How Smart Contracts Are Changing Contract Law and Enforcement

Introduction
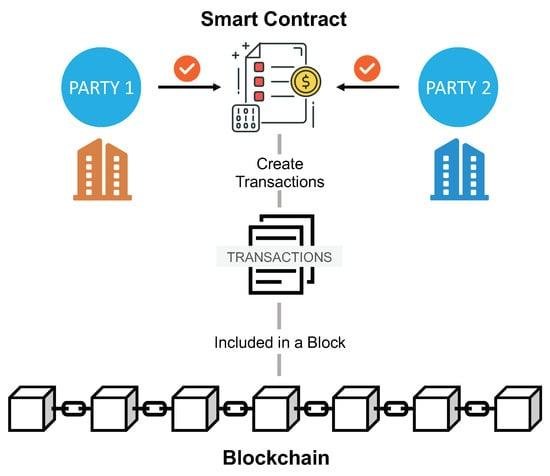
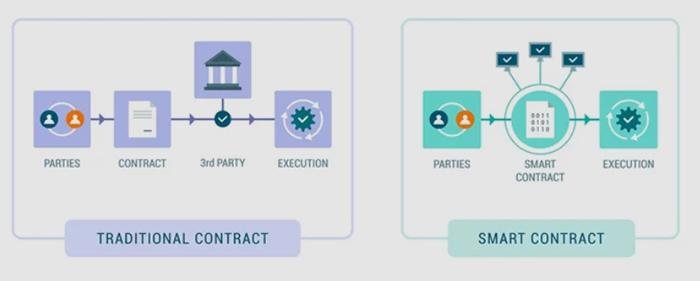
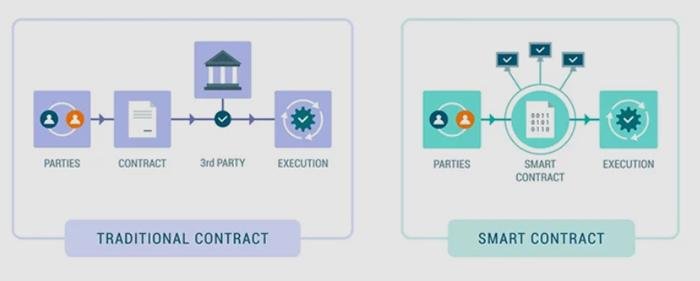
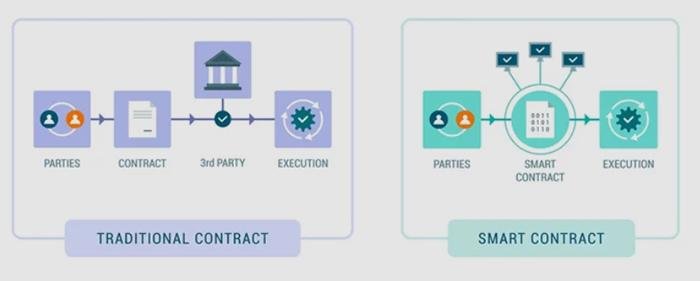
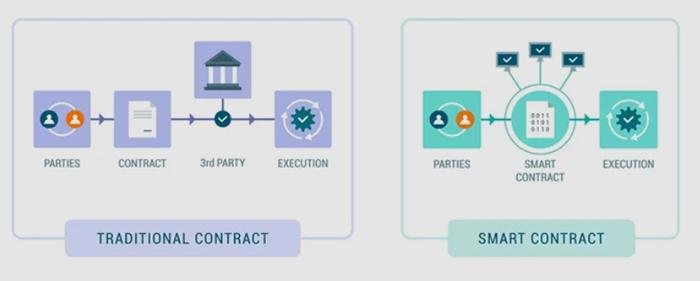
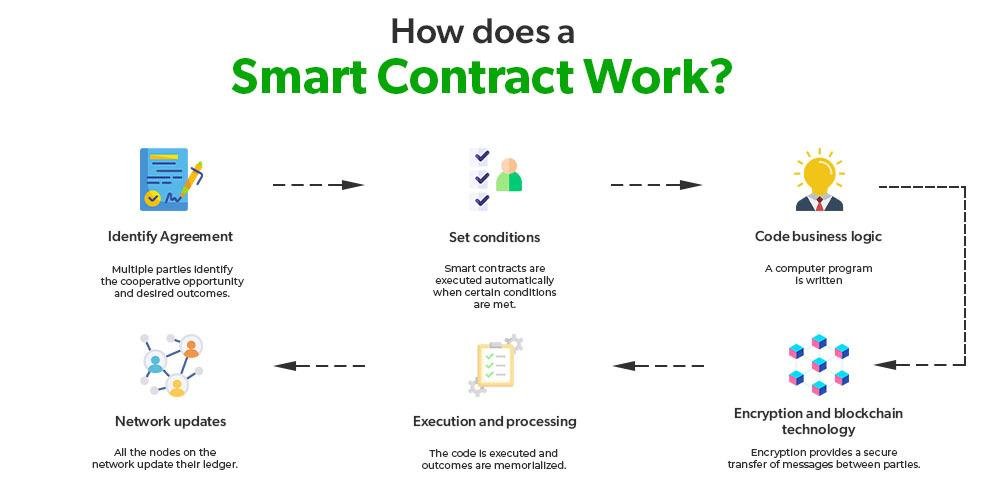
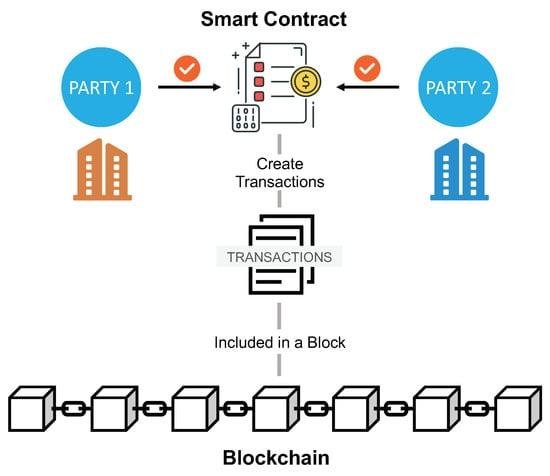
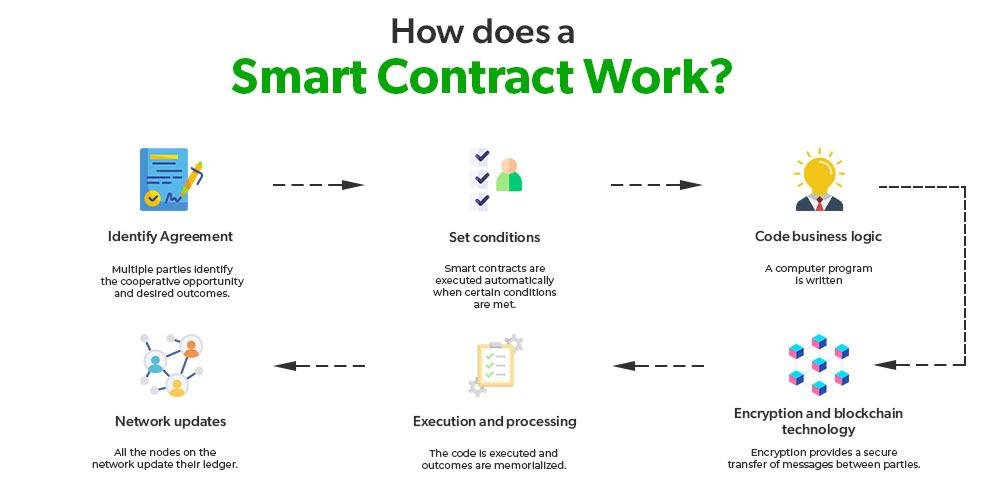
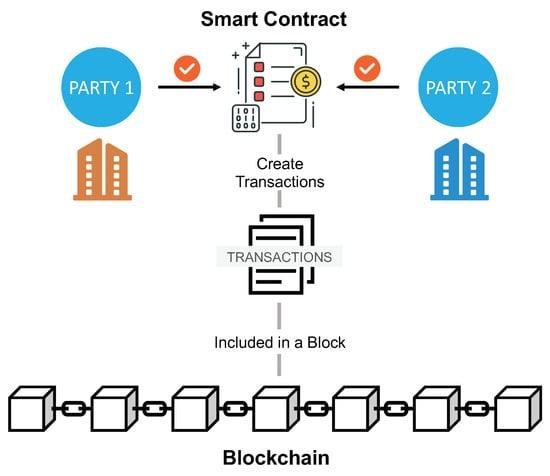
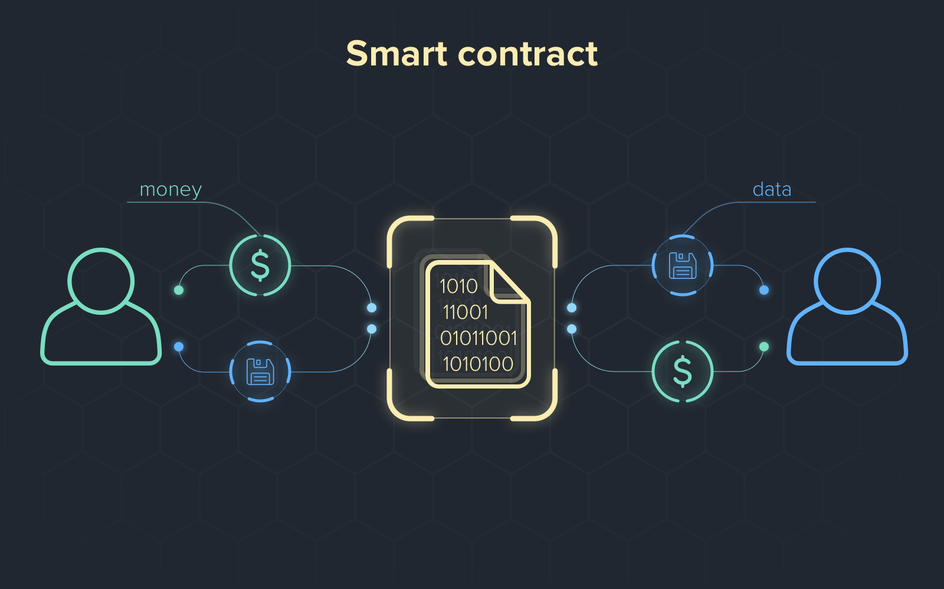
Smart contracts, powered by blockchain, are changing how contracts are made and enforced. Unlike traditional contracts that need lawyers or other intermediaries, smart contracts are self-executing and automatically carry out terms once specific conditions are met. This reduces the need for third parties, cuts down on human errors, and boosts transparency and trust. By embedding contract terms into code, smart contracts save time, reduce costs, and increase efficiency. As they gain popularity across industries, they are transforming legal processes and prompting a rethink of how contracts are handled in the digital age.
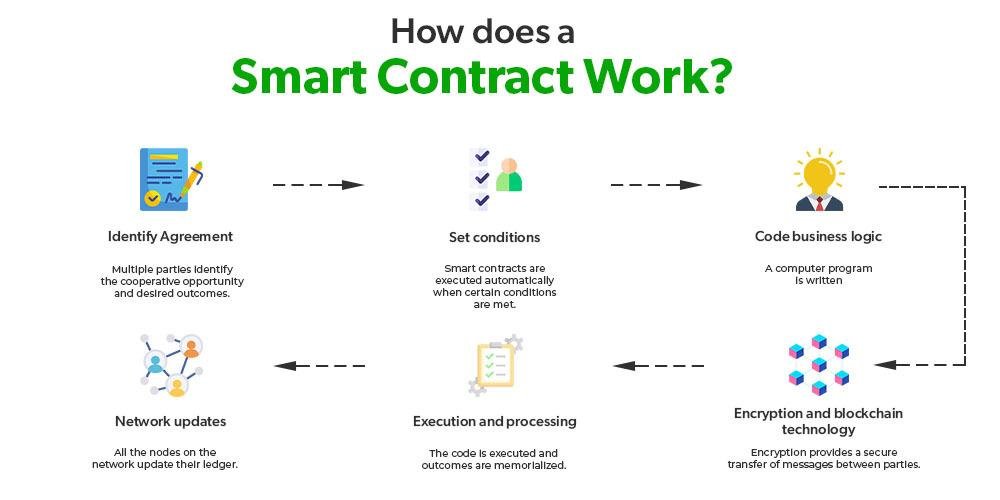
Automation of Contract Execution with Smart Contracts
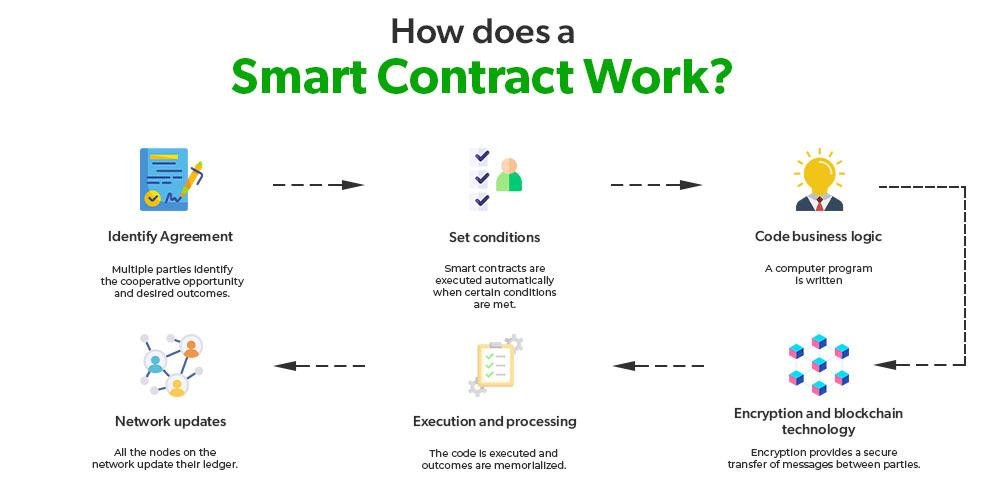
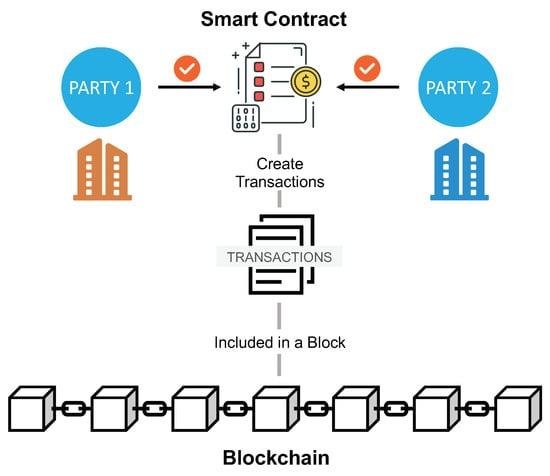
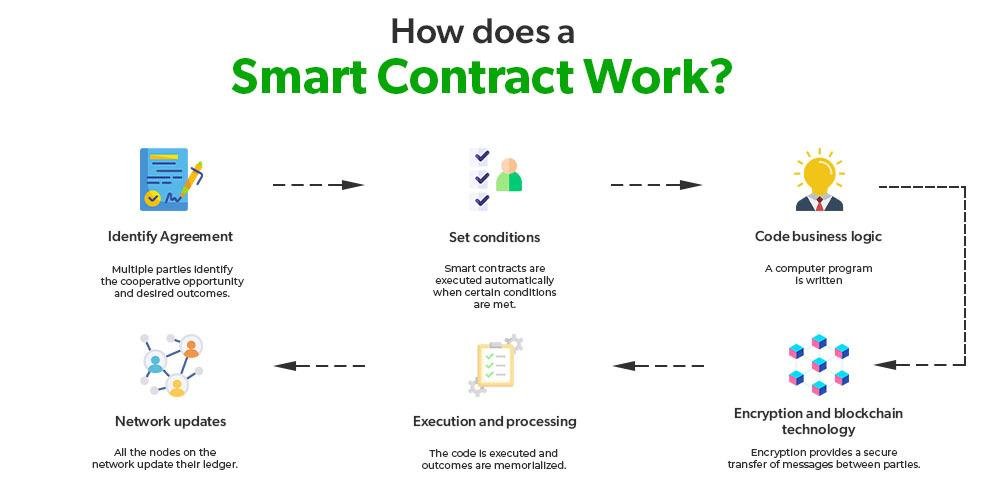
Smart contracts, powered by blockchain technology, are revolutionizing contract execution by automating the process, reducing the need for intermediaries, and improving efficiency. Here’s how they work:
Key Benefits:
- Clarity and Reduced Disputes:
- Terms and conditions are encoded into a digital format, ensuring all parties clearly understand their obligations.
- Reduces the risk of disputes as execution is based on objective data, not subjective interpretation.
- Speed and Efficiency:
- Smart contracts automatically execute when predetermined conditions are met, eliminating manual steps like verification and approval.
- Saves time, especially in industries like finance and supply chain management where speed is crucial.
- Cost Reduction:
- Eliminates the need for intermediaries (lawyers, notaries), lowering transaction costs.
- Blockchain’s transparency and security reduce the risk of fraud and manipulation.
- Enhanced Transparency:
- Blockchain technology provides a decentralized, tamper-proof record of the contract’s execution accessible to all parties involved.
Reduction of Legal Disputes with Smart Contracts
Smart contracts, powered by blockchain technology, are transforming contract law by reducing legal disputes. Here’s how:
Key Benefits:
- Transparency:
- All contract terms are visible to all parties and cannot be changed without consensus.
- Ensures everyone understands their obligations, reducing disputes caused by misunderstandings.
- Immutability:
- Once deployed, smart contracts cannot be altered, preventing tampering and offering more trust in the agreement.
- Automatic Execution:
- Smart contracts execute automatically when conditions are met, eliminating the need for manual intervention.
- This reduces reliance on lawyers or arbitrators, lowering costs and speeding up enforcement.
- Precision in Complex Transactions:
- Smart contracts can handle intricate conditions and contingencies, ensuring the agreement is fulfilled accurately and minimizing errors.
Challenges:
- Programming Errors: Mistakes in coding could cause unintended outcomes, leading to disputes.
- Legal Uncertainty: Legal frameworks for smart contracts are still developing, which could impact their enforceability.
Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention with Smart Contracts

Smart contracts, powered by blockchain technology, are reshaping contract law by offering enhanced security and preventing fraud. Here’s how:
Key Benefits:
- Immutability:
- Once a smart contract is created, it cannot be altered, preventing tampering or changes after the agreement is made.
- This eliminates the possibility of fraud and ensures the terms remain clear and indisputable.
- Decentralization:
- Smart contracts operate on a decentralized network, meaning there’s no central authority to hack or manipulate.
- Unlike traditional contracts, which rely on centralized systems, this reduces the risk of cyberattacks or data manipulation.
- Cryptographic Security:
- Every transaction within a smart contract is encrypted and linked to previous transactions, creating a secure and tamper-proof chain.
- This provides a transparent and verifiable audit trail that can be used to confirm contract execution and resolve disputes.
- Automation:
- Smart contracts automatically execute actions when predefined conditions are met, eliminating the need for manual intervention.
- This reduces the risk of human error or intentional manipulation, ensuring that contracts are executed fairly.
You May Also Like: Smart Contracts and Blockchain: What Lawyers Need to Know
Decentralization of Legal Processes with Smart Contracts
Smart contracts, powered by blockchain technology, are transforming contract law by decentralizing legal processes. Here’s how:
Key Benefits:
- Decentralization:
- No need for intermediaries like lawyers or notaries to enforce contracts.
- Parties can engage in transactions autonomously, without relying on a central authority, especially beneficial in cross-border agreements.
- Transparency:
- All transactions are recorded on a public blockchain, accessible to all involved parties.
- This creates trust and accountability, as everyone can verify the terms and execution of the contract independently.
- Immutability:
- Once a contract is executed, it cannot be altered or tampered with, ensuring a permanent and verifiable record.
- This reduces the risk of fraud and disputes.
- Cost Savings:
- Eliminates the need for costly intermediaries, reducing legal and administrative fees.
- Small businesses and startups can benefit from more affordable and efficient contract execution.
- Speed and Efficiency:
- Smart contracts execute automatically, often in real-time, speeding up processes and improving operational efficiency.
Cost Efficiency In Contract Management
Smart contracts, powered by blockchain technology, are transforming how businesses manage contracts, offering significant cost savings and efficiency. Here’s how:
Key Benefits:
- Reduced Need for Intermediaries:
- Smart contracts eliminate the need for lawyers, notaries, and other third parties, reducing legal fees and administrative costs.
- Automation speeds up the process, cutting down on manual oversight and intervention.
- Transparency and Immutability:
- All parties have access to the same information, ensuring the contract is executed exactly as agreed.
- This transparency reduces misunderstandings and the risk of costly litigation or disputes.
- Automated Execution:
- Transactions are automatically executed when conditions are met, speeding up contract fulfillment and reducing delays.
- This ensures timely payments and reduces the risk of late fees or penalties.
- Cost Savings in Record-Keeping:
- Smart contracts automatically record all transactions on the blockchain, providing a secure, tamper-proof audit trail.
- This simplifies compliance and auditing, saving time and resources.
- Efficiency in Operations:
- Automation improves overall business efficiency, enhances cash flow management, and provides a competitive advantage in fast-paced markets.
Global Accessibility And Standardization
Smart contracts, powered by blockchain technology, are transforming global contract law and enforcement by offering improved accessibility and standardization. Here’s how:
Key Benefits:
- Global Reach and Accessibility:
- Smart contracts allow parties from different countries to engage in transactions without needing intermediaries like lawyers or notaries.
- They provide a standardized platform for contract enforcement, making it easier for businesses in regions with limited legal infrastructure to participate in global trade.
- Automation and Efficiency:
- Smart contracts automatically execute terms once predefined conditions are met, reducing time, cost, and human error.
- This automation ensures that contracts are enforced impartially, offering efficiency and reducing reliance on intermediaries.
- Transparency and Trust:
- Since smart contracts are stored on a blockchain, all terms are visible, immutable, and accessible to all involved parties.
- This transparency fosters trust, reduces misunderstandings, and prevents disputes.
- Standardization Across Borders:
- Smart contracts can lead to industry-wide standard protocols and templates, simplifying cross-border agreements.
- Standardized contracts reduce complexity, making it easier to navigate international agreements.
Conclusion
Smart contracts are changing contract law by automating agreements using blockchain technology. These self-executing contracts reduce the need for middlemen, cutting costs and minimizing disputes. They offer transparency, security, and real-time enforcement, as terms are automatically carried out when conditions are met. However, smart contracts raise challenges, like the need for new laws to address issues of jurisdiction, liability, and how to interpret code as law. Overall, smart contracts bring efficiency and innovation but require legal systems to adapt.