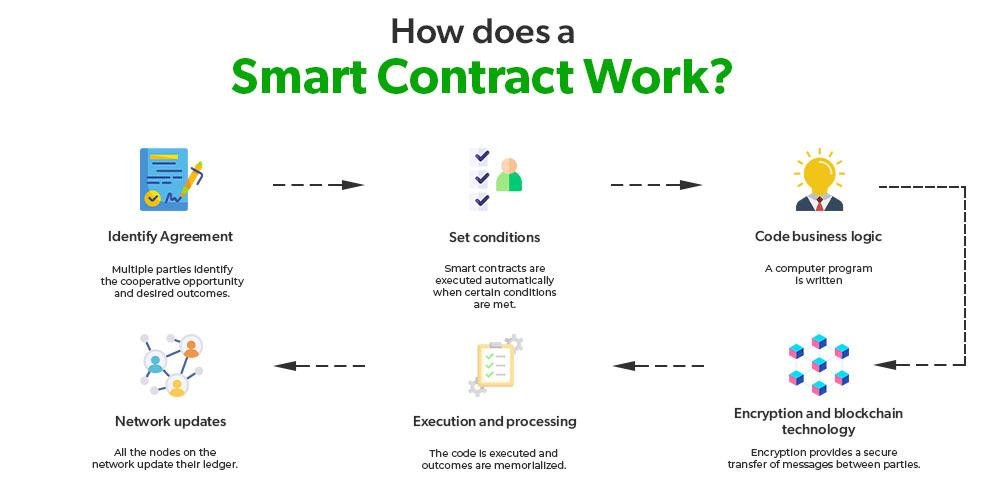
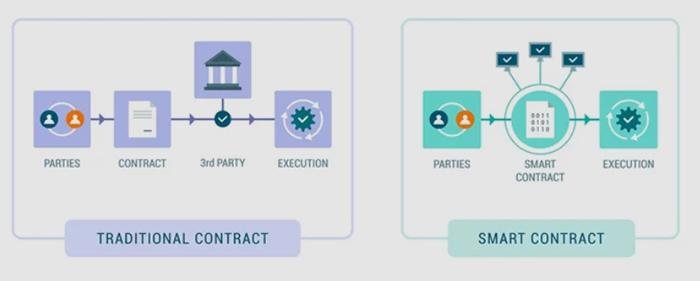
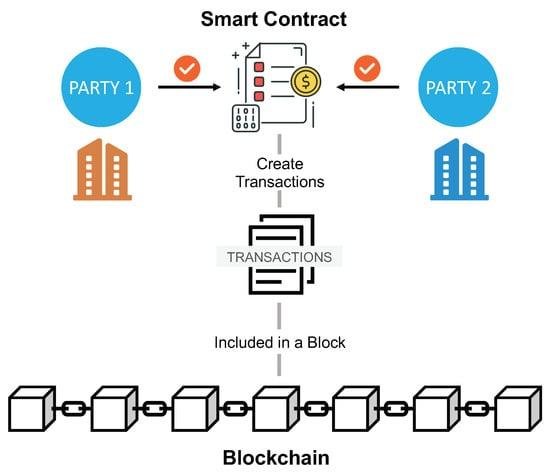
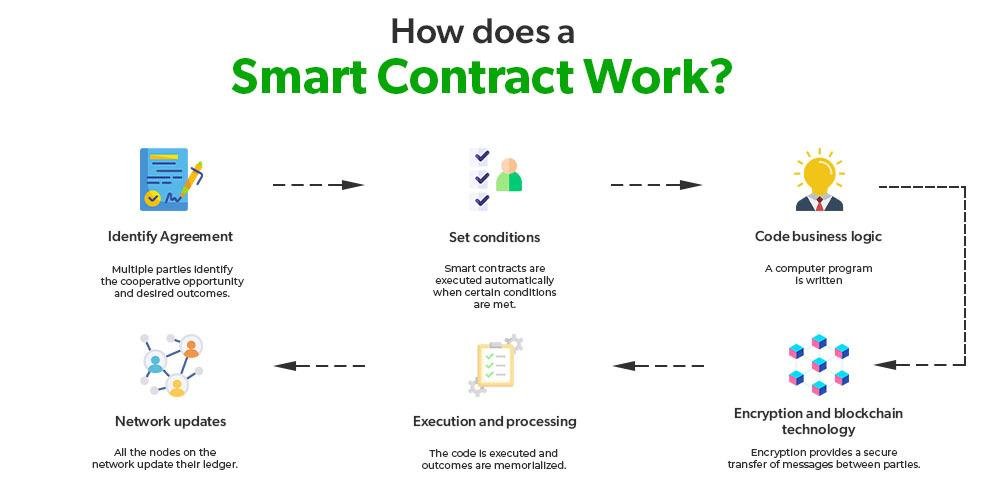
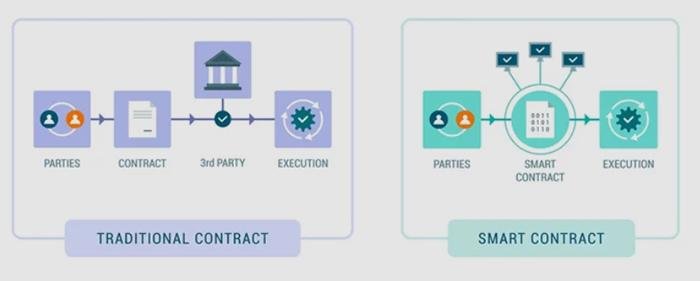
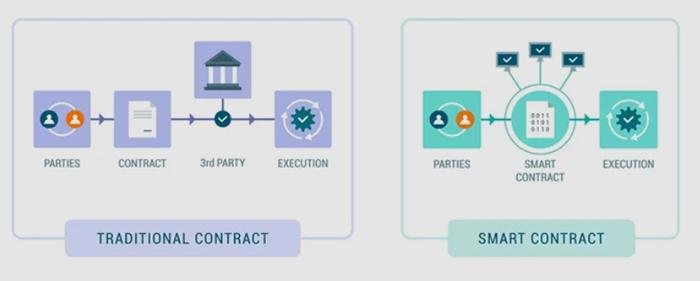
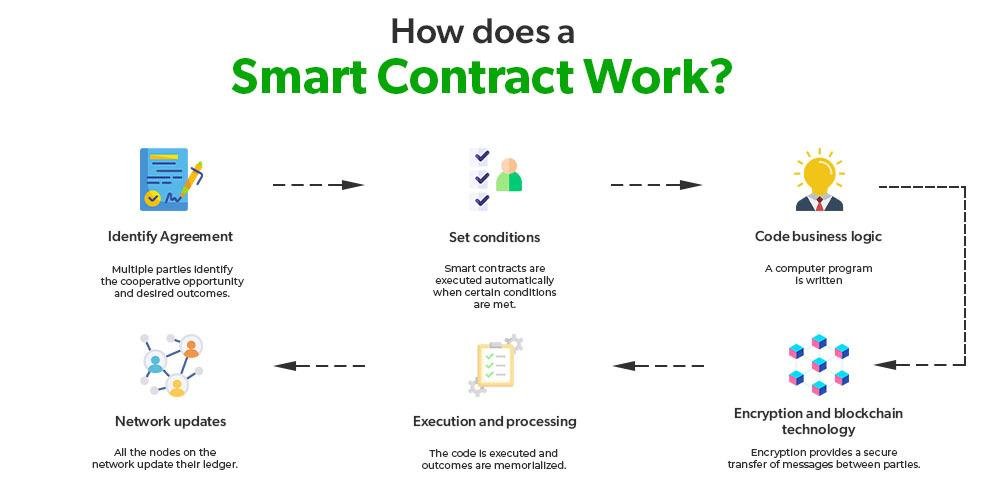
Smart Contracts and Data Privacy: Navigating the Legal Landscape
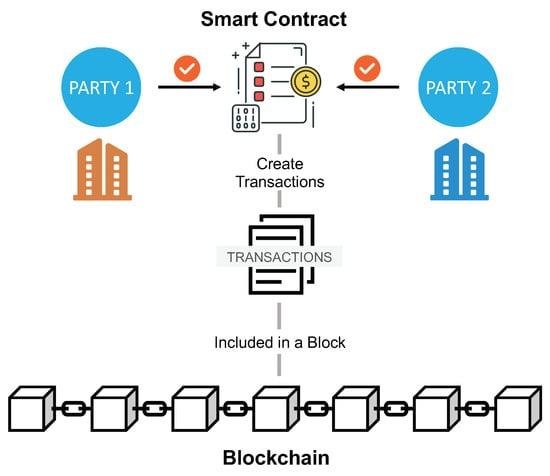
Introduction
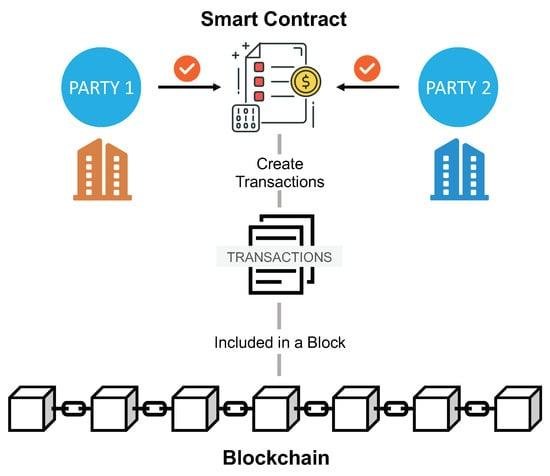
As digital transactions become more common, the relationship between technology and law is changing quickly. Among the new innovations, smart contracts are emerging as a game-changing tool. These self-executing agreements offer automation, transparency, and efficiency. However, as these digital contracts become more widely adopted, it’s increasingly important to understand how they affect data privacy. This article explores the legal complexities of smart contracts and the delicate balance between technological progress and the protection of personal data. We’ll dive into how smart contracts interact with privacy laws and discuss the potential challenges and benefits they bring.

Understanding the Interplay Between Smart Contracts and Data Privacy Regulations
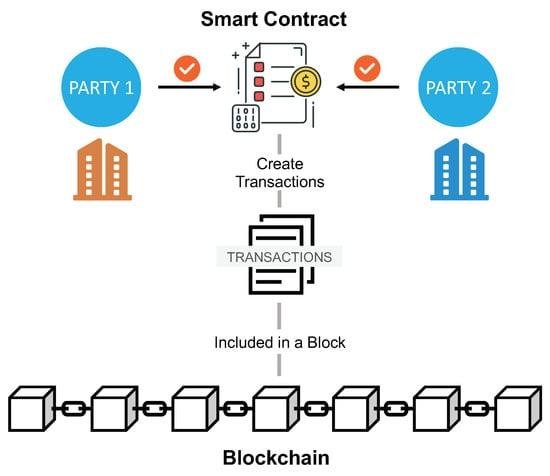
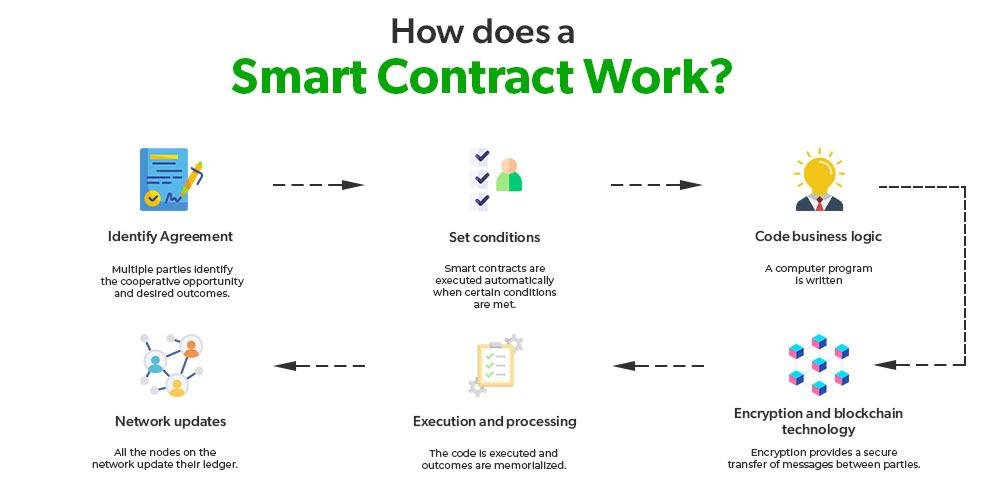
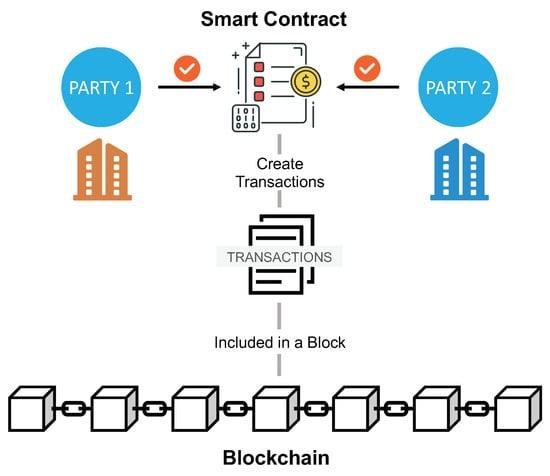
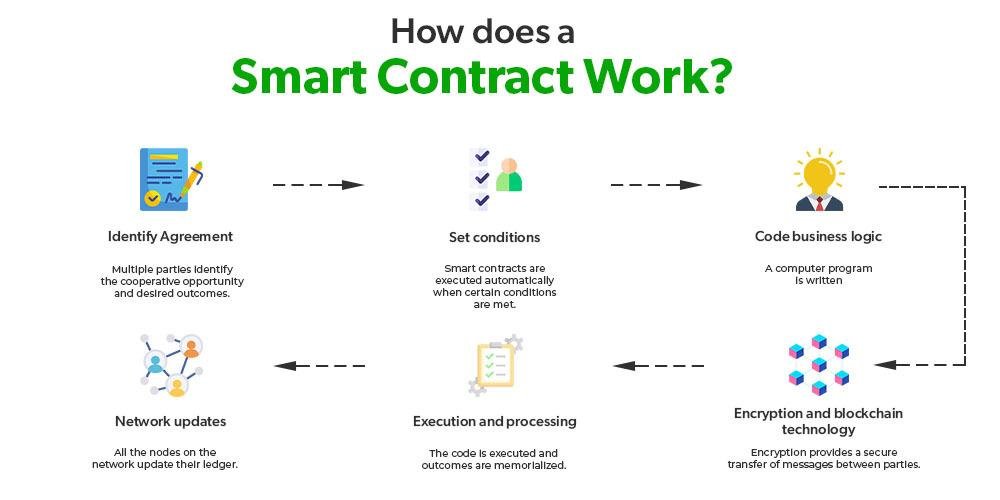
As more industries start using smart contracts, ensuring compliance with data privacy laws has become more important. Smart contracts are designed to automate agreements without needing a middleman, but they often deal with personal data in ways that can clash with established privacy laws. For example, laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) focus on protecting individual privacy, and blockchain’s unchangeable nature raises concerns about how personal data is processed and stored.
To address these concerns, businesses need to take a proactive approach by building privacy-by-design into their smart contract systems. This means:
- Anonymizing Data: Ensuring personal data is anonymized before being added to the blockchain.
- Data Minimization: Collecting only the data necessary to fulfill the contract, reducing exposure and risk.
- Data Access Control: Implementing strong authentication methods to limit access to sensitive data.
- Regular Audits: Conducting regular checks to ensure compliance with privacy regulations.
Below is a simplified overview of how smart contracts can align with key data privacy principles:
| Privacy Principle | Smart Contract Consideration |
|---|---|
| Lawfulness | Clear conditions for data processing in the contract. |
| Fairness | Transparent information on how data will be used. |
| Purpose Limitation | Defining specific purposes for data usage within the smart contract. |
Read More: Understanding Smart Contracts: What They Mean for the Legal Industry

Assessing the Impact of Blockchain Technology on Personal Data Protection
Blockchain is reshaping how personal data is stored and shared. Unlike traditional systems where data is centralized and vulnerable to breaches, blockchain distributes data across a network of computers, improving security. Blockchain uses encryption to make sure that personal data recorded on it remains unchanged and verifiable. This gives individuals more control over their data and ensures that historical records are secure.
However, blockchain’s unchangeable nature poses challenges, especially when it comes to laws like GDPR that emphasize user consent and the right to be forgotten. Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it can’t be easily deleted or changed, which could conflict with regulations that require data to be removed upon request.
| Consideration | Implications |
|---|---|
| Data Control | Empowers users to manage their own data permissions. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Challenges with GDPR and the right to be forgotten. |
| Security | Decentralization and encryption add layers of protection. |
| Transparency | Facilitates audits and tracking of data usage. |
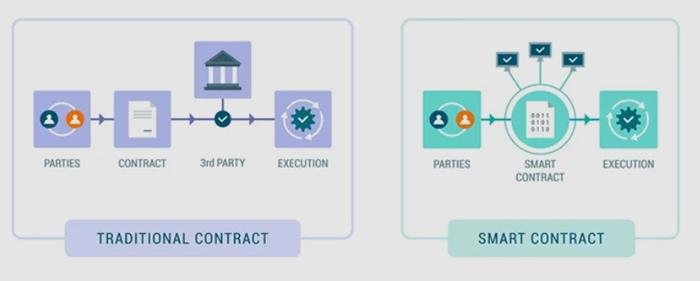
Best Practices for Implementing Data Privacy in Smart Contract Frameworks
To implement strong data privacy measures in smart contracts, businesses need to balance transparency with confidentiality. Here are some best practices:
- Minimize Data Collection: Only collect the data needed to fulfill the contract. This reduces risks and ensures compliance with privacy laws.
- Anonymization and Encryption: Use these techniques to protect sensitive data. For example, personal data can be stored off-chain while only necessary data (like a hash or ID) is stored on-chain.
- User Consent: Ensure your smart contracts have provisions for obtaining user consent on how their data will be handled.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular checks to ensure compliance with privacy laws like GDPR or CCPA.
- Decentralized Identity Solutions: Consider using solutions that let users control their own data-sharing preferences, adding an extra layer of privacy.
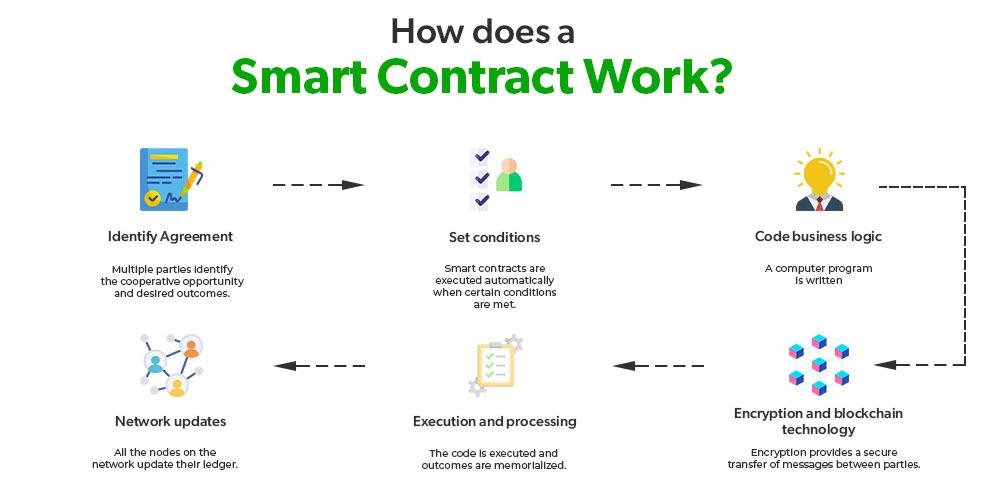
Future Trends in Smart Contracts and Their Implications for Legal Compliance
As smart contracts continue to evolve, they will play a bigger role in reshaping legal compliance. These contracts automate processes, reducing human error and improving efficiency. However, their automation and decentralization also present challenges for regulatory oversight. Moving forward, we can expect to see regulations adapt to accommodate these new technologies.
Some emerging trends to watch include:
- Dynamic Regulation: Laws that evolve with technology, keeping up with innovations in smart contracts.
- Privacy-Preserving Technologies: Solutions like zk-SNARKs (zero-knowledge proofs) to help protect private data while still allowing transactions to be verified.
- Compliance Tools: Systems to help businesses audit and ensure compliance with privacy regulations in smart contract systems.
| Key Focus Areas | Description |
|---|---|
| Dynamic Regulation | Adapting laws to cover evolving smart contract technologies. |
| Data Privacy Mechanisms | Solutions like zk-SNARKs for secure, private data handling. |
| Compliance Tools | Systems for auditing and ensuring adherence to regulations. |
In Conclusion
The intersection of smart contracts and data privacy presents both opportunities and challenges. While blockchain offers transparency and security, it also raises important questions about how personal data is handled. As the use of smart contracts grows, regulators and innovators must work together to find ways to balance the benefits of this technology with the protection of individual rights.
As we look ahead, the success of smart contracts will depend not only on technological advancements but also on the creation of strong legal frameworks that prioritize privacy. Developers, legal professionals, and users must collaborate to build a responsible approach to smart contracts, ensuring that innovation and privacy can coexist.
The road ahead is complex, but with careful planning and collaboration, we can navigate this new landscape and ensure that the promise of smart contracts is realized without compromising individual rights.