Introduction
In today’s digital age, where technology is reshaping business and law, smart contracts are emerging as a powerful tool that could change how agreements are made and enforced. These digital contracts use blockchain technology, which is secure and automatic, to make transactions more efficient and transparent. But as smart contracts become more popular, questions arise about how disputes will be handled. What happens if a party doesn’t meet its contractual obligations? Who is responsible, and how can disagreements be resolved when the contract is governed by code instead of human negotiation? This article explores how smart contracts work with dispute resolution and what systems can help solve conflicts in this new digital world.

Understanding Smart Contracts and Their Role in Modern Agreements
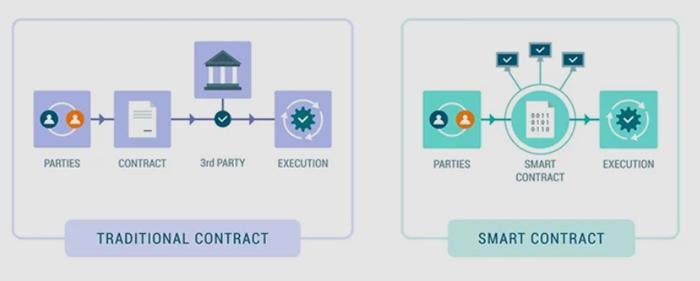
Smart contracts represent a major shift in how agreements are made, executed, and enforced. Unlike traditional contracts, which require intermediaries (like lawyers or courts) to enforce the terms, smart contracts use blockchain to automate and simplify the process. They work by specifying actions to take when certain conditions are met, making the process faster and less prone to human error. Essentially, these contracts are coded into a digital form, which brings precision and clarity to the agreement.
Smart contracts are becoming more important in the legal world, especially for resolving disputes. Some of their key advantages are:
- Immutability: Once a smart contract is on the blockchain, it can’t be changed, ensuring trust.
- Transparency: All actions are visible to everyone involved, making it easy to track and verify the contract’s execution.
- Speed: Automation allows for faster resolutions compared to traditional contracts.
- Cost-effective: By eliminating intermediaries, smart contracts can reduce costs.
To illustrate the functioning of smart contracts in dispute resolution, consider the following table, outlining how traditional contract methods compare with smart contract approaches:
| Aspect | Traditional Contracts | Smart Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | Manual intervention needed | Automated and instant |
| Trust Level | Dependent on third-party | Trustless environment |
| Time for Resolution | Potentially lengthy | Immediate |
| Fee Structure | Higher due to intermediaries | Lower due to automation |

Navigating Dispute Resolution Mechanisms in Smart Contracts
In smart contracts, there’s no central authority like a judge or arbitrator, which can make resolving disputes more challenging. To handle this, it’s useful to build dispute resolution mechanisms directly into the contract. Some options include:
- Arbitration Clauses: These specify how a neutral third party will resolve disputes.
- Escrow Services: Smart contracts can hold funds until both parties agree on a solution.
- Dispute Resolution Protocols: Predefined rules on how to handle disputes.
There are different ways to resolve disputes, and having a tiered approach (starting with negotiation and moving to mediation or arbitration if needed) can be effective. Here’s a brief summary of the most common methods:
| Method | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Negotiation | Parties discuss and attempt to resolve the dispute directly. | Cost-effective, quick resolution. |
| Mediation | A neutral third party facilitates a conversation between disputing parties. | Confidential, collaborative approach. |
| Arbitration | A third party makes a binding decision based on the presented evidence. | More formal, legally enforceable outcomes. |
Best Practices for Implementing Effective Dispute Resolution Strategies
To make smart contracts work smoothly, it’s important to have clear communication and a solid plan for resolving disputes. Here are some best practices:
- Clear Documentation: Ensure all contract terms and changes are clearly recorded.
- Transparent Processes: Have clear steps for identifying and resolving disputes.
- Regular Training: Keep all parties informed about the dispute resolution options available.
It’s also helpful to use independent third-party mediators who are neutral and familiar with blockchain and smart contracts. Here’s what to consider when choosing a mediator:
| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Experience | Proven track record in dispute resolution in tech contexts. |
| Impartiality | Neutral stance to ensure fair assessment. |
| Technical Knowledge | Familiarity with blockchain and smart contracts. |
Read Also: Legal Challenges and Risks Associated with Smart Contracts
Future Trends: The Evolution of Smart Contracts in Legal Frameworks
As technology evolves, smart contracts are expected to become an even bigger part of legal frameworks. Important trends that may influence this future include:
- Interoperability: Smart contracts will work across different legal systems and jurisdictions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Laws will adapt to include smart contracts, ensuring they meet legal standards.
- Accessibility: Smart contracts could make legal processes more affordable and accessible, allowing individuals to resolve disputes without expensive legal representation.
We may also see a hybrid model combining traditional legal methods with automated smart contract solutions, leading to new ways of resolving disputes that balance human judgment and technology.
| Factor | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Technological Advancements | Enhanced efficiency in resolving disputes. |
| Legal Recognition | Increased trust in smart contracts as enforceable agreements. |
| Consumer Acceptance | Wider adoption of smart contracts among businesses and individuals. |
Final Thoughts
Smart contracts provide a vision of a future where transactions are quicker, clearer, and safer. However, managing disputes in this digital space is still a challenge. Understanding how smart contracts interact with traditional legal systems is crucial for businesses and individuals alike. While the potential of smart contracts is vast, successful implementation requires clarity, fairness, and a willingness to adapt to new ways of resolving conflicts.
As we continue to explore and refine this technology, embracing smart contracts will streamline transactions and create a more equitable digital economy. Let’s keep an open dialogue and develop solutions that bridge technology and law, ensuring that smart contracts benefit everyone involved.


