Smart Contracts in Law: Revolutionizing Contract Management
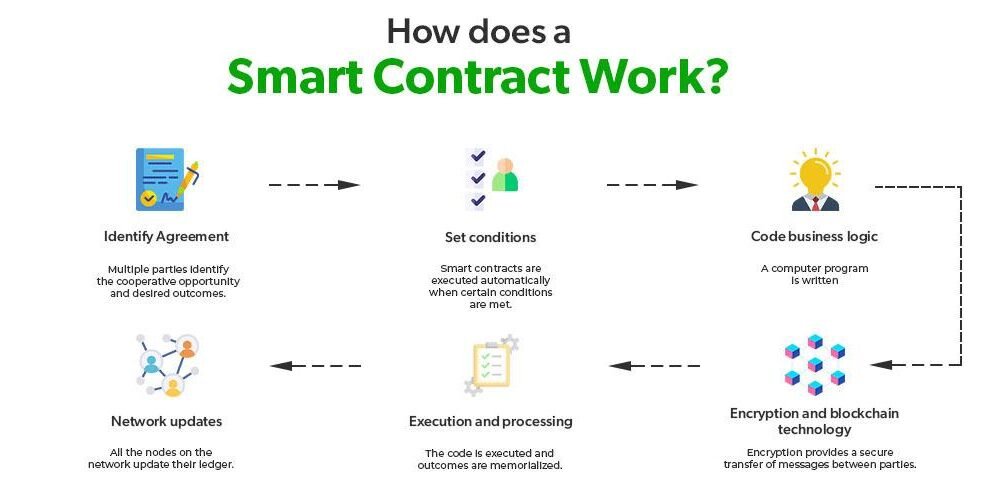
In an era marked by rapid technological advancement, the legal landscape is not immune to transformation. Enter smart contracts—a groundbreaking innovation that merges technology with legal principles, promising to redefine the way contracts are created, executed, and enforced. These self-executing agreements, with their terms directly written into code, are poised to streamline contract management, reduce the potential for disputes, and enhance transparency between parties. As the legal profession grapples with the challenges of traditional contract frameworks, smart contracts emerge as a beacon of efficiency and precision. This article delves into the intricate relationship between smart contracts and law, exploring how this digital paradigm shift is set to revolutionize contract management practices and the implications that come along with this evolution.
Understanding Smart Contracts: The Technology Behind the Transformation
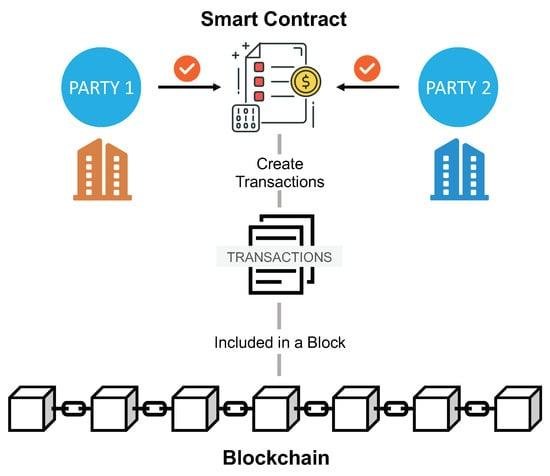
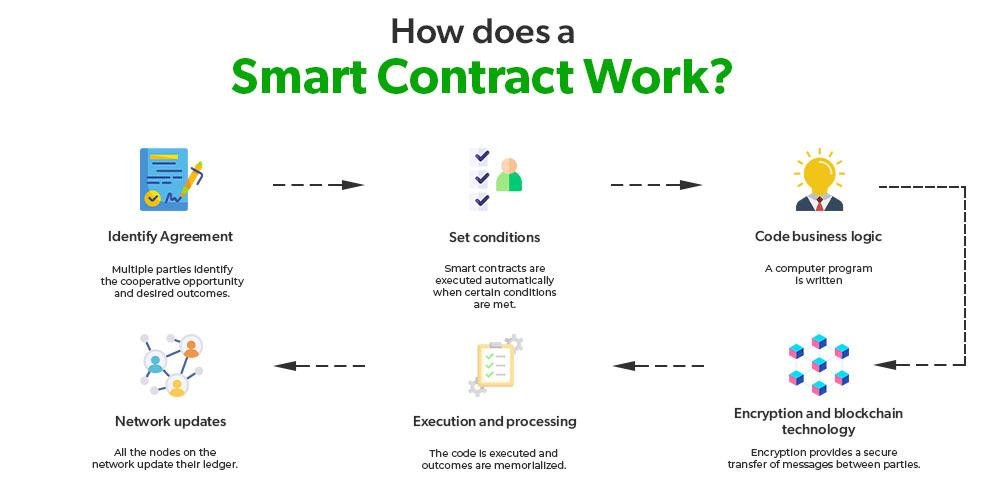
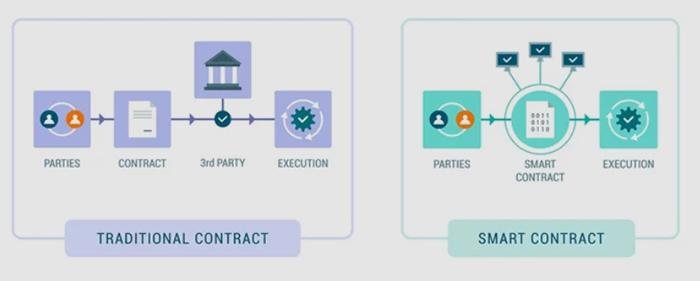
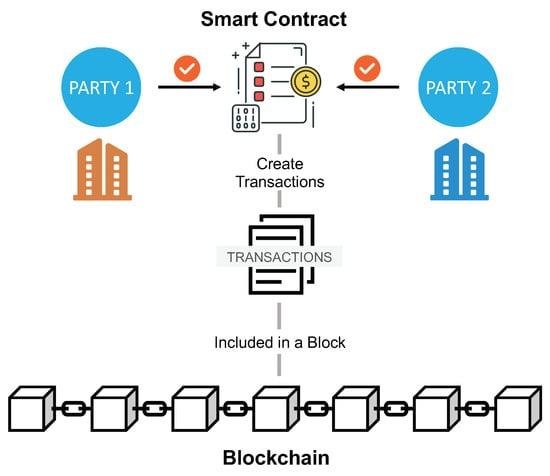
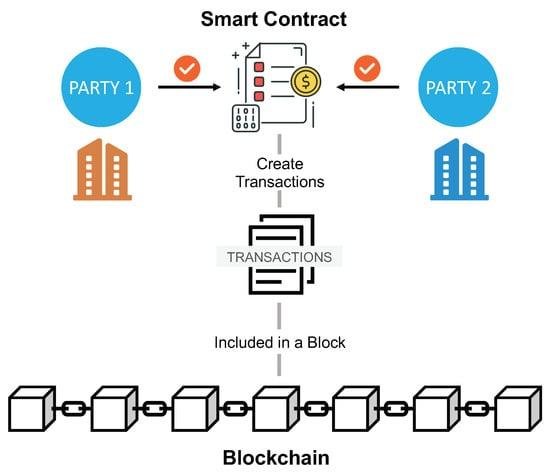
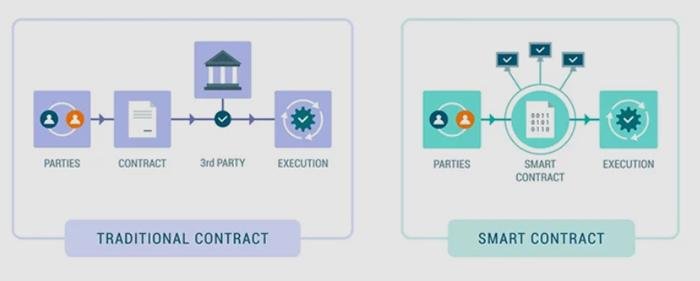
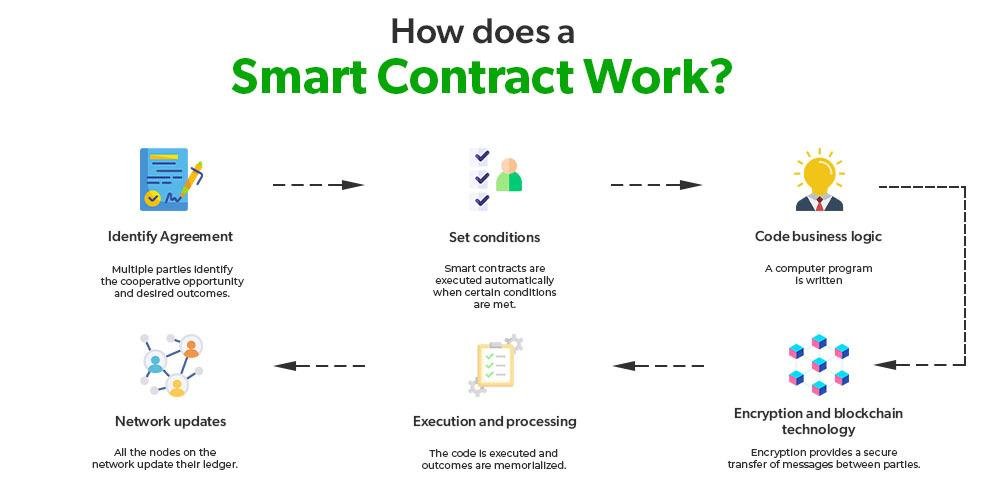
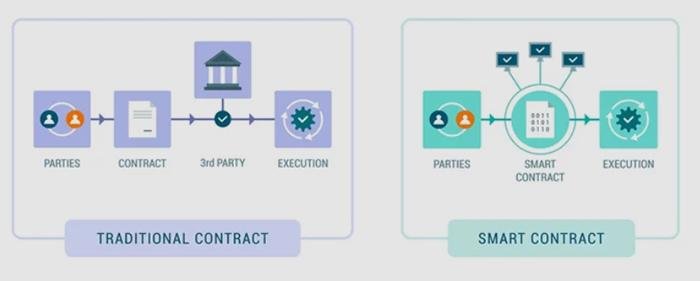
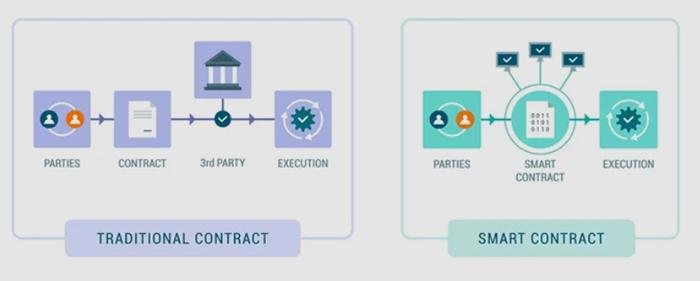
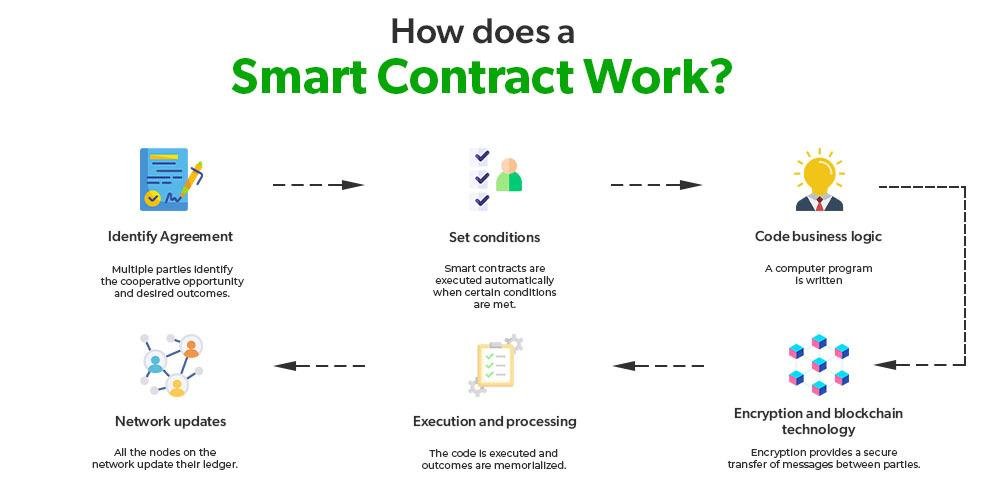
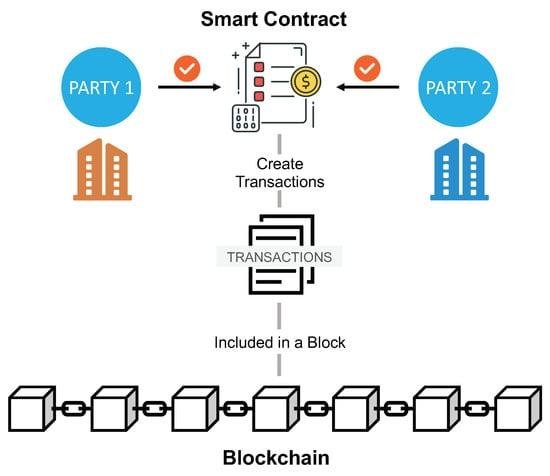
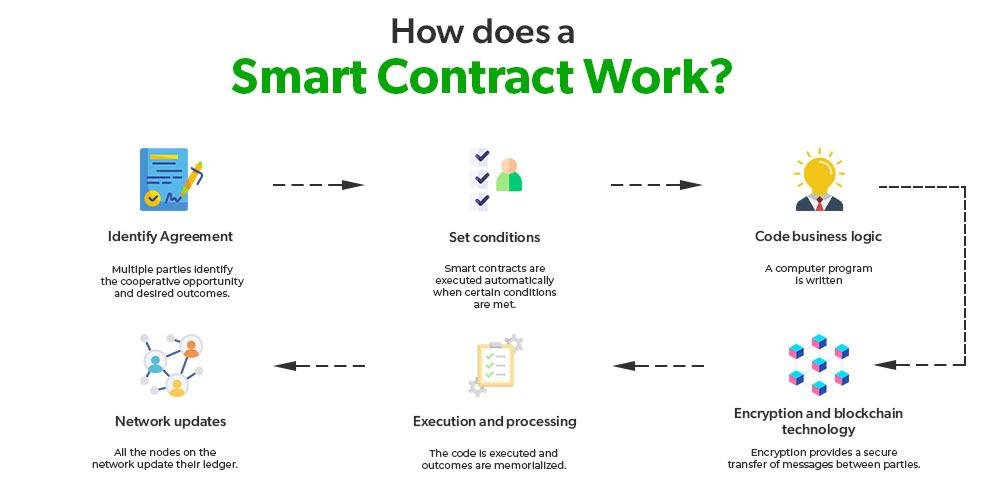
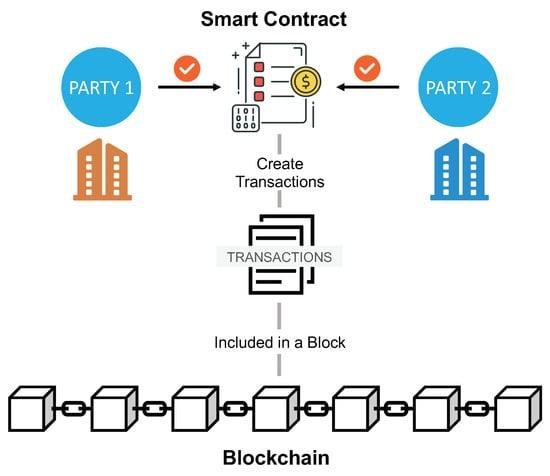
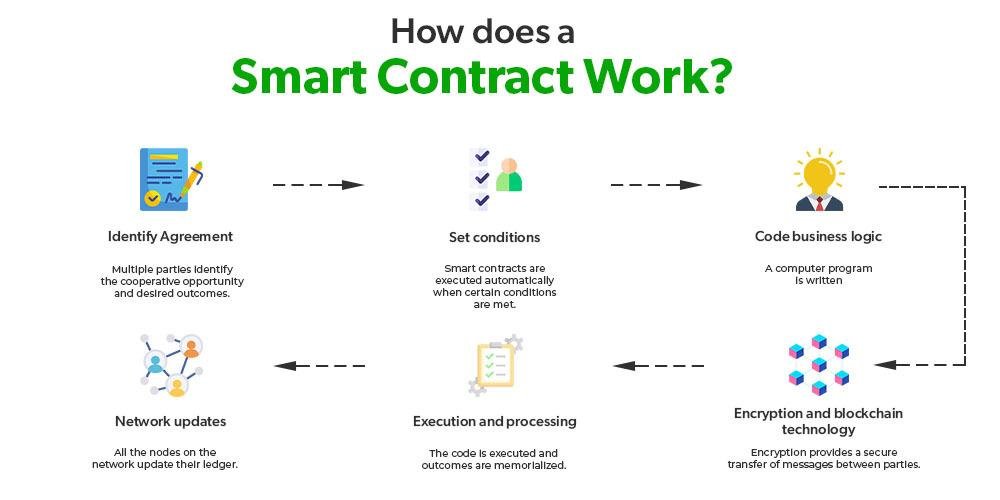
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, enabling them to automatically enforce and execute contractual stipulations without the need for intermediaries. Utilizing blockchain technology, these digital contracts operate on a decentralized platform that ensures transparency, security, and immutability. This revolutionizes traditional contract management by providing a trustless environment where parties can interact confidently, knowing that the terms will be enforced as coded. It allows for greater efficiency, lower costs, and reduced disputes, transforming how legal obligations are approached and upheld.
The key components of smart contracts include their programmable nature, which allows for complex conditions and actions, as well as their integration with oracles that can pull in data from the real world, making them versatile and adaptable. As this technology continues to evolve, industries are exploring various use cases, from automating transactions to facilitating compliance monitoring. Consider the following benefits of smart contracts:
- Automation: Minimizes human error and ongoing management tasks.
- Cost-effectiveness: Reduces the need for intermediaries like lawyers or notaries.
- Speed: Executes agreements almost instantly upon meeting pre-defined conditions.
- Security: Utilizes cryptographic methods to safeguard data integrity.
| Aspect | Traditional Contracts | Smart Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | Requires manual processing | Automated execution |
| Disputes | Often leads to litigation | Prevention through transparency |
| Cost | High due to intermediaries | Lower operational costs |

Legal Implications of Smart Contracts: Navigating Compliance and Enforcement
The integration of smart contracts into legal frameworks introduces significant implications for compliance and enforcement. As these self-executing contracts operate on blockchain technology, their immutable and transparent nature can challenge traditional legal principles. In particular, jurisdiction becomes a key concern, as the decentralized nature of blockchains may obscure which legal framework applies. Key considerations include:
- Regulatory Compliance: Smart contracts must adhere to relevant laws and regulations in various jurisdictions, necessitating an understanding of how they interact with existing legal systems.
- Enforceability: The enforceability of smart contracts can hinge on their ability to satisfy traditional contract elements, such as mutual consent, legality, and capacity.
- Dispute Resolution: Traditional mechanisms for dispute resolution, including litigation and arbitration, may need adaptation to address conflicts arising from smart contract executions.
To navigate these complexities, stakeholders must be vigilant in establishing frameworks that ensure compliance while leveraging the unique properties of smart contracts. Engaging legal professionals with expertise in technology law can facilitate the creation of robust agreements that protect parties involved. Furthermore, understanding liability issues is crucial; certain scenarios must delineate who bears responsibility when smart contracts fail due to code errors or external factors. The following table outlines potential liability scenarios related to smart contracts:
| Scenario | Potential Liability |
|---|---|
| Code Bug | Developer liability for failures |
| External Attack | Securities fraud or regulatory fines |
| Failed Execution | Loss of trust or reputational damage |

Enhancing Efficiency: Streamlining Contract Management Processes
In today’s fast-paced business environment, organizations are constantly seeking ways to enhance their operational workflows. Smart contracts offer a transformative solution by automating and digitizing the entire contract lifecycle. This technology enables various processes to run more smoothly, from initial drafting to final execution. As a result, legal teams can focus on strategic decision-making rather than getting bogged down in tedious administrative tasks. Some key benefits of utilizing smart contracts in contract management include:
- Reduced Time Delays: Automated processes minimize the time spent in negotiations and approvals.
- Increased Accuracy: Smart contracts minimize human error, ensuring that terms are executed exactly as intended.
- Improved Compliance: Blockchain technology automatically enforces compliance with regulations and contractual obligations.
Moreover, the integration of smart contracts allows for better visibility and tracking of contract performance through real-time analytics. This accessibility makes it easier for stakeholders to monitor key performance indicators and ensure adherence to terms. For organizations looking to quantify the benefits of smart contracts, the following table illustrates potential improvements in various metrics:
| Metrics | Before Smart Contracts | After Smart Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Time to Execute Contracts | Average 15-30 days | Average 2-3 days |
| Error Rate | 10% | 1% |
| Compliance Issues | 20% | 2% |

Best Practices for Implementing Smart Contracts in Legal Frameworks
When integrating smart contracts within existing legal frameworks, it’s essential to adhere to best practices that ensure effectiveness and compliance. Thorough legal review of the smart contract code should be prioritized, ensuring that all terms and provisions align with current laws and regulations. Engaging legal experts with a deep understanding of both traditional contract principles and blockchain technology can facilitate this process. Additionally, clear definitions of contract terms must be established within the code; vague language can lead to disputes regarding intent and execution.
Moreover, the importance of comprehensive documentation cannot be overstated. Documenting the decision-making process, coding sources, and testing outcomes will enhance transparency and trust for all parties involved. Data management practices should also be implemented to guarantee that sensitive information remains secure and private while adhering to applicable data protection laws. To further support this framework, organizations can consider creating a matrix of compliance that outlines how each aspect of the smart contract aligns with relevant legal standards. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also fosters a culture of accountability.
| Best Practices | Description |
|---|---|
| Legal Review | Engage legal professionals to ensure compliance with existing laws. |
| Clear Definitions | Use specific language to avoid ambiguity in contract terms. |
| Documentation | Maintain detailed records of the coding, decisions, and processes. |
| Data Management | Implement measures to protect sensitive information. |
| Compliance Matrix | Create a tool to visualize alignment with legal standards. |
To Conclude
the rise of smart contracts represents a transformative shift in the realm of contract management, ushering in a new era of efficiency, transparency, and security. As legal professionals and organizations begin to embrace this innovative technology, the potential for streamlining processes and reducing disputes becomes increasingly apparent. While challenges remain in terms of legal recognition and integration within existing frameworks, the momentum behind smart contracts is undeniable. As we stand at the intersection of law and technology, it will be fascinating to witness how this evolution shapes the landscape of contractual agreements in the years to come. The future of contract management may very well be written in code, and those who adapt to this change could redefine the boundaries of legal practice in unprecedented ways.