Smart Contracts and Blockchain: What Lawyers Need to Know

-
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Smart Contracts: Legal Implications and Challenges
- Blockchain Technology: Transforming Legal Practices
- Smart Contracts and Contract Law: Bridging the Gap
- Regulatory Landscape for Blockchain and Smart Contracts
- Intellectual Property and Blockchain: Protecting Digital Assets
- Dispute Resolution in the Era of Smart Contracts and Blockchain
- Conclusion
Introduction
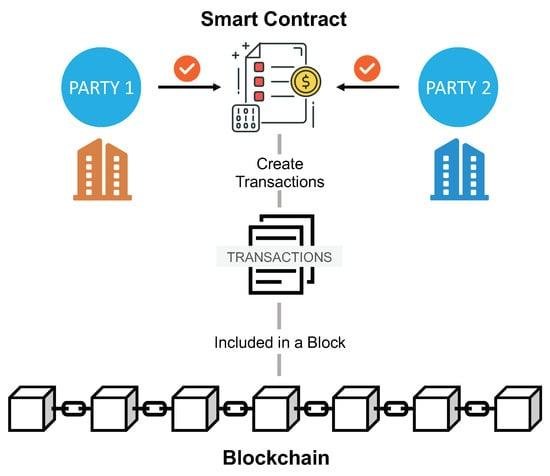
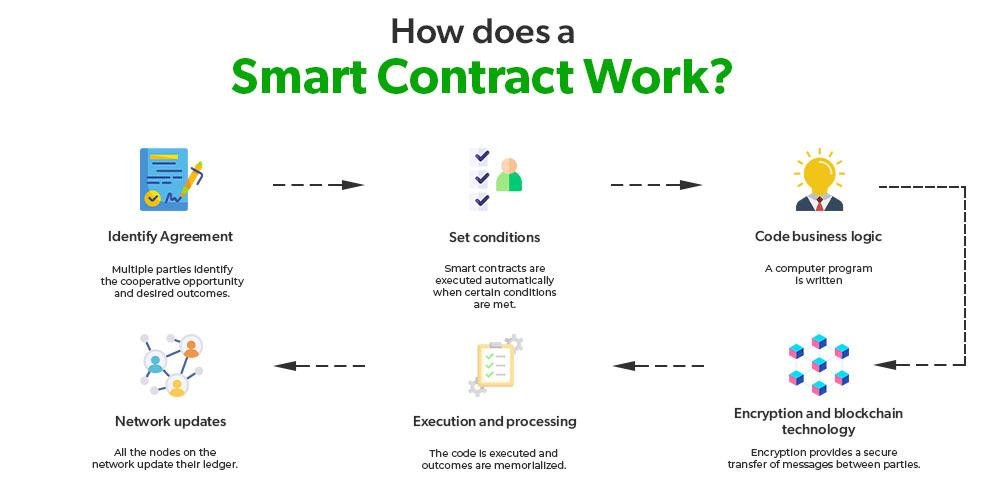
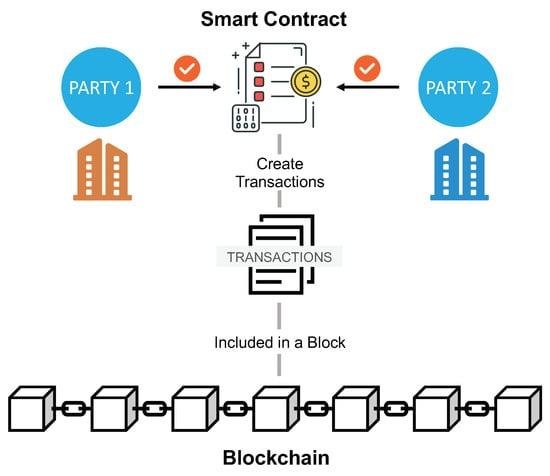
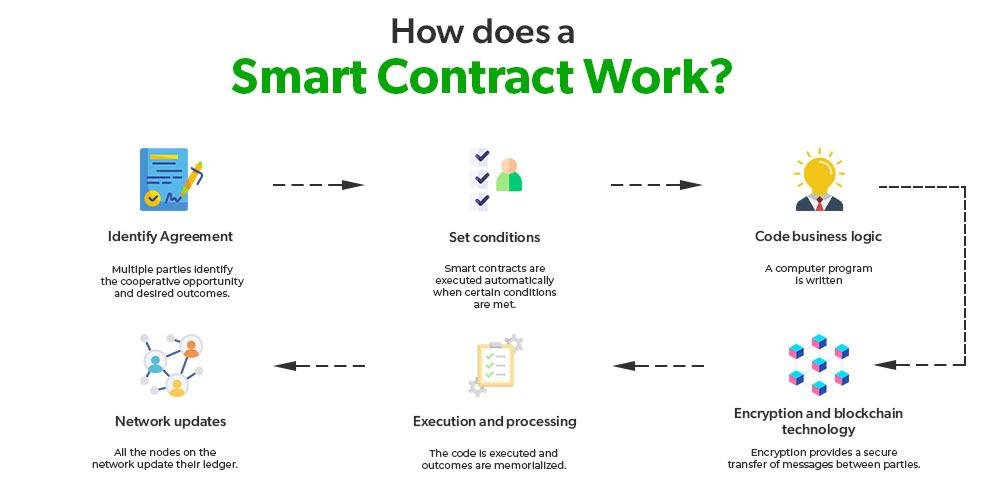
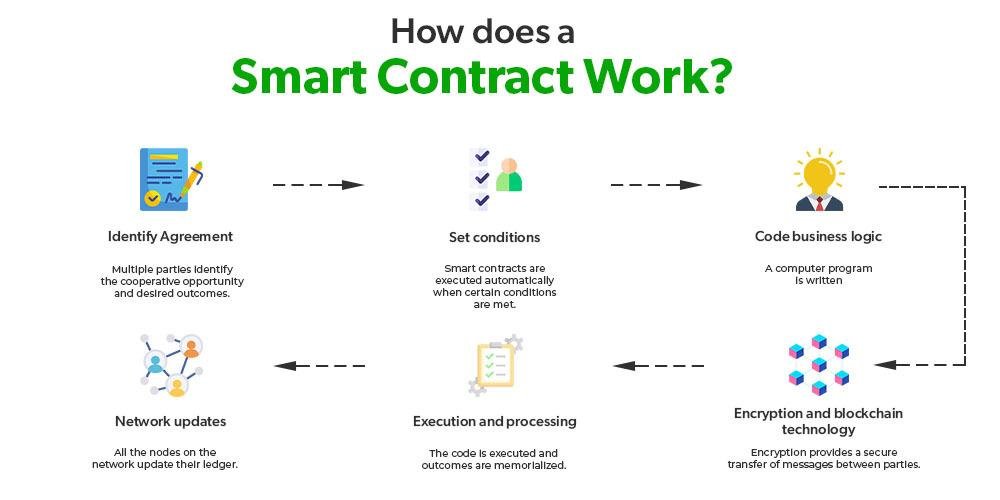
Smart contracts and blockchain technology are revolutionizing the legal landscape, offering new opportunities and challenges for legal professionals. At their core, smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They operate on blockchain platforms, which are decentralized, distributed ledgers that ensure transparency, security, and immutability of data. For lawyers, understanding these technologies is crucial as they increasingly intersect with various areas of law, including contract law, intellectual property, and regulatory compliance. Smart contracts promise efficiency and reduced transaction costs, but they also raise complex legal questions about enforceability, jurisdiction, and liability. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, legal practitioners must stay informed to effectively advise clients, draft compliant smart contracts, and navigate the emerging legal frameworks surrounding these digital innovations.
Understanding Smart Contracts: Legal Implications and Challenges
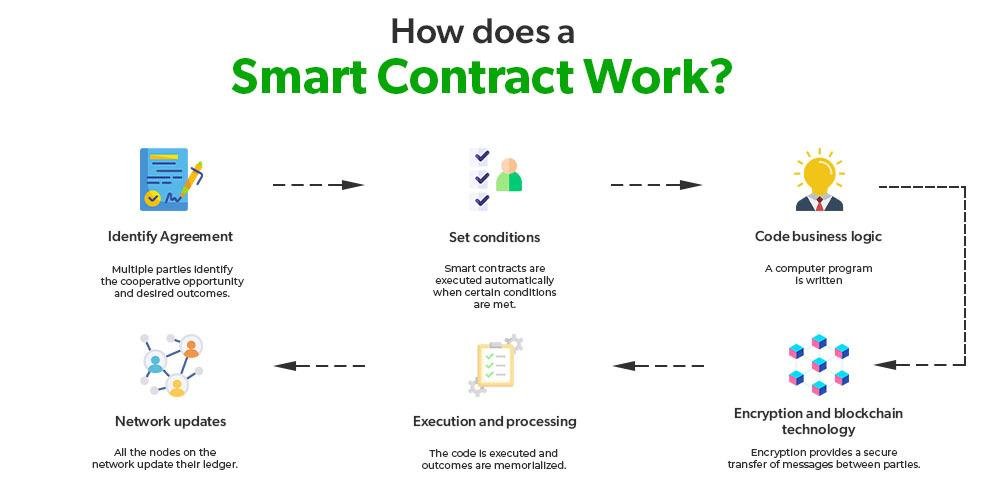
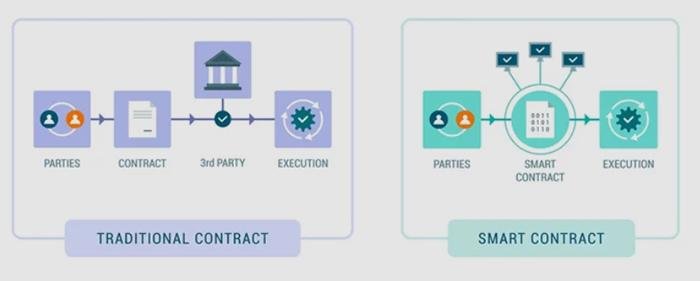
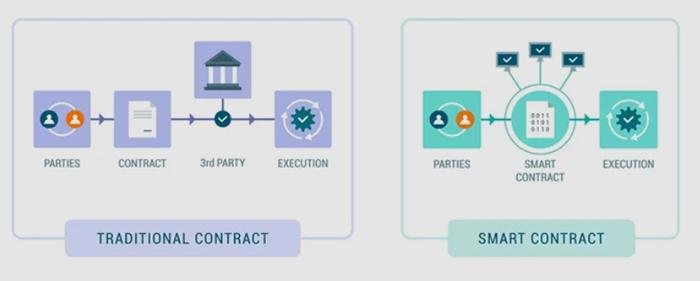
Smart contracts, a revolutionary application of blockchain technology, are transforming the legal landscape by automating and streamlining contractual processes. These self-executing contracts, with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, offer a new paradigm for legal professionals to consider. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, it is crucial for lawyers to understand the legal implications and challenges associated with smart contracts to effectively advise their clients and navigate this emerging field.
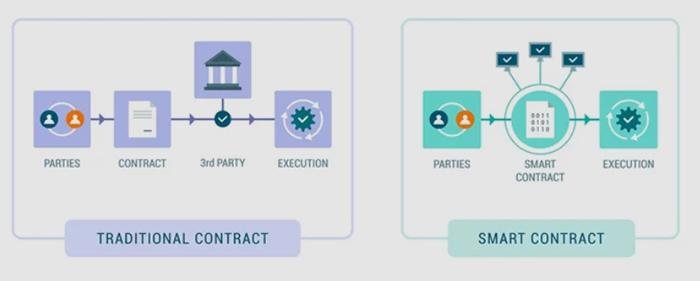
To begin with, smart contracts operate on decentralized blockchain networks, which provide a secure and transparent environment for executing agreements. This decentralization eliminates the need for intermediaries, such as banks or escrow agents, thereby reducing transaction costs and increasing efficiency. However, this also raises questions about the enforceability of smart contracts within existing legal frameworks. Traditional contracts are governed by legal principles that may not directly apply to code-based agreements, necessitating a reevaluation of how these principles are interpreted in the context of smart contracts.
Moreover, the immutable nature of blockchain presents both advantages and challenges. On one hand, the permanence of records ensures that once a smart contract is executed, it cannot be altered, providing a high level of security and trust. On the other hand, this immutability poses significant challenges in cases where contract terms need to be modified or terminated due to unforeseen circumstances. Lawyers must consider how to incorporate flexibility into smart contracts while maintaining their integrity, possibly through the use of oracles or other mechanisms that allow for external inputs and adjustments.
Another critical aspect for legal professionals to consider is the issue of jurisdiction. Since blockchain networks are global and decentralized, determining the applicable law and jurisdiction for disputes arising from smart contracts can be complex. This complexity is compounded by the pseudonymous nature of blockchain participants, which can make it difficult to identify parties and hold them accountable. Lawyers must be adept at navigating these jurisdictional challenges and advising clients on how to structure smart contracts to minimize legal risks.
Furthermore, the question of liability in smart contracts is a pressing concern. In traditional contracts, liability is typically assigned based on the actions or omissions of the parties involved. However, in smart contracts, the code itself executes the terms, raising questions about who is responsible if the contract fails to perform as intended. Legal professionals must consider how liability is allocated in smart contracts and whether existing legal doctrines, such as negligence or breach of contract, can be applied to code-based agreements.
In addition to these challenges, lawyers must also be aware of the potential for regulatory scrutiny. As smart contracts gain popularity, regulators are increasingly interested in how they fit within existing legal frameworks and whether new regulations are necessary. Legal professionals must stay informed about regulatory developments and advise clients on compliance to avoid potential legal pitfalls.
In conclusion, while smart contracts offer significant benefits in terms of efficiency and security, they also present unique legal challenges that require careful consideration. Lawyers must be proactive in understanding the technical and legal aspects of smart contracts to effectively guide their clients through this evolving landscape. By doing so, they can help ensure that smart contracts are used in a manner that is both legally sound and beneficial to all parties involved.
Blockchain Technology: Transforming Legal Practices
Blockchain technology is rapidly transforming various industries, and the legal sector is no exception. At the heart of this transformation are smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, it is crucial for legal professionals to understand how these innovations are reshaping legal practices and what implications they hold for the future.
To begin with, smart contracts offer a level of automation and efficiency that traditional contracts cannot match. By eliminating the need for intermediaries, such as banks or escrow agents, smart contracts reduce transaction costs and minimize the potential for human error. This is particularly beneficial in complex transactions involving multiple parties, where the risk of miscommunication or oversight is high. Moreover, the immutable nature of blockchain ensures that once a smart contract is executed, it cannot be altered, providing a high level of security and trust.
However, the adoption of smart contracts also presents new challenges for legal professionals. One of the primary concerns is the legal recognition and enforceability of these digital agreements. While smart contracts are designed to execute automatically when certain conditions are met, questions remain about their status under existing legal frameworks. For instance, how do traditional contract principles, such as offer, acceptance, and consideration, apply to smart contracts? Furthermore, in the event of a dispute, how can parties seek recourse if the contract is coded to execute without human intervention?
In addition to these legal considerations, there are technical challenges that lawyers must navigate. Understanding the underlying technology of blockchain and the coding of smart contracts is essential for providing competent legal advice. This requires a new set of skills and knowledge that many legal professionals may not yet possess. Consequently, there is a growing demand for legal experts who can bridge the gap between technology and law, ensuring that smart contracts are drafted and executed in a manner that aligns with legal standards and client expectations.
Moreover, the integration of blockchain technology into legal practices extends beyond smart contracts. Blockchain’s decentralized and transparent nature offers potential applications in areas such as intellectual property, real estate, and supply chain management. For example, blockchain can be used to create a tamper-proof record of intellectual property rights, providing a clear chain of custody and reducing the risk of infringement. Similarly, in real estate transactions, blockchain can streamline the process by providing a secure and transparent ledger of property ownership and transfer.
As blockchain technology continues to develop, it is imperative for legal professionals to stay informed about these advancements and their implications. This involves not only understanding the technical aspects of blockchain and smart contracts but also considering the broader impact on legal practices and the justice system as a whole. By embracing these innovations, lawyers can enhance their practice, offer more efficient and secure services to their clients, and ultimately contribute to the evolution of the legal profession in the digital age.
In conclusion, while blockchain technology and smart contracts present both opportunities and challenges for the legal sector, they are undeniably reshaping the landscape of legal practices. As these technologies become more prevalent, lawyers must adapt and evolve, acquiring the necessary skills and knowledge to navigate this new terrain. By doing so, they can ensure that they remain at the forefront of legal innovation, providing valuable insights and services in an increasingly digital world.
Smart Contracts and Contract Law: Bridging the Gap

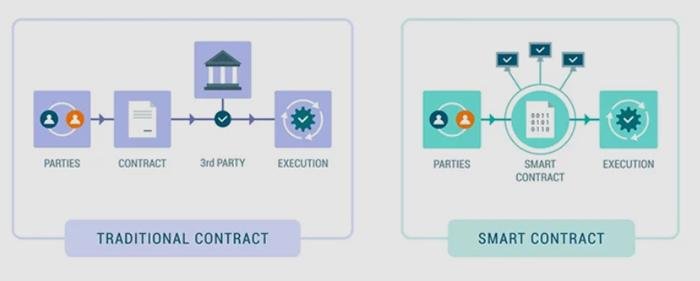
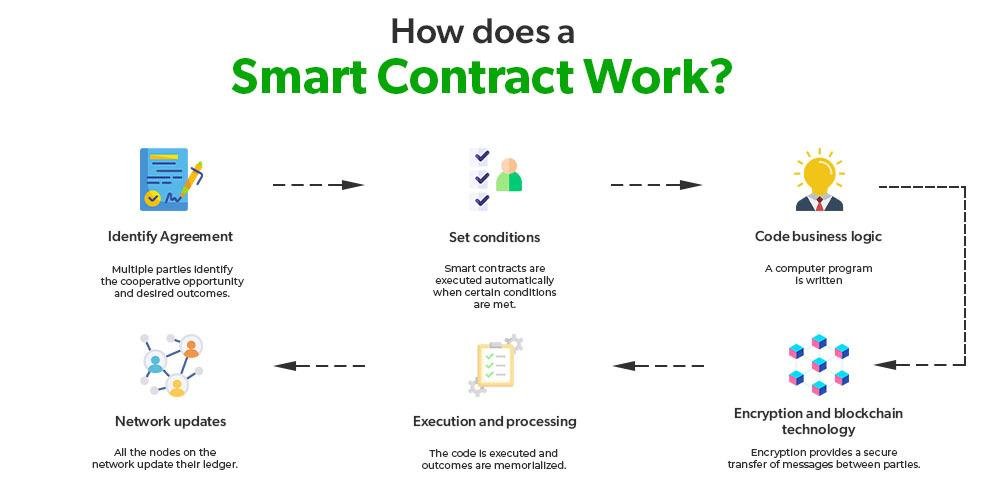
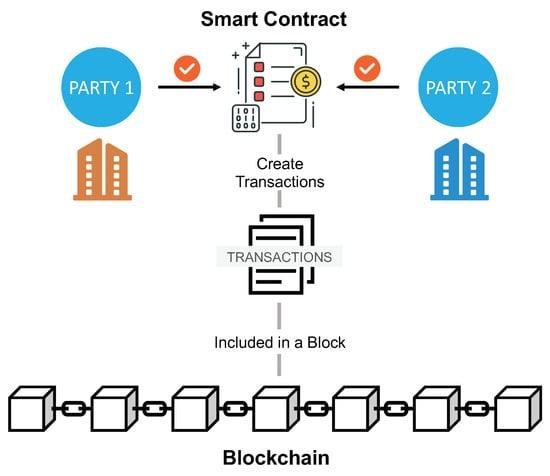
Smart contracts, a revolutionary application of blockchain technology, are transforming the landscape of contract law, presenting both opportunities and challenges for legal professionals. At their core, smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. These contracts automatically enforce and execute the terms when predetermined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries. As blockchain technology underpins these contracts, it ensures transparency, security, and immutability, which are highly desirable attributes in the legal domain. However, the integration of smart contracts into traditional contract law raises several questions that lawyers must address to bridge the gap between these two worlds.
To begin with, the legal enforceability of smart contracts is a primary concern. Traditional contracts are governed by established legal principles, such as offer, acceptance, consideration, and mutual intent. Lawyers must consider how these principles apply to smart contracts, which are often devoid of the formalities present in conventional agreements. For instance, the concept of “offer and acceptance” may be redefined in the context of a smart contract, where the code itself represents the offer, and the execution of the code signifies acceptance. Consequently, legal professionals must adapt their understanding of these principles to ensure that smart contracts are legally binding and enforceable.
Moreover, the issue of jurisdiction presents another challenge. Blockchain technology operates on a decentralized network that transcends geographical boundaries, making it difficult to determine which jurisdiction’s laws apply to a smart contract. This lack of a clear legal framework can lead to disputes and complications, particularly when parties from different countries are involved. Lawyers must navigate this complex landscape by drafting smart contracts that include explicit jurisdictional clauses or by advocating for the development of international legal standards that address these concerns.
In addition to jurisdictional issues, the potential for coding errors or unforeseen circumstances poses significant risks. Unlike traditional contracts, which can be amended or interpreted by courts, smart contracts are rigid and inflexible once deployed on the blockchain. This rigidity can lead to unintended consequences if the code does not account for every possible scenario. Therefore, lawyers must work closely with developers to ensure that smart contracts are meticulously coded and thoroughly tested. Furthermore, they should consider incorporating mechanisms for dispute resolution or contract modification to address any issues that may arise post-deployment.
Another critical aspect that lawyers must consider is the intersection of smart contracts with existing regulatory frameworks. Various industries, such as finance, healthcare, and real estate, are subject to stringent regulations that may not align with the automated nature of smart contracts. Legal professionals must ensure that these contracts comply with relevant laws and regulations, which may require innovative approaches to contract drafting and execution. This may involve integrating compliance checks within the smart contract code or developing hybrid contracts that combine traditional legal agreements with smart contract elements.
As the adoption of smart contracts continues to grow, lawyers have a pivotal role in bridging the gap between this emerging technology and traditional contract law. By understanding the nuances of smart contracts and addressing the associated legal challenges, they can help clients harness the benefits of blockchain technology while mitigating potential risks. Ultimately, the successful integration of smart contracts into the legal landscape will require collaboration between legal professionals, technologists, and regulators to create a robust framework that supports innovation while safeguarding legal principles.
Regulatory Landscape for Blockchain and Smart Contracts
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the intersection of technology and law becomes increasingly complex, particularly with the advent of blockchain and smart contracts. These innovations promise to revolutionize various industries by enhancing transparency, efficiency, and security. However, they also present unique challenges and considerations for legal professionals navigating the regulatory landscape. Understanding the intricacies of blockchain and smart contracts is essential for lawyers who wish to effectively advise their clients and anticipate potential legal issues.
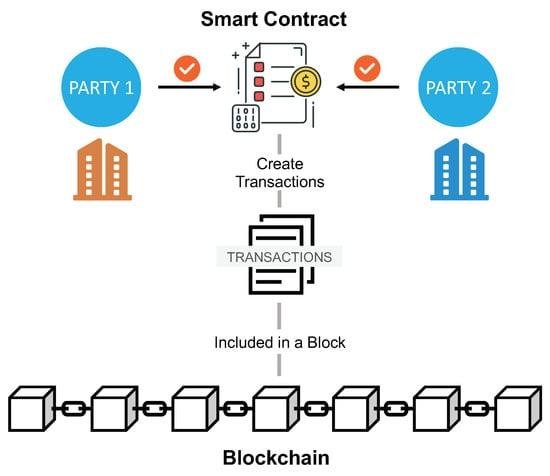
Blockchain technology, at its core, is a decentralized ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. This decentralization ensures that the data is immutable and transparent, making it an attractive option for industries that require secure and verifiable records. Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, operate on blockchain platforms. They automatically enforce and execute the terms of a contract when predefined conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries and potentially lowering transaction costs.
Despite their potential benefits, blockchain and smart contracts pose significant regulatory challenges. One of the primary concerns is the legal recognition and enforceability of smart contracts. Traditional contract law is based on principles that may not easily apply to digital agreements. For instance, issues such as offer, acceptance, and consideration need to be re-evaluated in the context of code-based contracts. Lawyers must consider how existing laws can be interpreted to accommodate these new forms of agreements and whether new legislation is necessary to address their unique characteristics.
Moreover, the decentralized nature of blockchain raises questions about jurisdiction and applicable law. Transactions on a blockchain can occur across multiple jurisdictions, complicating the determination of which legal system governs a particular transaction. This complexity necessitates a nuanced understanding of international law and the development of strategies to address cross-border legal issues. Lawyers must be prepared to navigate these challenges and advise their clients on how to structure transactions to minimize legal risks.
Data privacy and security are also critical concerns in the regulatory landscape of blockchain and smart contracts. While blockchain is often lauded for its security features, the transparency of the ledger can conflict with data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. Lawyers need to understand how to balance the transparency of blockchain with the privacy rights of individuals, ensuring compliance with relevant data protection laws.
Furthermore, the regulatory environment for blockchain and smart contracts is continually evolving. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are grappling with how to effectively regulate these technologies without stifling innovation. Lawyers must stay informed about legislative developments and regulatory guidance to provide accurate and timely advice to their clients. This requires a proactive approach to legal education and a willingness to engage with policymakers and industry stakeholders.
In conclusion, the regulatory landscape for blockchain and smart contracts presents both opportunities and challenges for legal professionals. By understanding the technological underpinnings and legal implications of these innovations, lawyers can better serve their clients and contribute to the development of a legal framework that supports the growth of blockchain technology. As the technology continues to advance, staying informed and adaptable will be key to navigating the complexities of this dynamic field.
Intellectual Property and Blockchain: Protecting Digital Assets
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital technology, the intersection of intellectual property and blockchain presents both opportunities and challenges for legal professionals. As blockchain technology continues to gain traction, its application in the realm of intellectual property is becoming increasingly significant. At the heart of this intersection lies the concept of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts operate on blockchain platforms, offering a new paradigm for managing and protecting digital assets.
To understand the implications of smart contracts for intellectual property, it is essential to first grasp the fundamental characteristics of blockchain technology. Blockchain is a decentralized ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring that the data is secure, transparent, and immutable. This decentralized nature provides a robust framework for verifying ownership and provenance of digital assets, which is crucial in the realm of intellectual property. As digital assets become more prevalent, the need for secure and efficient methods of managing these assets becomes paramount.
Smart contracts offer a promising solution by automating the execution of contractual terms without the need for intermediaries. This automation not only reduces the potential for human error but also enhances the efficiency of transactions. For intellectual property, this means that licensing agreements, royalty payments, and other contractual obligations can be executed seamlessly, ensuring that creators and rights holders are compensated fairly and promptly. Moreover, the transparency and immutability of blockchain records provide an indisputable trail of ownership and usage rights, which is invaluable in resolving disputes.
However, the integration of smart contracts and blockchain into the intellectual property domain is not without its challenges. One of the primary concerns is the legal recognition and enforceability of smart contracts. While the code itself is self-executing, the legal framework surrounding these contracts is still evolving. Lawyers must navigate the complexities of ensuring that smart contracts comply with existing legal standards and are recognized by courts. This requires a deep understanding of both the technical aspects of blockchain and the legal principles governing contracts.
Furthermore, the global nature of blockchain technology presents jurisdictional challenges. Intellectual property laws vary significantly across different countries, and the decentralized nature of blockchain means that transactions can occur across borders with ease. Legal professionals must be adept at addressing these jurisdictional issues and ensuring that smart contracts are designed to comply with the relevant legal requirements in each jurisdiction.
In addition to these challenges, there are also opportunities for innovation. Blockchain technology can facilitate the creation of new business models for intellectual property management. For instance, tokenization of digital assets allows for fractional ownership and new forms of monetization. This opens up possibilities for creators to reach wider audiences and generate revenue in novel ways. Lawyers who are well-versed in blockchain technology can play a crucial role in advising clients on how to leverage these opportunities while navigating the associated legal complexities.
In conclusion, the integration of smart contracts and blockchain into the intellectual property landscape is a dynamic and evolving field. Legal professionals must stay informed about the latest developments in technology and law to effectively protect and manage digital assets. By understanding the potential and challenges of smart contracts, lawyers can provide valuable guidance to clients seeking to navigate this new frontier. As the digital world continues to expand, the role of legal expertise in safeguarding intellectual property will be more important than ever.
Dispute Resolution in the Era of Smart Contracts and Blockchain
In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, smart contracts and blockchain have emerged as transformative forces, reshaping various sectors, including the legal field. For lawyers, understanding these innovations is crucial, particularly in the realm of dispute resolution. Smart contracts, essentially self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, operate on blockchain technology, a decentralized and immutable ledger. This combination promises increased efficiency and reduced costs, but it also presents unique challenges and considerations for legal professionals.
To begin with, the immutable nature of blockchain, while offering security and transparency, complicates the resolution of disputes. Once a smart contract is executed, it is nearly impossible to alter, which raises questions about how to address errors or unforeseen circumstances. Traditional contracts allow for renegotiation or amendment, but smart contracts lack this flexibility. Consequently, lawyers must anticipate potential issues during the drafting phase, ensuring that the code accurately reflects the parties’ intentions and includes mechanisms for dispute resolution.
Moreover, the decentralized nature of blockchain poses jurisdictional challenges. Since blockchain operates across borders without a central authority, determining the applicable law and jurisdiction in case of a dispute can be complex. Lawyers must consider these factors when advising clients on smart contract transactions, potentially incorporating choice of law and forum selection clauses to mitigate uncertainty. Additionally, the anonymity often associated with blockchain transactions can hinder the identification of parties involved, complicating the enforcement of legal rights.
Despite these challenges, smart contracts offer opportunities for innovation in dispute resolution. For instance, they can incorporate automated dispute resolution mechanisms, such as arbitration clauses that trigger upon certain conditions. This can streamline the resolution process, reducing the need for court intervention. However, lawyers must ensure that these mechanisms comply with legal standards and protect their clients’ rights.
Furthermore, the role of lawyers in this new era extends beyond traditional legal advice. They must collaborate with technologists to bridge the gap between legal language and code, ensuring that smart contracts are both legally sound and technically robust. This interdisciplinary approach is essential for preventing disputes and effectively resolving them when they arise.
In addition to understanding the technical aspects, lawyers must stay informed about the evolving regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain and smart contracts. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are grappling with how to address these technologies, and legal professionals must be prepared to navigate this shifting terrain. This includes advising clients on compliance with existing laws and anticipating future regulatory developments.
As the use of smart contracts and blockchain continues to grow, lawyers must also consider the ethical implications. The automation of contractual processes raises questions about accountability and the potential for bias in coded decision-making. Legal professionals have a responsibility to ensure that these technologies are used ethically and that their clients’ interests are protected.
In conclusion, the advent of smart contracts and blockchain presents both challenges and opportunities for dispute resolution in the legal field. Lawyers must adapt to this new landscape by understanding the technical, jurisdictional, and regulatory complexities involved. By doing so, they can effectively guide their clients through the intricacies of smart contracts, ensuring that disputes are resolved efficiently and fairly. As technology continues to advance, the role of lawyers will undoubtedly evolve, requiring a proactive and informed approach to harness the potential of these innovations while safeguarding legal rights and ethical standards.
Conclusion
Smart contracts and blockchain technology are revolutionizing the legal landscape by offering decentralized, transparent, and automated solutions for executing agreements. Lawyers need to understand the technical underpinnings of blockchain to effectively navigate its implications on contract law, including issues of enforceability, jurisdiction, and security. Smart contracts, which are self-executing with the terms directly written into code, present unique challenges and opportunities in legal practice. They require lawyers to adapt traditional legal concepts to a digital framework, ensuring that these contracts are legally binding and compliant with existing regulations. Additionally, lawyers must be aware of the potential for disputes arising from coding errors or unforeseen circumstances, necessitating a blend of legal and technical expertise. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, legal professionals must stay informed and agile, integrating these innovations into their practice to better serve their clients and uphold the integrity of legal agreements in a digital age.