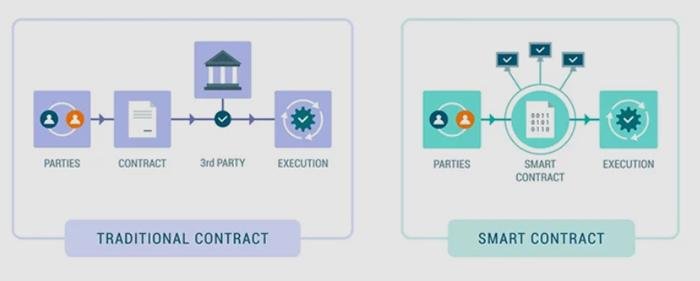
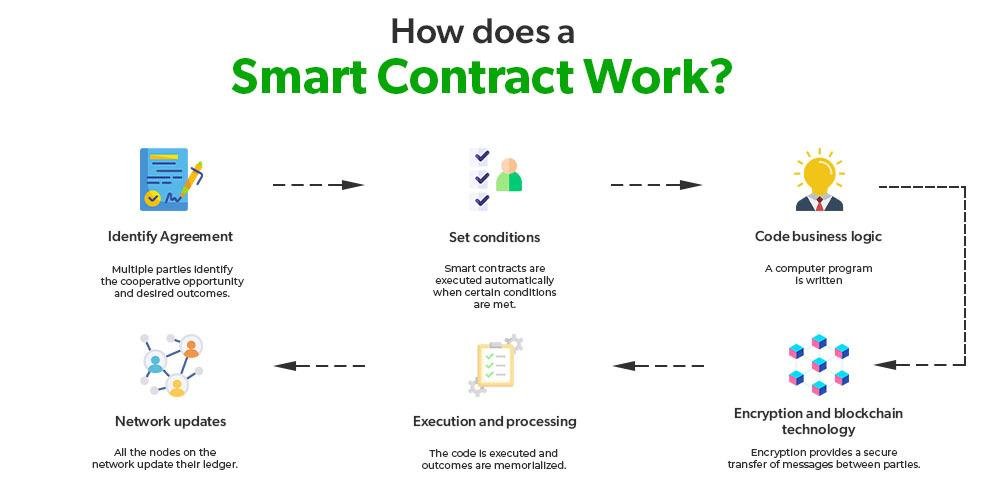
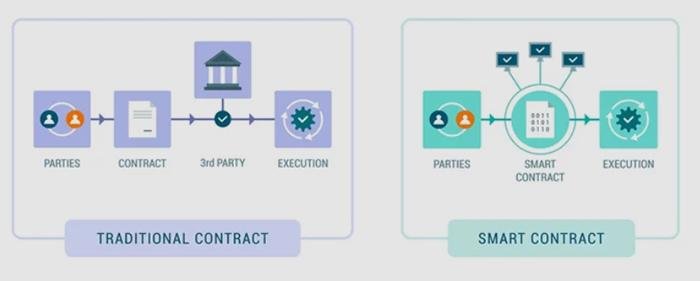
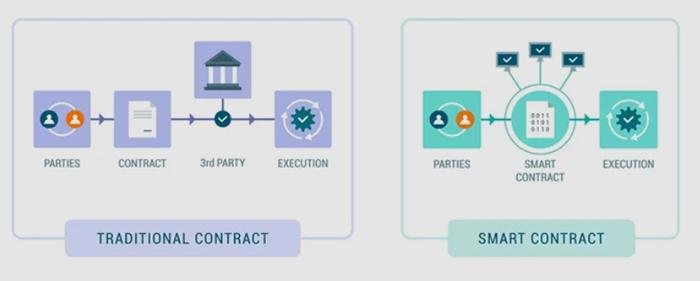
Optimizing Cybersecurity: Best Practices for Legal Professionals

Introduction
The legal sector has increasingly become a target for cybercriminals due to its reliance on digital technologies and the sensitive nature of the information handled. Law firms house vast amounts of confidential data, including client information, case files, financial records, and communications. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, understanding the unique challenges that legal professionals face is paramount for developing effective cybersecurity strategies. This overview will highlight the types of data at risk, common cyber threats, and the potential fallout from cyber incidents.
Sensitive data in the legal sector often involves confidential client information protected by attorney-client privilege. Violations of this privilege could lead to significant legal ramifications and loss of client trust. Moreover, compliance with legal regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) adds another layer of complexity to data handling practices. A breach not only threatens client relationships but can also lead to fines and other legal consequences.
Legal professionals encounter various cyber threats, including phishing, ransomware, and data breaches. For example, in 2020, the American Bar Association reported a significant increase in phishing attacks targeting legal firms, compromising sensitive information. The consequences of these incidents range from reputational damage to financial loss and erosion of client trust. As legal professionals navigate this challenging landscape, a proactive approach to cybersecurity is essential for safeguarding their practice and client relationships.
Understanding the Legal and Regulatory Framework
Legal professionals must comprehend the intricate regulations governing data privacy and cybersecurity. Familiarity with these frameworks is vital not only for compliance but also to bolster the firm’s overall cybersecurity posture. This section will discuss pertinent regulations and standards that impact legal firms, shedding light on potential liabilities and obligations.
The GDPR is a central regulation that affects any law firm handling client data from EU jurisdictions. It mandates stringent requirements surrounding data storage, management, and breach notifications. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines of up to 4% of annual revenue. Similarly, the HIPAA imposes strict regulations on the handling of healthcare information, requiring law firms dealing with medical records to implement specific safeguards and reporting procedures in case of data breaches.
Furthermore, state-specific data protection laws can vary widely, adding complexity to compliance efforts. For instance, California’s Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) provides consumers with extensive rights regarding their personal data and imposes obligations on businesses, including law firms, on how client data is collected and used. By understanding these regulations, legal professionals can not only ensure compliance but also mitigate the risks associated with potential data breaches.
Developing a Comprehensive Cybersecurity Policy
Creating a tailored cybersecurity policy is essential for any law firm seeking to fortify its cybersecurity measures. This policy should cover all facets of cybersecurity, including data handling protocols, incident response guidelines, and employee training programs. Here, we outline the key components that must be incorporated into an effective cybersecurity policy.
A pivotal aspect of a comprehensive cybersecurity policy is data classification and handling. Legal firms must establish guidelines for categorizing data based on sensitivity and criticality, allowing for appropriate handling protocols. For instance, public documents may be managed differently than confidential case files. This classification aids in determining which data needs heightened protection measures and streamlines the incident response process when security breaches occur.
Another crucial component is the incident response plan. It should detail step-by-step procedures for detecting, responding to, and recovering from cybersecurity incidents. Incorporating role-based access controls into user access management is equally important. This principle of least privilege ensures that employees only have access to the information necessary for their roles, reducing the risk of insider threats. Additionally, as remote work becomes more prevalent, it is imperative to implement remote work protocols that include secure VPN usage and effective mobile device management.
Read More: Building a Compliance-Focused Tech Stack for Your Law Firm
Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Despite advanced technological defenses, the human element remains a critical vulnerability in cybersecurity. Legal professionals must prioritize creating a culture of cybersecurity awareness within their firms. Comprehensive training programs empower employees to recognize and respond effectively to potential cyber threats, minimizing the likelihood of human error leading to security breaches.
Regular training sessions should cover various topics, including recognizing phishing attempts, handling sensitive information securely, and the importance of strong password practices. Training should not be a one-off event but rather an ongoing process that adapts to new threats as they arise. For instance, simulating phishing attacks can help employees better identify malicious attempts in real scenarios, thereby enhancing their skills and response capabilities.
A robust communication strategy is also vital for fostering cybersecurity awareness. Providing resources such as newsletters, cybersecurity tips, and updates on emerging threats ensures all employees are informed and vigilant. Encouraging an open dialogue about cybersecurity challenges within the firm empowers employees to take ownership of their cybersecurity responsibilities and report potential incidents without fear of repercussion. By cultivating a proactive cybersecurity culture, law firms can significantly reduce their vulnerability to cyber threats.
Conclusion
As the legal sector continues to navigate the complexities of cybersecurity, implementing best practices is crucial for protecting sensitive client information and ensuring compliance with legal regulations. By understanding the unique challenges of the field, developing comprehensive cybersecurity policies, and investing in employee training, legal professionals can build a robust cybersecurity framework.
In an era where cyber threats are ever-evolving, law firms must take proactive measures to safeguard their data and maintain client trust. By prioritizing cybersecurity, legal professionals can not only mitigate risks but also ensure their practice remains resilient in the face of potential cyber incidents.
FAQ Section:
- What are the primary cyber threats facing legal professionals today?
Legal professionals face a multitude of cyber threats, including phishing attacks, ransomware, insider threats, malware, and data breaches. Phishing attacks, where cybercriminals impersonate trusted sources to steal sensitive information, have become increasingly prevalent in legal settings. - How does the GDPR affect law firms?
The GDPR mandates that law firms handling client data from EU jurisdictions comply with strict data protection regulations, including obtaining client consent for data processing and implementing breach notification procedures. Non-compliance can result in significant financial penalties. - Why is employee training crucial in legal cybersecurity?
Employees are often the weakest link in cybersecurity. Training programs enhance awareness about potential cyber threats, enabling employees to recognize and respond effectively to phishing attempts and other security risks, thus reducing the likelihood of human error leading to breaches. - What should be included in a law firm’s cybersecurity policy?
A comprehensive cybersecurity policy should include data classification and handling guidelines, an incident response plan, user access management protocols, and remote work security measures. These components collectively strengthen the firm’s security posture. - What are the consequences of failing to maintain cybersecurity in a law firm?
Failing to maintain proper cybersecurity can lead to reputational damage, financial losses, legal repercussions, and a significant impact on client trust. Breached sensitive information can result in lawsuits, regulatory penalties, and loss of business from existing and potential clients.