Cloud Computing’s Impact on E-Discovery and Data Storage

-
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Cloud Computing’s Role in Streamlining E-Discovery Processes
- Enhancing Data Storage Solutions Through Cloud Technology
- The Cost Benefits of Cloud-Based E-Discovery Tools
- Security Challenges in Cloud Storage for E-Discovery
- Compliance and Regulatory Considerations in Cloud E-Discovery
- Future Trends in Cloud Computing and E-Discovery Integration
- Conclusion
Introduction
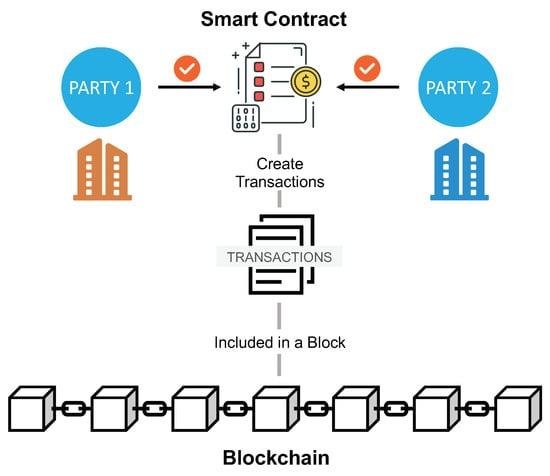
Cloud computing has revolutionized the landscape of e-discovery and data storage, offering organizations unprecedented scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. As legal and regulatory requirements for data management become increasingly complex, cloud solutions enable businesses to store vast amounts of information securely while facilitating rapid access and retrieval during e-discovery processes. The ability to leverage advanced analytics and machine learning within cloud environments enhances the efficiency of identifying relevant data, reducing the time and resources traditionally required for legal investigations. Furthermore, the cloud’s collaborative capabilities allow for seamless sharing and management of documents among legal teams, clients, and stakeholders, ultimately transforming how organizations approach data storage and e-discovery in an era defined by digital transformation.
Cloud Computing’s Role in Streamlining E-Discovery Processes
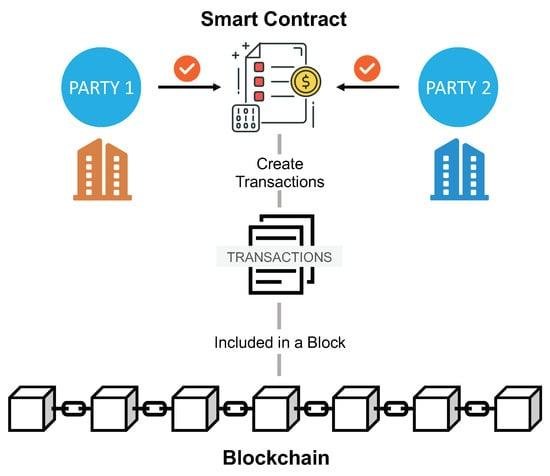
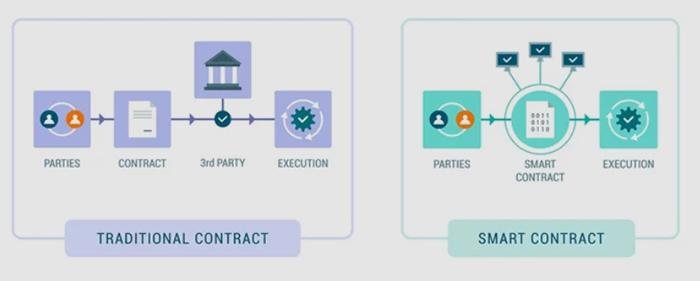
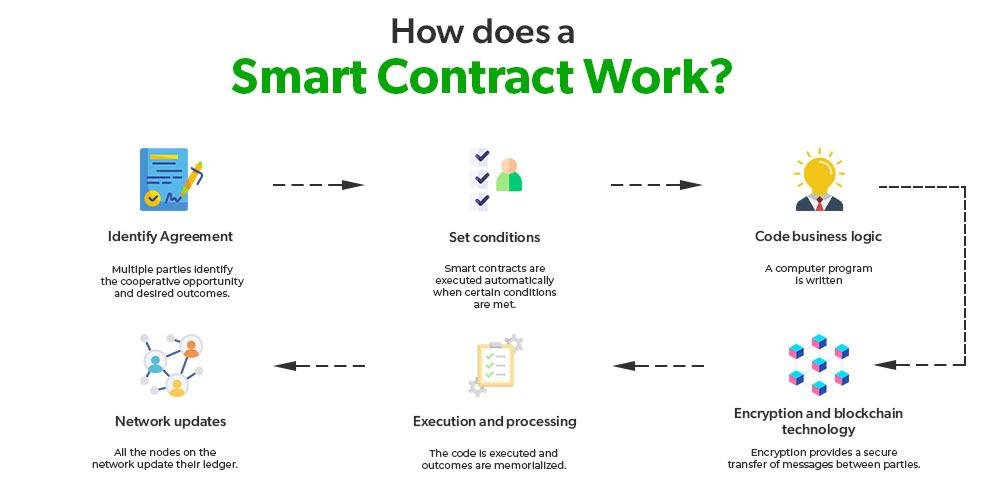
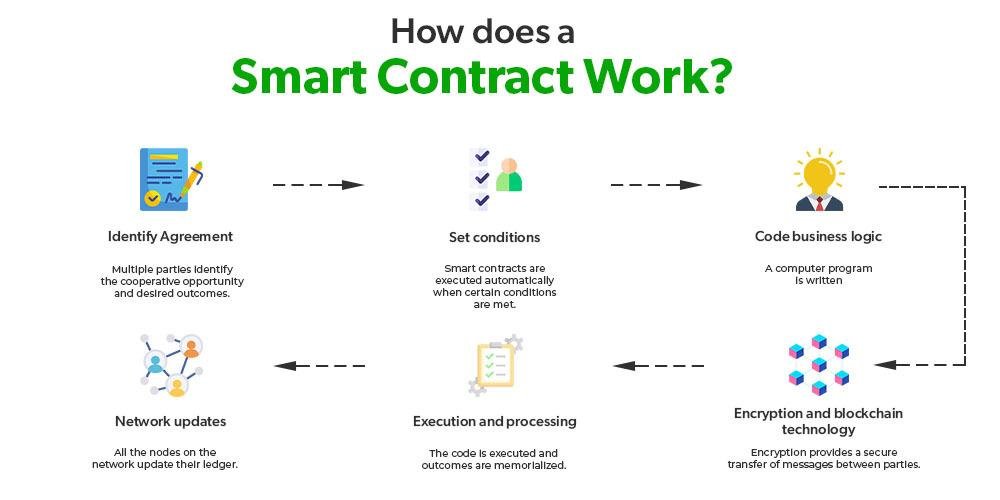
Cloud computing has revolutionized various sectors, and its impact on e-discovery processes is particularly noteworthy. As organizations increasingly rely on digital data, the need for efficient and effective e-discovery solutions has become paramount. E-discovery, the process of identifying, collecting, and producing electronically stored information (ESI) for legal proceedings, can be complex and resource-intensive. However, cloud computing offers a streamlined approach that enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of these processes.
One of the most significant advantages of cloud computing in e-discovery is its ability to provide scalable storage solutions. Traditional data storage methods often require substantial physical infrastructure, which can be both costly and time-consuming to manage. In contrast, cloud services allow organizations to store vast amounts of data without the need for extensive on-premises hardware. This scalability not only reduces costs but also enables organizations to quickly adapt to fluctuating data volumes, which is particularly beneficial during litigation when the amount of data required can vary dramatically.
Moreover, cloud computing facilitates easier access to data, which is crucial during e-discovery. With cloud-based solutions, legal teams can access necessary information from anywhere, at any time, provided they have an internet connection. This flexibility is particularly advantageous for organizations with remote teams or those that operate across multiple locations. By eliminating geographical barriers, cloud computing ensures that legal professionals can collaborate more effectively, share insights, and make informed decisions in real-time, ultimately expediting the e-discovery process.
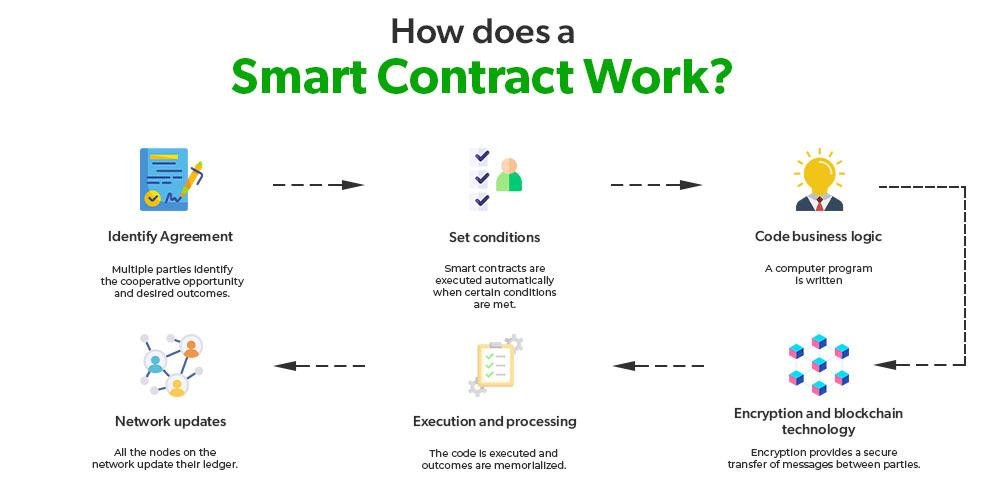
In addition to accessibility, cloud computing enhances the organization and management of data. Advanced cloud platforms often come equipped with sophisticated tools for data categorization, indexing, and searching. These features allow legal teams to quickly locate relevant documents and information, significantly reducing the time spent on manual searches. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning within cloud solutions can automate many aspects of the e-discovery process, such as predictive coding and data analysis. By leveraging these technologies, organizations can improve accuracy and efficiency, minimizing the risk of human error and ensuring that critical information is not overlooked.
Security is another critical aspect of e-discovery that cloud computing addresses effectively. As organizations handle sensitive data during legal proceedings, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of this information is paramount. Leading cloud service providers invest heavily in robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. These features not only protect data from unauthorized access but also help organizations comply with various legal and regulatory requirements. Consequently, legal teams can focus on their core responsibilities without the constant worry of data breaches or compliance issues.
Furthermore, the cost-effectiveness of cloud computing cannot be overstated. By reducing the need for physical infrastructure and associated maintenance costs, organizations can allocate resources more efficiently. This financial flexibility allows legal teams to invest in other critical areas, such as talent acquisition or advanced e-discovery tools, ultimately enhancing their overall capabilities.
In conclusion, cloud computing plays a pivotal role in streamlining e-discovery processes by providing scalable storage solutions, enhancing accessibility, improving data management, ensuring security, and offering cost-effective alternatives. As organizations continue to navigate the complexities of digital data in legal contexts, embracing cloud technology will undoubtedly lead to more efficient and effective e-discovery practices. The future of e-discovery is not only about managing data but also about leveraging innovative solutions that empower legal professionals to work smarter and more collaboratively.
Enhancing Data Storage Solutions Through Cloud Technology
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way organizations manage and store data, particularly in the realm of e-discovery. As businesses increasingly rely on digital information, the need for efficient, scalable, and secure data storage solutions has become paramount. The advent of cloud technology has not only addressed these needs but has also enhanced the overall process of data management, making it more streamlined and effective.
One of the most significant advantages of cloud technology is its ability to provide scalable storage solutions. Traditional data storage methods often require substantial upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure, which can be both costly and time-consuming. In contrast, cloud storage allows organizations to pay for only the storage they need, with the flexibility to scale up or down as requirements change. This adaptability is particularly beneficial in the context of e-discovery, where the volume of data can fluctuate dramatically based on the nature of legal proceedings. By leveraging cloud solutions, organizations can efficiently manage large datasets without the burden of maintaining physical servers.
Moreover, cloud technology enhances data accessibility, enabling legal teams to retrieve and analyze information from virtually anywhere with an internet connection. This level of accessibility is crucial in e-discovery, where timely access to data can significantly impact the outcome of legal cases. With cloud-based storage, teams can collaborate in real-time, sharing insights and findings instantaneously, which fosters a more agile and responsive approach to legal challenges. This collaborative environment not only improves efficiency but also enhances the quality of the work produced, as multiple perspectives can be integrated into the analysis.
In addition to scalability and accessibility, cloud computing offers robust security features that are essential for protecting sensitive data during the e-discovery process. Many cloud service providers implement advanced encryption protocols and multi-factor authentication to safeguard information from unauthorized access. This is particularly important in legal contexts, where the confidentiality of data is paramount. By utilizing cloud storage, organizations can benefit from the expertise of specialized providers who are dedicated to maintaining high security standards, thus alleviating some of the burdens associated with data protection.
Furthermore, cloud technology facilitates automated data management processes, which can significantly reduce the time and effort required for e-discovery. Advanced algorithms and machine learning tools can be employed to categorize and index data, making it easier to locate relevant information quickly. This automation not only streamlines the e-discovery process but also minimizes the risk of human error, ensuring that critical data is not overlooked. As a result, legal teams can focus their efforts on strategic analysis rather than getting bogged down in the minutiae of data retrieval.
As organizations continue to navigate the complexities of data storage and e-discovery, the integration of cloud technology will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping their strategies. The combination of scalability, accessibility, security, and automation offered by cloud solutions presents a compelling case for their adoption. By embracing these advancements, organizations can enhance their data storage capabilities, ultimately leading to more efficient and effective e-discovery processes. In a landscape where data is increasingly recognized as a valuable asset, leveraging cloud technology is not just a trend; it is a strategic imperative that can provide a competitive edge in the ever-evolving digital world.
The Cost Benefits of Cloud-Based E-Discovery Tools

In the rapidly evolving landscape of legal technology, cloud-based e-discovery tools have emerged as a transformative force, offering significant cost benefits that are reshaping how organizations manage their data. Traditionally, e-discovery processes were often cumbersome and expensive, requiring substantial investments in hardware, software, and personnel. However, the advent of cloud computing has streamlined these processes, allowing organizations to leverage scalable resources that can adapt to their specific needs. This shift not only reduces upfront costs but also minimizes ongoing expenses associated with maintaining physical infrastructure.
One of the most compelling advantages of cloud-based e-discovery tools is their ability to provide on-demand access to vast amounts of data. Organizations no longer need to invest in extensive physical storage solutions, which can be both costly and space-consuming. Instead, cloud services offer flexible storage options that can be adjusted based on the volume of data being processed. This scalability means that companies can pay only for the storage they actually use, leading to significant savings over time. Furthermore, the elimination of the need for physical servers reduces maintenance costs and the associated labor required to manage these systems.
In addition to storage savings, cloud-based e-discovery tools often come with integrated features that enhance efficiency and reduce the time spent on data retrieval and analysis. For instance, many cloud platforms incorporate advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities that can expedite the review process. By automating repetitive tasks, these tools allow legal teams to focus their efforts on more complex issues, ultimately leading to faster case resolutions. This increased efficiency translates into lower billable hours, which can significantly reduce overall legal costs.
Moreover, the collaborative nature of cloud computing fosters improved communication and coordination among legal teams, regardless of their physical location. With cloud-based e-discovery tools, multiple users can access and work on the same data set simultaneously, facilitating real-time collaboration. This capability not only enhances productivity but also ensures that all team members are working with the most current information, reducing the risk of errors that can arise from outdated data. As a result, organizations can respond more swiftly to legal inquiries and demands, further minimizing potential costs associated with delays.
Another important aspect to consider is the security and compliance features that many cloud-based e-discovery solutions offer. While concerns about data security in the cloud are valid, reputable providers invest heavily in robust security measures, including encryption and regular audits, to protect sensitive information. By utilizing these advanced security protocols, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with data breaches, which can lead to costly legal ramifications. Additionally, many cloud providers ensure compliance with industry regulations, which can alleviate the burden of navigating complex legal requirements.
In conclusion, the cost benefits of cloud-based e-discovery tools are substantial and multifaceted. By reducing the need for physical infrastructure, enhancing efficiency through automation, facilitating collaboration, and providing robust security measures, these tools empower organizations to manage their e-discovery processes more effectively and economically. As the legal landscape continues to evolve, embracing cloud technology will not only be a strategic advantage but also a necessary step for organizations seeking to optimize their operations and reduce costs in an increasingly competitive environment. The transition to cloud-based solutions represents not just a technological shift but a fundamental change in how legal professionals approach the challenges of e-discovery and data management.
Security Challenges in Cloud Storage for E-Discovery
As organizations increasingly turn to cloud computing for their data storage needs, the implications for e-discovery processes become more pronounced, particularly concerning security challenges. The transition from traditional on-premises storage to cloud-based solutions offers numerous advantages, including scalability, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility. However, these benefits come with a unique set of security concerns that can complicate e-discovery efforts. Understanding these challenges is crucial for legal professionals and organizations alike, as they navigate the complexities of data management in a cloud environment.
One of the primary security challenges in cloud storage for e-discovery is the potential for unauthorized access to sensitive data. In a cloud environment, data is often stored on shared servers, which can increase the risk of breaches. Cybercriminals may exploit vulnerabilities in cloud infrastructure, leading to unauthorized access to confidential information. This risk is particularly concerning for organizations that handle sensitive data, such as personal identifiable information (PII) or proprietary business information. Consequently, organizations must implement robust access controls and encryption measures to safeguard their data, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information.
Moreover, the shared nature of cloud storage can complicate data governance and compliance with legal regulations. Organizations must be aware of where their data is stored and how it is managed, as different jurisdictions may have varying laws regarding data protection and privacy. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe imposes strict requirements on data handling, and non-compliance can result in significant penalties. As such, organizations must work closely with their cloud service providers to ensure that data storage practices align with legal obligations, which can be a daunting task given the complexity of cloud environments.
In addition to unauthorized access and compliance issues, the potential for data loss poses another significant security challenge in cloud storage for e-discovery. While cloud providers typically implement redundancy measures to protect against data loss, incidents such as accidental deletion, hardware failures, or even natural disasters can still occur. Organizations must have contingency plans in place to recover lost data, which may involve maintaining local backups or utilizing third-party recovery services. This necessity for data recovery solutions can complicate e-discovery processes, as legal teams may need to account for the possibility of missing or incomplete data during investigations.
Furthermore, the dynamic nature of cloud environments can lead to challenges in data preservation. In e-discovery, the ability to preserve data in its original state is critical for legal proceedings. However, the fluidity of cloud storage—where data can be modified, deleted, or moved—can hinder this process. Organizations must establish clear protocols for data preservation, ensuring that relevant information is retained in a manner that complies with legal standards. This often requires collaboration between IT departments and legal teams to create a comprehensive strategy that addresses both technical and legal requirements.
Lastly, the reliance on third-party cloud service providers introduces an additional layer of risk. Organizations must carefully vet their providers to ensure they have robust security measures in place. This includes assessing their compliance with industry standards and understanding their incident response protocols. The relationship between organizations and cloud providers is critical, as any lapse in security on the provider’s part can have dire consequences for the organization’s data integrity and legal standing.
In conclusion, while cloud computing offers significant advantages for data storage and e-discovery, it also presents a range of security challenges that organizations must navigate. By understanding these challenges and implementing effective strategies, organizations can better protect their data and ensure compliance with legal requirements, ultimately enhancing their e-discovery processes in an increasingly digital landscape.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations in Cloud E-Discovery
As organizations increasingly turn to cloud computing for their data storage and management needs, the implications for e-discovery processes become more pronounced, particularly in the realm of compliance and regulatory considerations. The shift to cloud environments introduces a myriad of challenges and opportunities that legal and compliance teams must navigate carefully. One of the most significant aspects of this transition is the need to understand how data stored in the cloud is governed by various regulations, which can vary widely depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the data itself.
In the context of e-discovery, compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States is paramount. These regulations impose strict requirements on how data is collected, stored, and processed, and failure to comply can result in severe penalties. As organizations utilize cloud services, they must ensure that their cloud providers adhere to these regulations, which often necessitates a thorough examination of the provider’s compliance certifications and data handling practices. This scrutiny is essential, as the responsibility for compliance does not solely rest with the cloud provider; organizations must also demonstrate due diligence in their selection of service providers.
Moreover, the dynamic nature of cloud environments complicates e-discovery efforts. Data can be stored across multiple locations and jurisdictions, which can lead to challenges in identifying where data resides and which laws apply. For instance, if a company uses a cloud service that stores data in multiple countries, it may inadvertently violate local data protection laws if it fails to account for the specific regulations governing data in those jurisdictions. Therefore, organizations must develop comprehensive data mapping strategies that not only identify where data is stored but also clarify the legal implications of accessing and retrieving that data during e-discovery.
In addition to understanding regulatory requirements, organizations must also consider the contractual obligations associated with their cloud services. Service Level Agreements (SLAs) often outline the responsibilities of the cloud provider regarding data security, availability, and compliance. It is crucial for organizations to negotiate these agreements carefully, ensuring that they include provisions that address e-discovery needs, such as data retrieval timelines and the ability to access data in a usable format. By doing so, organizations can mitigate risks associated with potential non-compliance during legal proceedings.
Furthermore, the rapid evolution of technology and cloud services means that compliance frameworks must be continuously updated. Organizations should stay informed about emerging regulations and best practices in cloud e-discovery to ensure that their processes remain robust and effective. This proactive approach not only helps in maintaining compliance but also enhances the organization’s overall data governance strategy.
As organizations embrace cloud computing, the intersection of e-discovery and compliance becomes increasingly complex. By understanding the regulatory landscape, carefully selecting cloud providers, and establishing clear contractual obligations, organizations can navigate these challenges effectively. Ultimately, a well-structured approach to compliance and regulatory considerations in cloud e-discovery not only safeguards organizations against legal pitfalls but also fosters a culture of accountability and transparency in data management practices. In this evolving digital landscape, the ability to adapt and respond to compliance challenges will be a defining factor in an organization’s success in leveraging cloud technology for e-discovery and beyond.
Future Trends in Cloud Computing and E-Discovery Integration
As organizations increasingly rely on cloud computing, the integration of this technology with e-discovery processes is poised to evolve significantly. The future of cloud computing in the realm of e-discovery is characterized by a growing emphasis on efficiency, scalability, and security. As legal professionals navigate the complexities of data management, the cloud offers innovative solutions that streamline the e-discovery process, making it more accessible and effective.
One of the most notable trends is the shift towards automated e-discovery tools that leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies are becoming integral to cloud-based platforms, enabling legal teams to sift through vast amounts of data with unprecedented speed and accuracy. By automating routine tasks such as data collection, processing, and review, organizations can significantly reduce the time and costs associated with e-discovery. This automation not only enhances productivity but also allows legal professionals to focus on more strategic aspects of their cases, thereby improving overall outcomes.
Moreover, the scalability of cloud solutions is transforming how organizations approach data storage and management. As businesses generate and accumulate more data than ever before, the ability to scale storage capacity on-demand is crucial. Cloud providers are increasingly offering flexible storage options that can adapt to the fluctuating needs of organizations. This adaptability ensures that legal teams can efficiently manage large volumes of data during e-discovery without the constraints of traditional on-premises systems. Consequently, organizations can respond more swiftly to legal requests and regulatory inquiries, enhancing their compliance posture.
In addition to scalability, security remains a paramount concern in the integration of cloud computing and e-discovery. As data breaches and cyber threats become more sophisticated, cloud providers are investing heavily in advanced security measures to protect sensitive information. Encryption, multi-factor authentication, and robust access controls are just a few of the security features that are becoming standard in cloud-based e-discovery solutions. As organizations increasingly recognize the importance of safeguarding their data, the demand for secure cloud environments will continue to rise, driving innovation in this area.
Furthermore, the rise of hybrid cloud solutions is another trend shaping the future of e-discovery. Many organizations are opting for a combination of public and private cloud environments to balance the need for flexibility with the desire for enhanced security. This hybrid approach allows legal teams to store sensitive data in private clouds while leveraging the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public clouds for less sensitive information. As a result, organizations can tailor their e-discovery strategies to meet specific regulatory requirements and risk management objectives.
As we look ahead, the integration of cloud computing and e-discovery will also be influenced by evolving regulations and compliance standards. Legal professionals must stay abreast of changes in data privacy laws and industry-specific regulations that impact how data is stored and accessed. Cloud providers are likely to respond by enhancing their offerings to ensure compliance, thereby fostering a more secure and efficient e-discovery process.
In conclusion, the future of cloud computing and e-discovery integration is bright, marked by advancements in automation, scalability, security, and compliance. As organizations continue to embrace cloud technologies, they will find themselves better equipped to handle the complexities of e-discovery in an increasingly data-driven world. This evolution not only promises to enhance the efficiency of legal processes but also ensures that organizations can navigate the challenges of data management with greater confidence and agility.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has significantly transformed e-discovery and data storage by enhancing scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. It allows organizations to store vast amounts of data securely and retrieve it efficiently during legal proceedings. The ability to leverage advanced analytics and machine learning in the cloud further streamlines the e-discovery process, enabling quicker identification and review of relevant information. However, challenges such as data privacy, compliance, and security must be addressed. Overall, cloud computing has revolutionized how organizations manage and process data, making e-discovery more efficient while providing robust storage solutions.