevant data to produce accurate results. However, the legal industry often grapples with data that is fragmented, inconsistent, or outdated. This poses a dual challenge: not only must law firms ensure that they are collecting and using data in a manner that respects privacy, but they must also invest in data management practices that enhance the quality of the information being fed into AI systems. This may involve implementing robust data governance frameworks, conducting regular audits, and training staff on best practices for data handling.
Furthermore, as AI technologies evolve, so too do the methods employed by malicious actors seeking to exploit vulnerabilities in data security. Law firms must remain vigilant and proactive in their approach to cybersecurity, continuously updating their systems and protocols to mitigate risks. This includes investing in advanced security measures, conducting regular risk assessments, and fostering a culture of awareness among employees regarding data privacy issues.
In conclusion, while the potential benefits of AI in legal practices are substantial, the challenges associated with data privacy cannot be underestimated. Legal professionals must navigate a complex regulatory environment, ensure transparency in data usage, maintain high data quality, and adopt robust cybersecurity measures. By addressing these challenges head-on, law firms can harness the power of AI while safeguarding the privacy and trust of their clients, ultimately paving the way for a more efficient and secure legal landscape.
Integration with Existing Systems

The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) solutions into legal practices presents a myriad of challenges, particularly when it comes to aligning these advanced technologies with existing systems. Legal firms often rely on a complex web of software and processes that have been developed over many years, and introducing AI into this environment requires careful consideration and strategic planning. One of the primary hurdles is the compatibility of AI tools with legacy systems. Many legal practices utilize outdated software that may not support the advanced functionalities of modern AI applications. This incompatibility can lead to significant disruptions in workflow, as firms may need to invest in upgrading or replacing existing systems to facilitate a seamless integration.
Moreover, the data silos that often exist within legal practices can complicate the integration process. Legal firms typically manage vast amounts of sensitive information across various departments, and these data repositories may not communicate effectively with new AI solutions. Consequently, the challenge lies in ensuring that AI systems can access and analyze relevant data without compromising security or violating privacy regulations. This necessitates a thorough assessment of data governance policies and the implementation of robust security measures to protect client confidentiality while enabling AI to function optimally.
In addition to technical compatibility, there is also the issue of user adoption. Legal professionals, who may be accustomed to traditional methods of practice, can be resistant to change, particularly when it involves new technologies. This resistance can stem from a lack of understanding of AI capabilities or concerns about job displacement. Therefore, it is crucial for firms to invest in comprehensive training programs that not only educate staff about the functionalities of AI tools but also demonstrate their potential to enhance productivity and improve client outcomes. By fostering a culture of innovation and encouraging open dialogue about the benefits of AI, firms can mitigate resistance and promote a smoother transition.
Furthermore, the integration of AI solutions often requires a reevaluation of existing workflows and processes. Legal practices must critically assess how AI can be incorporated into their operations without disrupting established procedures. This may involve redesigning workflows to leverage AI capabilities effectively, which can be a daunting task for firms that have long relied on traditional methods. Engaging stakeholders from various departments in this process is essential, as their insights can help identify areas where AI can add value and streamline operations.
Another significant challenge is the ongoing maintenance and support of AI systems once they are integrated. Legal practices must ensure that they have the necessary resources and expertise to manage these technologies effectively. This includes not only technical support but also continuous monitoring and evaluation of AI performance to ensure that it meets the evolving needs of the firm. As legal practices navigate the complexities of AI integration, they must remain agile and adaptable, ready to make adjustments as technology and legal requirements evolve.
In conclusion, while the integration of AI solutions into legal practices holds great promise for enhancing efficiency and improving service delivery, it is fraught with challenges. From ensuring compatibility with existing systems to fostering user adoption and maintaining ongoing support, legal firms must approach this transition with a strategic mindset. By addressing these challenges head-on, legal practices can harness the full potential of AI, ultimately transforming the way they operate and serve their clients.
Resistance to Change Among Staff
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) solutions into legal practices has the potential to revolutionize the industry, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in various tasks. However, one of the most significant challenges faced during this transition is the resistance to change among staff. This resistance can stem from a variety of factors, including fear of job displacement, a lack of understanding of the technology, and the comfort of established workflows. As legal professionals grapple with the implications of AI, it becomes crucial to address these concerns to facilitate a smoother implementation process.
To begin with, the fear of job displacement is a prominent issue that often leads to apprehension among legal staff. Many employees may perceive AI as a threat to their roles, believing that automation will render their skills obsolete. This fear can create a defensive attitude towards new technologies, resulting in reluctance to engage with AI tools. Consequently, it is essential for legal firms to communicate the complementary nature of AI, emphasizing that these technologies are designed to augment human capabilities rather than replace them. By highlighting the potential for AI to handle repetitive tasks, such as document review and legal research, firms can reassure staff that their expertise will remain invaluable in more complex and nuanced areas of legal practice.
Moreover, a lack of understanding regarding AI technology can exacerbate resistance among staff. Many legal professionals may not possess a technical background, leading to misconceptions about how AI operates and its potential benefits. This knowledge gap can foster skepticism and hinder the adoption of AI solutions. To mitigate this issue, legal practices should invest in comprehensive training programs that educate staff about AI functionalities and applications within the legal context. By providing hands-on experience and demonstrating successful case studies, firms can cultivate a more informed workforce that is better equipped to embrace technological advancements.
In addition to fear and misunderstanding, the comfort of established workflows plays a significant role in resistance to change. Legal practices often rely on traditional methods that have been honed over years, creating a sense of stability and predictability. Introducing AI solutions can disrupt these established processes, leading to discomfort and pushback from staff who may be hesitant to alter their routines. To address this challenge, it is vital for firms to adopt a gradual approach to implementation. By piloting AI tools in specific areas before a full-scale rollout, firms can allow staff to acclimate to the changes at a manageable pace. This incremental strategy not only reduces anxiety but also provides opportunities for feedback and adjustment, fostering a sense of ownership among employees.
Furthermore, leadership plays a critical role in overcoming resistance to change. When firm leaders actively champion AI initiatives and demonstrate their commitment to integrating these technologies, it can inspire confidence among staff. Transparent communication about the rationale behind adopting AI, along with the anticipated benefits for both the firm and its employees, can help alleviate concerns. Additionally, involving staff in the decision-making process can create a sense of collaboration and shared purpose, further reducing resistance.
In conclusion, while the implementation of AI solutions in legal practices presents numerous advantages, overcoming resistance to change among staff is essential for successful integration. By addressing fears of job displacement, providing education and training, adopting gradual implementation strategies, and fostering strong leadership support, legal firms can create an environment conducive to embracing technological advancements. Ultimately, navigating these challenges will not only enhance the efficiency of legal practices but also empower staff to thrive in an increasingly digital landscape.
Ethical and Regulatory Compliance
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into legal practices presents a myriad of challenges, particularly in the realm of ethical and regulatory compliance. As law firms increasingly adopt AI technologies to enhance efficiency and improve client services, they must navigate a complex landscape of ethical considerations and regulatory frameworks that govern the legal profession. This complexity is compounded by the rapid pace of technological advancement, which often outstrips existing regulations, leaving legal practitioners in a precarious position.
One of the foremost ethical challenges in implementing AI solutions is the potential for bias in algorithmic decision-making. AI systems are trained on historical data, which may reflect existing biases within the legal system. Consequently, if these biases are not adequately addressed, AI tools could inadvertently perpetuate discrimination in legal outcomes. For instance, predictive policing algorithms have faced scrutiny for disproportionately targeting marginalized communities, raising significant ethical concerns about fairness and justice. Legal practitioners must therefore ensure that the AI systems they employ are rigorously tested for bias and that they implement measures to mitigate any identified disparities.
Moreover, the issue of transparency in AI decision-making processes poses another ethical dilemma. Legal professionals are bound by principles of accountability and the duty to provide clients with clear and comprehensible advice. However, many AI systems operate as “black boxes,” making it difficult for practitioners to understand how decisions are made. This lack of transparency can hinder a lawyer’s ability to explain the rationale behind certain recommendations or outcomes, potentially undermining client trust. To address this challenge, law firms must prioritize the selection of AI tools that offer explainability, ensuring that the underlying processes are accessible and understandable.
In addition to ethical considerations, regulatory compliance presents a formidable challenge for legal practices adopting AI solutions. The legal profession is governed by a myriad of regulations that vary by jurisdiction, and the introduction of AI technologies complicates compliance with these rules. For instance, data privacy laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, impose strict requirements on how personal data is collected, processed, and stored. Legal practitioners must be vigilant in ensuring that their AI systems comply with these regulations, particularly when handling sensitive client information. Failure to adhere to data protection laws can result in severe penalties and damage to a firm’s reputation.
Furthermore, the evolving nature of AI technology means that regulatory frameworks often lag behind advancements in the field. This disconnect creates uncertainty for legal practitioners who must navigate an ambiguous regulatory environment. As AI continues to evolve, regulators are grappling with how to establish guidelines that protect clients while fostering innovation. Legal professionals must stay informed about emerging regulations and actively participate in discussions surrounding the ethical use of AI in the legal sector. By engaging with regulatory bodies, law firms can contribute to the development of frameworks that balance innovation with ethical considerations.
In conclusion, the challenges of ethical and regulatory compliance in implementing AI solutions in legal practices are multifaceted and require careful consideration. Legal practitioners must address issues of bias and transparency while ensuring adherence to complex regulatory requirements. As the legal landscape continues to evolve alongside technological advancements, it is imperative for law firms to remain proactive in their approach to AI integration. By prioritizing ethical considerations and engaging with regulatory developments, legal professionals can harness the potential of AI while upholding the integrity of the legal profession.
Conclusion
Implementing AI solutions in legal practices presents several challenges, including data privacy concerns, the need for significant investment in technology and training, resistance to change from legal professionals, and the complexity of integrating AI with existing systems. Additionally, the legal industry’s regulatory environment can complicate the adoption of AI, as firms must navigate compliance issues while ensuring the ethical use of technology. Overcoming these challenges requires a strategic approach that includes stakeholder engagement, ongoing education, and a clear understanding of the potential benefits and limitations of AI in the legal context.