Smart Contracts: Legal Challenges in Cross-Border Transactions
Introduction
As technology continues to change how businesses and people interact, smart contracts are emerging as a game-changing tool. These self-executing agreements, built on blockchain technology, offer a more efficient and transparent way of handling transactions, especially for international deals where trust and clarity are crucial. However, while smart contracts have great potential, they also bring several legal challenges that need careful consideration. As countries try to adapt their laws to include smart contracts, questions about their enforceability, which laws apply, and who is responsible in case something goes wrong are becoming more urgent. This article explores these legal issues and looks at how smart contracts are shaping the future of cross-border transactions.
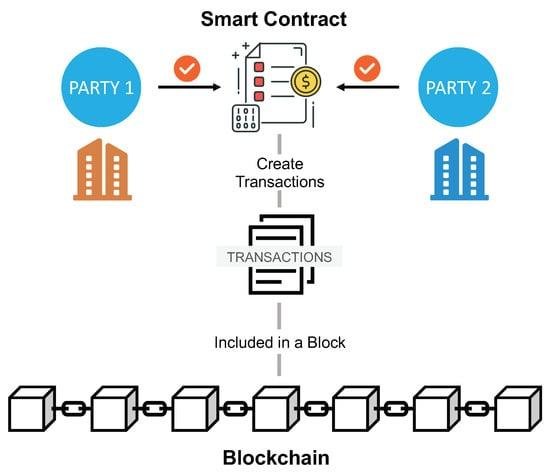
Navigating the Maze of Jurisdiction: Understanding Legal Frameworks for Smart Contracts
One of the biggest challenges with smart contracts is understanding which legal rules apply, especially when parties are in different countries. Since blockchain is decentralized, there’s no clear-cut answer to which laws govern a contract. The laws of each country or region might differ, and this can lead to confusion about whether a smart contract is enforceable. Key factors that influence jurisdiction include:
- Location of the parties: Where are the people or businesses involved located?
- Blockchain platform: What blockchain is being used for the contract?
- Agreed-upon laws: Did the parties agree on which country’s laws would apply?
For example, a smart contract created in one country might be recognized there but rejected in another. Here’s a simple summary of how different countries are handling smart contracts:
| Country | Legal Stance on Smart Contracts |
|---|---|
| United States | Generally recognized under UETA and ESIGN Act. |
| European Union | Guided by eIDAS regulation; varying interpretations among member states. |
| China | Growing acceptance, but strict regulations on blockchain technology. |
| India | Legal status is unclear; ongoing discussions for comprehensive regulations. |
You May Also Like: Legal Challenges and Risks Associated with Smart Contracts

The Role of Blockchain in Ensuring Compliance: Bridging Gaps in Cross-Border Transactions
Blockchain technology helps solve some of the challenges in international transactions by creating a secure and transparent record of all transactions. This helps ensure that both sides can trust each other, reducing the risk of fraud. Because blockchain is decentralized, no single entity has control over it, making it easier to follow various countries’ laws.
Blockchain also helps automate compliance through smart contracts. These self-executing contracts automatically follow the agreed terms, reducing the time and costs that would normally be spent on compliance checks. Though legal challenges exist regarding enforceability and jurisdiction, smart contracts offer a way to streamline compliance. Key benefits include:
- Transparency: All parties can see transaction details, making audits easier.
- Cost reduction: Fewer intermediaries, like lawyers or banks, reduce expenses.
- Automated compliance: The contract can be programmed to meet legal requirements automatically.
Dispute Resolution in the Digital Age: Addressing Challenges in Smart Contract Enforcement
The decentralized nature of blockchain means that disputes may involve legal systems in multiple countries, each with different rules. To address this, new methods for resolving disputes are being developed, such as:
- Arbitration: A formal process where a neutral party makes a binding decision.
- Mediation: A less formal process where a mediator helps parties reach an agreement.
By using these approaches, smart contract users can reduce the risk of unresolved conflicts and create more trust in the technology.

Best Practices for Drafting Smart Contracts: Recommendations for Legal Clarity and Security
To ensure smart contracts are effective and secure across borders, it’s important to focus on both legal clarity and technical security. This means creating contracts that clearly define terms, rights, and responsibilities in simple language. Some best practices for drafting smart contracts include:
- Clear Documentation: Write terms in a way that everyone can understand, avoiding complex legal jargon.
- Security Audits: Regularly check the code for bugs or vulnerabilities to avoid hacking.
- Multi-signature Security: Use multiple approvals before executing a transaction, increasing security.
- Flexibility: Include options for modifying or terminating the contract if circumstances change.
Here’s a quick summary of best practices for drafting secure smart contracts:
| Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
| Documentation | Detailed terms and clear language |
| Code Audits | Regular reviews to identify vulnerabilities |
| Multi-signature | Delay execution until multiple approvals |
| Flexibility | Provisions for modifications and termination |
In Summary
Smart contracts offer great promise in transforming cross-border transactions by making them faster, more transparent, and more efficient. However, the legal complexities surrounding them can’t be ignored. From questions about which laws apply to how disputes should be handled, there’s a lot to consider.
As technology continues to evolve, so must our legal frameworks. Businesses, lawyers, and tech experts need to work together to ensure that laws keep up with the rapid changes brought about by smart contracts. The future of these contracts depends not just on their technological potential, but on how well we address the legal challenges that come with them. As we continue to explore this exciting new frontier, we must be mindful of both the opportunities and the complexities that smart contracts present.


