E-Discovery Fundamentals: Key Steps and Best Practices for Big Data Management

Table of Contents
Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, the exponential growth of data presents both opportunities and challenges for organizations navigating the complexities of e-discovery. As businesses increasingly rely on vast amounts of information generated from various sources—such as emails, social media, cloud storage, and IoT devices—preparing for e-discovery has become a critical component of legal and compliance strategies. This introduction explores the essential steps organizations must take to effectively manage and streamline the e-discovery process in the age of big data, emphasizing the importance of robust data governance, advanced technology solutions, and proactive planning to ensure compliance and mitigate risks in legal proceedings.
Understanding E-Discovery Fundamentals
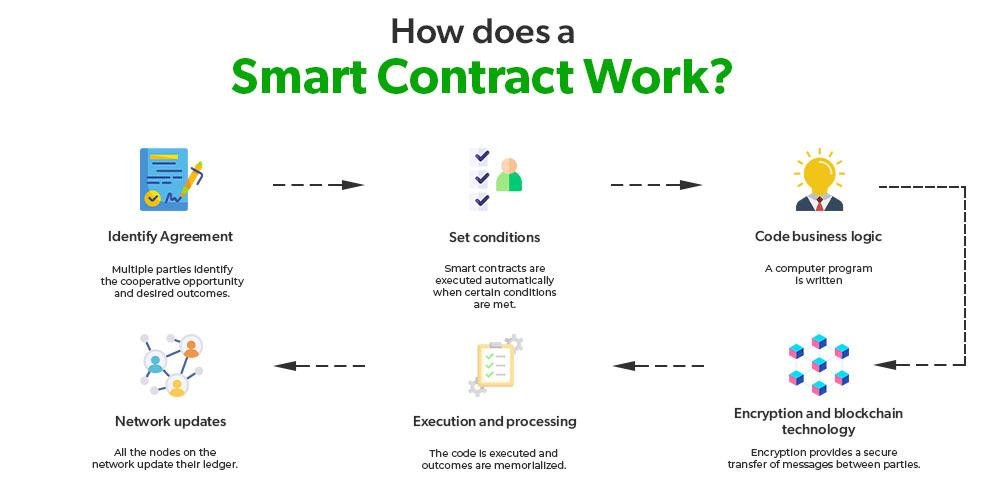
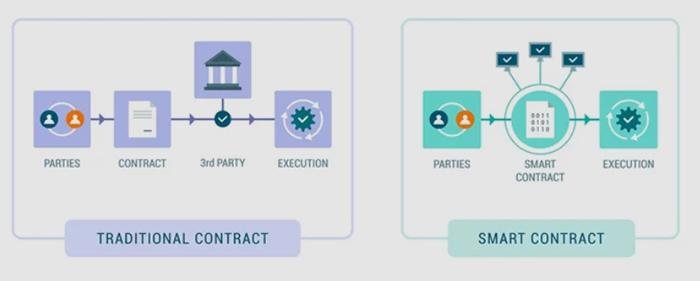
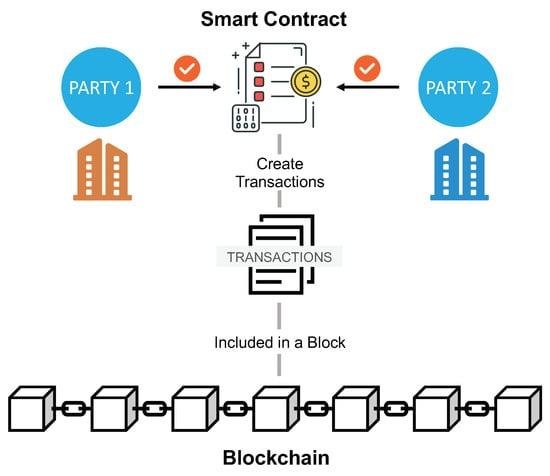
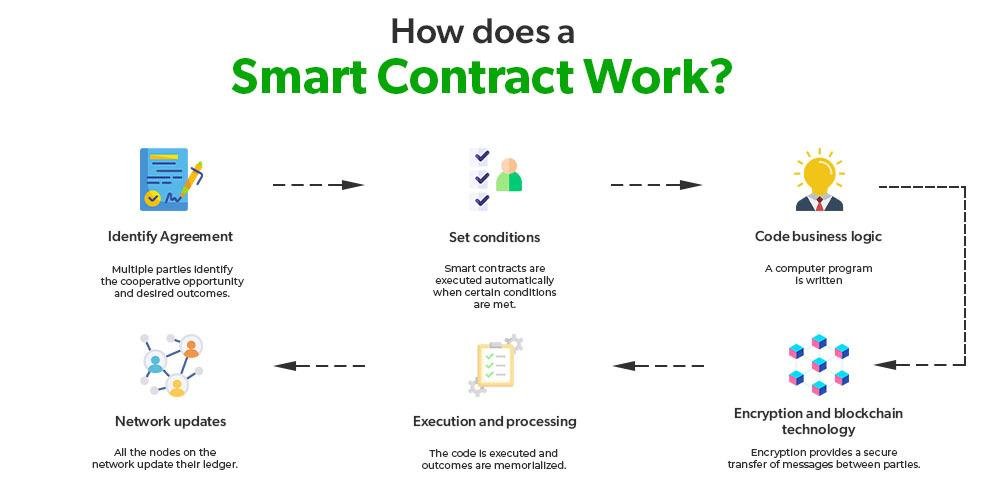
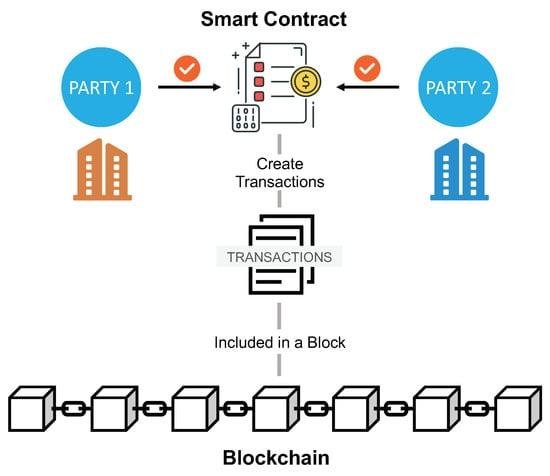
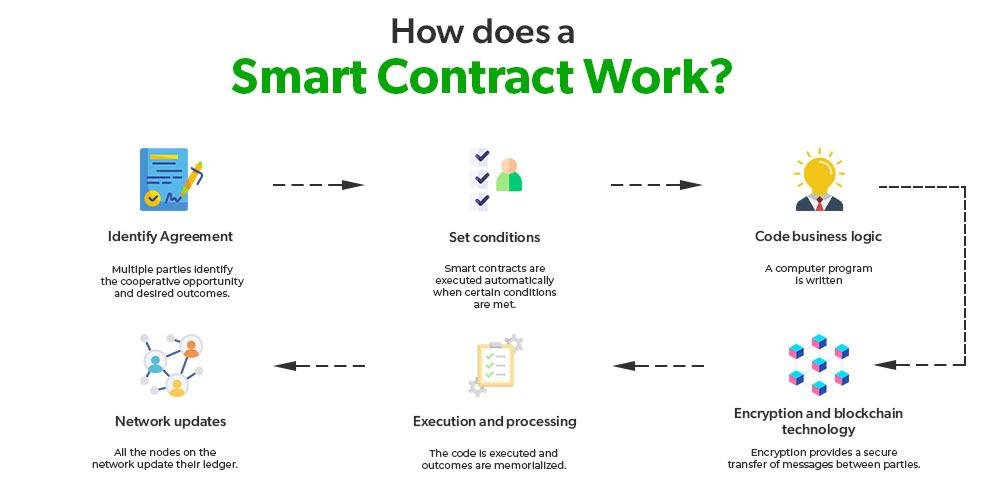
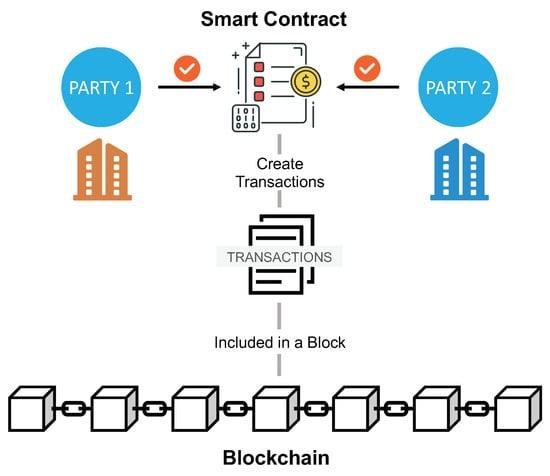
E-discovery, or electronic discovery, is a crucial process for legal professionals in today’s digital world. It involves identifying, collecting, and producing electronically stored information (ESI) in response to legal requests. As the amount of digital data grows, understanding the basics of e-discovery becomes essential for navigating legal challenges effectively.
Key Stages of E-Discovery:
- Identification:
- Determine what data is relevant to the case.
- Types of ESI include emails, documents, social media content, and metadata.
- Understanding where this information is stored (e.g., cloud storage) is crucial.
- Preservation:
- Ensure that identified data remains unchanged and intact.
- Failing to preserve ESI can result in legal penalties or adverse decisions in court.
- Implement strong data management policies to prevent data loss or corruption.
- Collection:
- Gather the relevant ESI in a way that maintains its integrity.
- Use specialized tools to collect data forensically, ensuring it’s reliable.
- Be cautious of data spoliation (accidental loss or alteration of data).
- Processing:
- Organize and prepare the collected data for review.
- Filter out irrelevant information and remove duplicates to streamline the process.
- Efficient processing is essential to help legal teams focus on pertinent information.
- Review:
- Analyze the organized data to find relevant evidence for litigation.
- This phase is often labor-intensive and requires attention to detail.
- Technologies like AI and machine learning can assist in speeding up the review while maintaining accuracy.
- Production:
- Deliver the relevant ESI to opposing parties or the court in a legally acceptable format.
- Ensure clear communication and follow established protocols to avoid disputes.
Read Also: How Data Privacy Regulations Are Shaping E-Discovery
Key Challenges in Big Data E-Discovery
As organizations increasingly rely on electronic evidence for legal proceedings, the rise of big data has introduced significant challenges in e-discovery. E-discovery involves identifying, collecting, and analyzing electronic information in response to legal requests. The complexities of managing large volumes of diverse and dynamic data can hinder effective e-discovery. Here are the key challenges organizations face in this landscape:
Key Challenges:
- Volume of Data:
- Organizations must sift through massive amounts of data from various sources like emails, social media, and cloud storage.
- The sheer volume makes it challenging to identify relevant information efficiently.
- Increased time and resources are required for thorough e-discovery.
- Diversity of Data Types:
- Big data includes various formats, such as unstructured data (text documents, images, videos, audio files).
- Different data types require advanced tools for effective processing and analysis.
- Organizations need to invest in sophisticated e-discovery solutions, which can be costly.
- Dynamic Nature of Data:
- Data is constantly being created, modified, and deleted, complicating the collection process.
- This fluidity can result in gaps where critical evidence may be lost or overlooked.
- Rapid data generation may also lead to including outdated or irrelevant information in e-discovery.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance:
- Organizations must comply with laws like the GDPR and CCPA, which impose strict requirements on handling personal data.
- Compliance can complicate the e-discovery process, necessitating additional measures to protect sensitive information.
- Organizations may face legal repercussions if they fail to meet these regulations.
- Skills Gap:
- There is a growing demand for professionals with expertise in data analytics and e-discovery.
- Many organizations struggle to find qualified personnel, leading to inefficiencies.
- Teams may lack the knowledge to use advanced e-discovery tools effectively.
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning:
- While AI and machine learning can improve efficiency and accuracy, they require expertise to implement and manage.
- Organizations must balance leveraging these advanced technologies with ensuring that their teams are properly trained.
- This balance can be challenging and resource-intensive.
Best Practices for Data Collection and Preservation
In today’s digital age, effective data collection and preservation are crucial for organizations facing legal challenges. As the volume of data grows, implementing best practices ensures that relevant information is identified and maintained with integrity. Here are the key practices organizations should adopt:
Best Practices:
- Establish a Data Governance Framework:
- Create clear policies and procedures for data management.
- Include classification, retention, and deletion protocols.
- Categorize data based on relevance and sensitivity to streamline the e-discovery process.
- Implement Robust Data Collection Strategies:
- Identify all sources of potentially relevant data (e.g., emails, cloud storage, social media).
- Use specialized e-discovery tools for collection to maintain the integrity of data.
- Ensure that metadata is preserved, as it is vital for authenticity.
- Involve Legal and IT Teams Early:
- Foster collaboration between legal and IT departments from the start.
- Legal teams provide insights on necessary data, while IT teams advise on technical aspects.
- This partnership enhances efficiency and reduces the risk of missing critical data.
- Prioritize Employee Training and Awareness:
- Educate employees on data preservation practices and their importance.
- Foster a culture of compliance by encouraging staff to recognize and report potential data risks.
- Conduct regular training sessions on e-discovery protocols.
- Stay Updated on Legal Standards and Regulations:
- Keep abreast of changes in e-discovery laws and best practices.
- Engage with legal experts and participate in industry forums for insights into emerging trends.
- This vigilance helps ensure compliance and minimizes legal exposure.
- Conduct Regular Audits of Data Management Practices:
- Perform audits to identify gaps in data collection and preservation efforts.
- Use findings to make timely adjustments to data management practices.
- Continuous refinement enhances readiness for e-discovery.
Leveraging Technology for Efficient E-Discovery
In today’s digital age, effective data collection and preservation are crucial for organizations facing legal challenges. As the volume of data grows, implementing best practices ensures that relevant information is identified and maintained with integrity. Here are the key practices organizations should adopt:
Best Practices:
- Establish a Data Governance Framework:
- Create clear policies and procedures for data management.
- Include classification, retention, and deletion protocols.
- Categorize data based on relevance and sensitivity to streamline the e-discovery process.
- Implement Robust Data Collection Strategies:
- Identify all sources of potentially relevant data (e.g., emails, cloud storage, social media).
- Use specialized e-discovery tools for collection to maintain the integrity of data.
- Ensure that metadata is preserved, as it is vital for authenticity.
- Involve Legal and IT Teams Early:
- Foster collaboration between legal and IT departments from the start.
- Legal teams provide insights on necessary data, while IT teams advise on technical aspects.
- This partnership enhances efficiency and reduces the risk of missing critical data.
- Prioritize Employee Training and Awareness:
- Educate employees on data preservation practices and their importance.
- Foster a culture of compliance by encouraging staff to recognize and report potential data risks.
- Conduct regular training sessions on e-discovery protocols.
- Stay Updated on Legal Standards and Regulations:
- Keep abreast of changes in e-discovery laws and best practices.
- Engage with legal experts and participate in industry forums for insights into emerging trends.
- This vigilance helps ensure compliance and minimizes legal exposure.
- Conduct Regular Audits of Data Management Practices:
- Perform audits to identify gaps in data collection and preservation efforts.
- Use findings to make timely adjustments to data management practices.
- Continuous refinement enhances readiness for e-discovery.
Legal Considerations in Big Data E-Discovery
As technology evolves, the intersection of law and big data presents complex challenges, especially in e-discovery. Legal professionals must navigate various legal considerations to manage electronic evidence effectively while ensuring compliance with regulations. Here are the key legal considerations in big data e-discovery:
Key Legal Considerations:
- Data Privacy:
- Regulatory Compliance: Be aware of regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
- Data Handling: Understand how data is collected, stored, and processed to protect individual rights and comply with legal standards.
- Volume of Data:
- Sifting Through Data: Organizations often deal with terabytes of information, including emails, documents, and social media.
- Proportionality Principle: Courts expect a balance between the need for information and the burden of producing it. Develop clear criteria to identify relevant data.
- Data Retention Policies:
- Establish Policies: Organizations should have robust data retention policies that comply with legal requirements.
- Avoid Spoliation: Clearly outline how long data will be kept and when it will be disposed of to prevent destruction of evidence, which can lead to legal sanctions.
- Technology in E-Discovery:
- Utilize Advanced Tools: Use software solutions for data processing, analysis, and review to enhance efficiency.
- Ensure Reliability: Ensure that the technologies comply with legal standards and protect sensitive information effectively.
- Collaboration Across Teams:
- Involve Legal, IT, and Compliance: Foster communication and understanding among legal, IT, and compliance teams to prepare for e-discovery challenges.
- Mitigate Risks: A collaborative approach enhances e-discovery effectiveness and reduces risks related to data management and compliance.
Addressing the legal considerations of e-discovery in the age of big data requires a proactive and strategic approach. By understanding privacy regulations, managing data volume, establishing retention policies, leveraging technology, and fostering collaboration, organizations can navigate the complexities of e-discovery while safeguarding their interests in a data-driven world.
Future Trends in E-Discovery and Big Data Management
As organizations navigate the complexities of the digital world, the intersection of e-discovery and big data management is becoming increasingly important. The future of e-discovery is set to evolve dramatically due to advancements in technology, growing data volumes, and the need for more efficient processes. Here are the key trends to watch:
Key Trends:
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning:
- Enhanced Speed and Accuracy: AI technologies improve the speed and accuracy of data retrieval.
- Automation of Routine Tasks: Tasks like document review and data classification can be automated, reducing time and costs for legal teams.
- Adoption of Cloud-Based Solutions:
- Streamlined Data Management: Cloud technology allows easier access to data and real-time collaboration among legal teams, regardless of location.
- Focus on Security and Compliance: Organizations must ensure data security and compliance with regulations as they migrate to the cloud.
- Evolving Regulatory Landscape:
- Adaptation to New Laws: Organizations must update their e-discovery strategies to comply with regulations like the GDPR and CCPA.
- Proactive Compliance Strategies: Legal teams will need to stay informed about regulatory changes and may require specialized training and resources.
- Rise of Remote Work:
- Data Fragmentation Challenges: Employees accessing data from various locations increases the potential for fragmented information.
- Comprehensive Data Governance: Organizations need a thorough approach to ensure all data sources are accounted for in e-discovery processes.
- Expansion of Data Analytics:
- Deeper Insights from Data: Advanced analytics tools allow legal teams to identify patterns and trends within their data.
- Informed Decision-Making: This capability enhances e-discovery quality and empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, preparing for e-discovery in the age of big data requires organizations to adopt proactive strategies that encompass robust data management practices, advanced technology solutions, and comprehensive legal compliance. By implementing effective data governance frameworks, leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning for data analysis, and ensuring ongoing training for legal and IT teams, organizations can navigate the complexities of e-discovery more efficiently. This preparation not only mitigates risks associated with data breaches and legal challenges but also enhances the overall ability to respond to litigation and regulatory inquiries in a timely and cost-effective manner.