Streamlining Legal Transactions with Smart Contracts

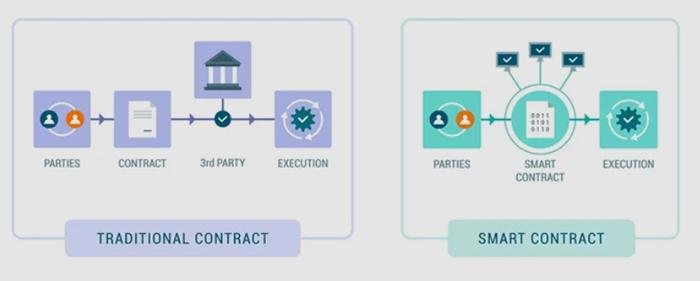
In an era where technology shapes the landscape of nearly every industry, the legal sector stands on the brink of a revolution driven by innovation. Enter smart contracts—self-executing agreements with the terms directly written into code. As organizations grapple with the complexities, inefficiencies, and costs often associated with traditional legal transactions, these digital agreements offer a compelling alternative. By automating processes, enhancing transparency, and reducing the need for intermediaries, smart contracts promise a streamlined approach to legal dealings. This article delves into the transformative potential of smart contracts, exploring how they can reshape not only the mechanics of transactions but also the very principles of trust and accountability within the legal framework. Join us as we uncover the nuances of this technology and its implications for the future of law.
Harnessing Efficiency through Automation in Legal Transactions
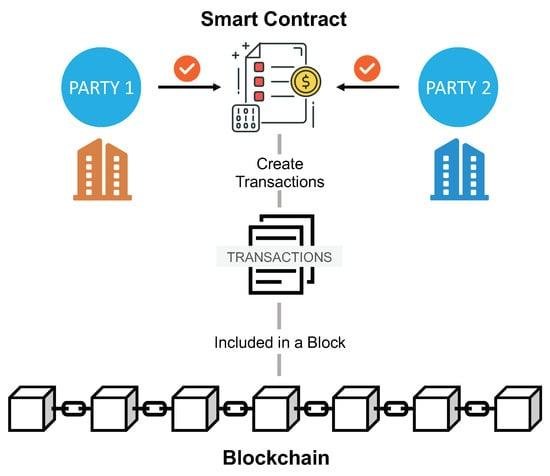
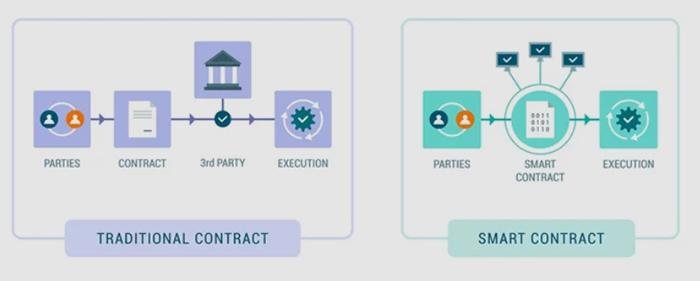
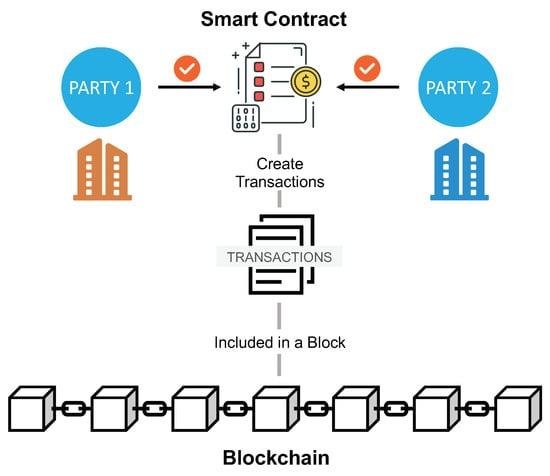
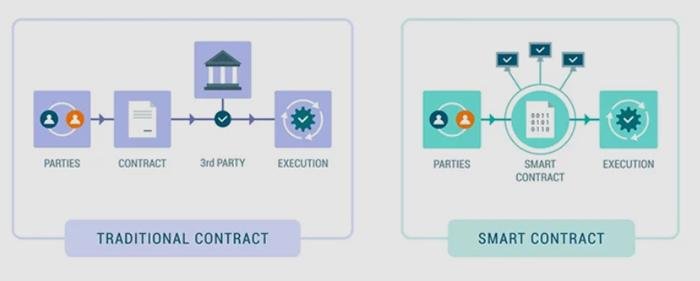
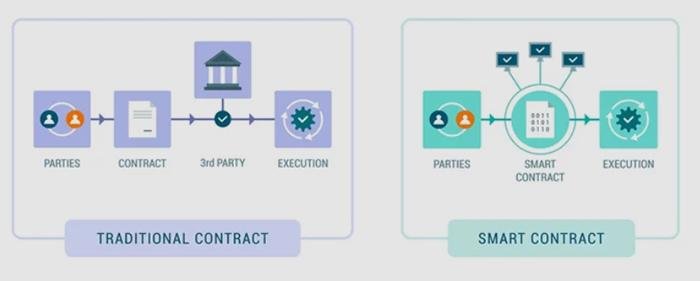
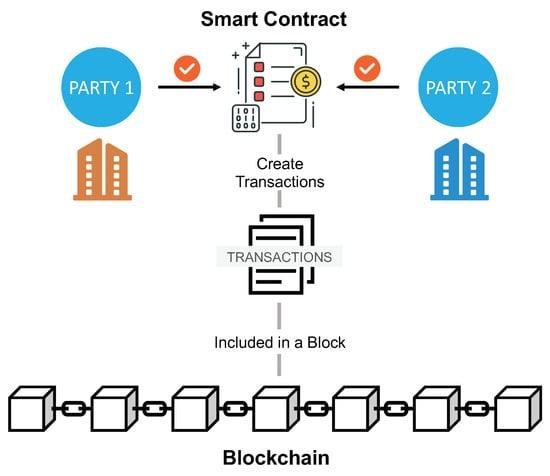
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, the introduction of smart contracts revolutionizes how legal transactions are conducted. These self-executing agreements, written directly into lines of code, minimize the need for intermediaries, thereby enhancing efficiency. By automating terms and conditions, smart contracts enable faster execution, reducing the time spent on negotiation and paperwork. Key benefits include:
- Cost Reduction: Decreasing reliance on legal advisors and administrative tasks lowers overall transaction costs.
- Increased Transparency: All parties have clear visibility into the contract terms, fostering trust and mitigating disputes.
- Enhanced Security: Built on blockchain technology, smart contracts are tamper-proof, ensuring the integrity of the transaction.
Moreover, the integration of automation in legal processes paves the way for better compliance and risk management. With programmable agreements, firms can embed compliance checks within the contract itself, ensuring that all legal obligations are met without manual oversight. This innovation not only brings speed but also offers significant improvements in tracking and auditing. A simple comparison is illustrated below:
| Traditional Process | With Smart Contracts |
|---|---|
| Manual contract drafting and review | Automated execution based on pre-defined rules |
| Long processing times | Instant execution upon condition fulfillment |
| High possibility of human error | Elimination of human error through automation |
Enhancing Trust and Transparency with Blockchain Technology
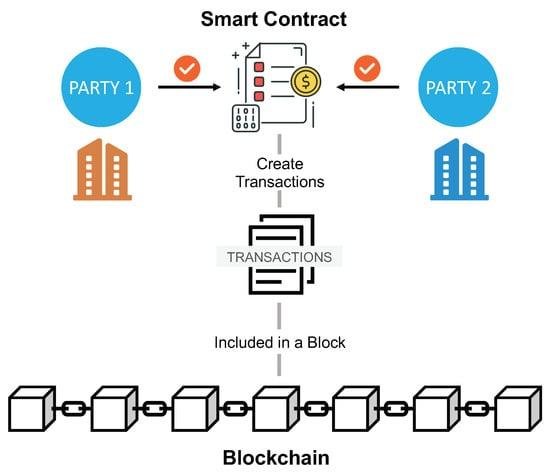
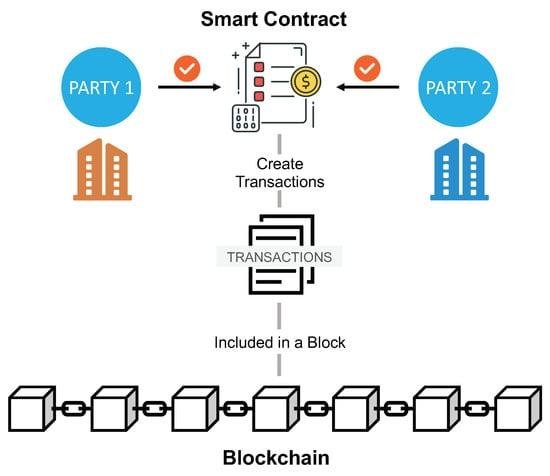
In the digital landscape, trust and transparency remain paramount, particularly in legal transactions. By leveraging blockchain technology, stakeholders can engage in an environment where every action leaves a clear and immutable record. Smart contracts, as self-executing contracts written in code and deployed on a blockchain, facilitate seamless interactions without the need for intermediaries. The inherent characteristics of blockchain—decentralization, transparency, and security—ensure that all parties can verify the terms of an agreement and the execution of actions without the risk of manipulation. This ability to independently verify contract performance bolsters trust between participants, paving the way for more collaborative and less contentious business relationships.
Moreover, the use of blockchain enhances accountability through its transparent ledger system. Every transaction executed via smart contracts is recorded and can be audited by involved parties, offering unparalleled visibility into contract performance. The following features highlight how blockchain amplifies trust and transparency in legal dealings:
- Immutable Records: Once a transaction is confirmed, it cannot be altered, ensuring reliability.
- Real-Time Updates: Participants can access the latest data instantly, reducing disputes due to miscommunication.
- Decentralization: Without a single point of control, the risk of fraud is minimized, fostering a more trustworthy environment.

Navigating Regulatory Landscapes for Smart Contract Adoption
As organizations increasingly turn to smart contracts for their automated and secure transaction needs, understanding the intricacies of regulatory frameworks becomes imperative. Navigating through various jurisdictions reveals a patchwork of rules governing digital agreements. Key considerations include:
- Compliance Standards: Each region has its own legal requirements, necessitating a robust understanding of local laws.
- Consumer Protection: Smart contracts must be designed to protect users from potential fraud and misunderstandings.
- Data Privacy Regulations: Adhering to regulations like GDPR ensures respectful handling of personal data.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Navigating the ownership of code and content plays a crucial role in contract formulation.
To streamline the adoption of smart contracts, businesses must establish a proactive approach to regulatory compliance. Working closely with legal experts can illuminate potential pitfalls, while also leveraging existing frameworks to guide the creation of enforceable agreements. It may be beneficial to create a roadmap that includes:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Conduct a thorough regulatory review of relevant jurisdictions. |
| 2 | Engage with legal specialists in blockchain and technology law. |
| 3 | Create smart contract templates that comply with identified regulations. |
| 4 | Implement ongoing compliance monitoring and updates as regulations evolve. |

Best Practices for Drafting and Implementing Smart Contracts
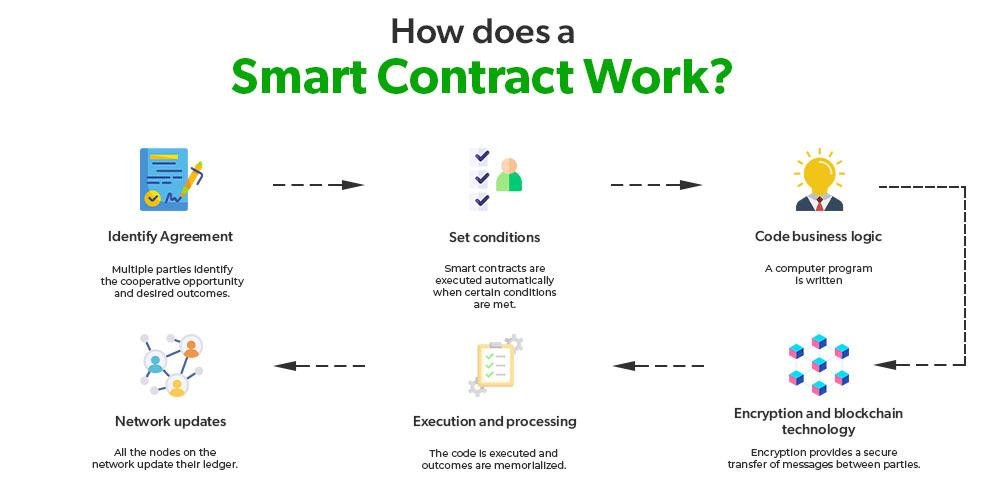
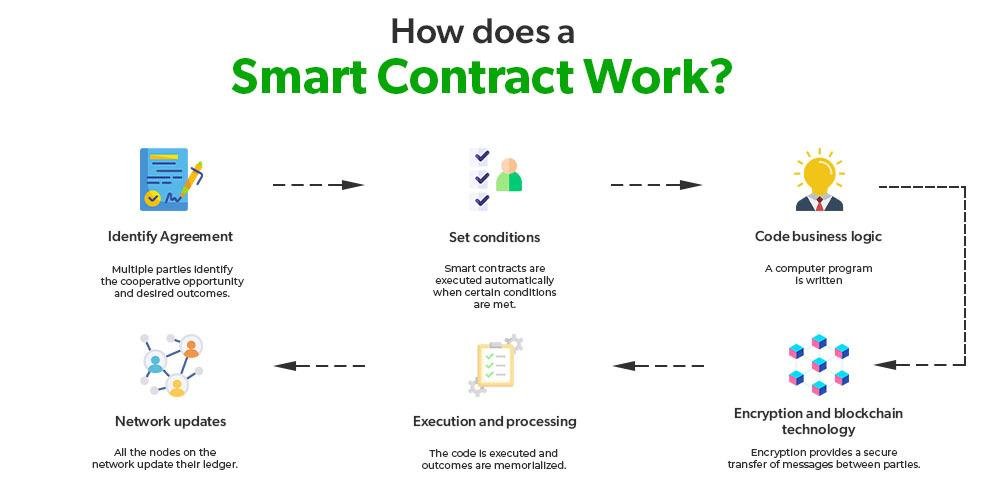
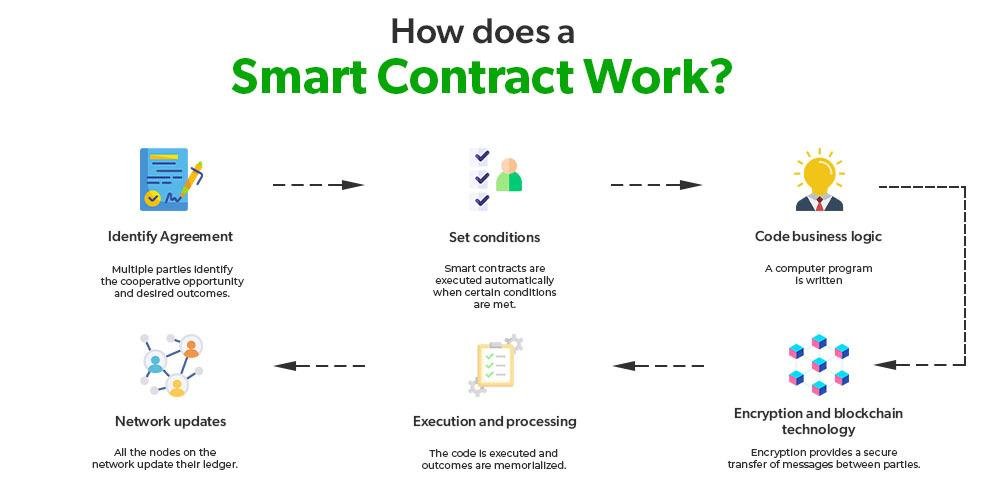
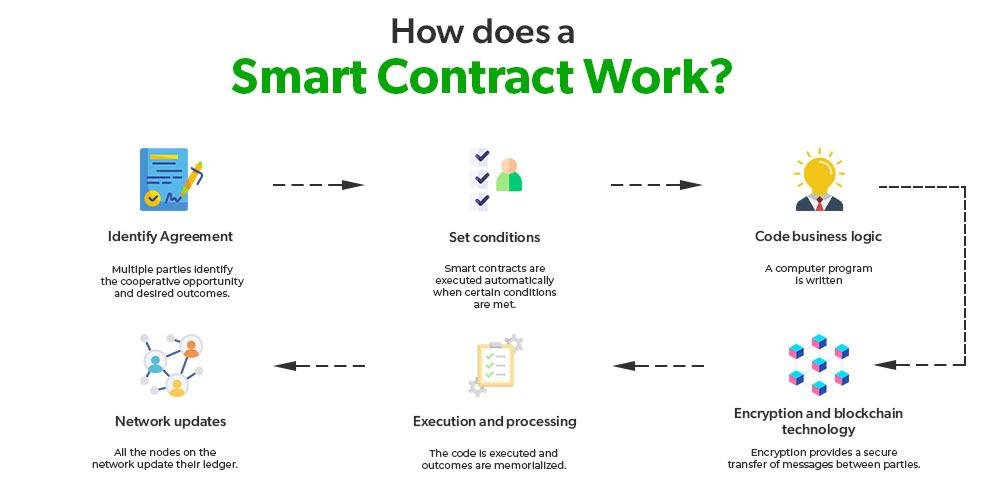
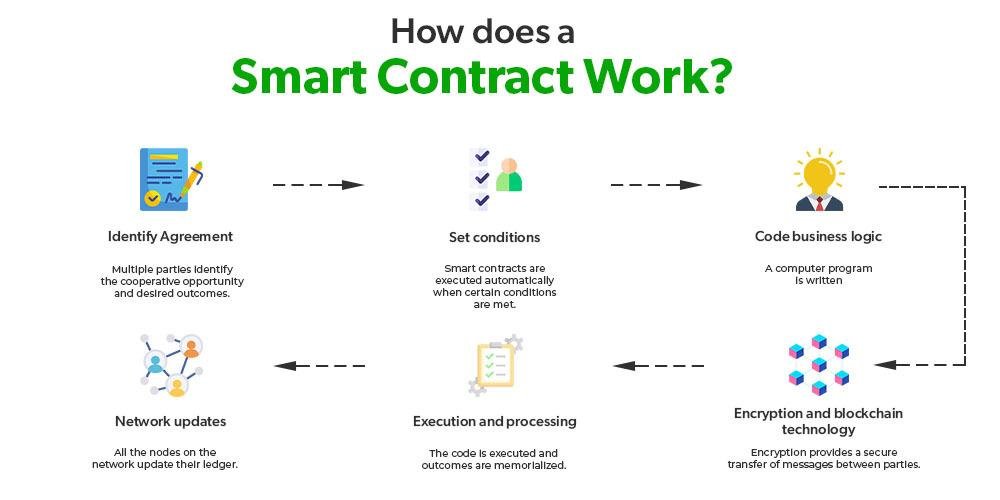
To effectively draft and implement smart contracts, it is crucial to follow some essential principles that ensure reliability and security. Focus on clear and precise language to describe the terms and conditions of the contract. Utilizing formal verification techniques can help in identifying any potential vulnerabilities in the code. Remember to keep the smart contract modular; this enhances maintainability and allows for easier updates in the future. Building in an option for dispute resolution is also recommended, as it provides a clear pathway for addressing issues that may arise post-deployment.
Additionally, it’s important to prioritize testing and auditing before launching your smart contract on the blockchain. Engage with third-party services for comprehensive audits to uncover flaws that might have been overlooked. When implementing, ensure that the contract is deployed on a reliable platform that meets your project’s needs. A well-defined governance structure should be established to manage any modifications or updates to the smart contract, minimizing the risks associated with unforeseen changes. Below is a simple table summarizing key best practices:
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Clear Language | Use straightforward terminology to avoid ambiguity. |
| Formal Verification | Employ techniques to ensure the code’s correctness. |
| Modularity | Design contracts in a way that allows for easy updates. |
| Testing and Auditing | Conduct thorough tests and audits prior to deployment. |
| Governance Structure | Establish a process for managing changes post-deployment. |
Future Outlook
As we stand on the brink of a digital revolution, the integration of smart contracts into the legal landscape offers a glimpse of a future where transactions are not only streamlined but also fortified against the pitfalls of traditional processes. In a world increasingly driven by technology, these self-executing contracts promise to bridge the gap between efficient transaction execution and unwavering trust.
Organizations and individuals alike can harness the power of blockchain to eliminate inefficiencies, reduce costs, and foster transparency, while simultaneously transforming the way we perceive agreements. However, the journey toward widespread adoption will necessitate a careful navigation through legal frameworks, regulatory considerations, and potential cybersecurity challenges.
Ultimately, as we delve into the complexities and nuances of this evolving field, it becomes clear that while smart contracts hold remarkable potential, they also remind us of the enduring human element in legal transactions. The future may very well be coded in lines of programming, but it will thrive on the principles of justice, reliability, and mutual respect that have long defined our interactions. As we embrace this innovative journey, let us proceed with vigilance, curiosity, and a commitment to shaping a future where technology and law coexist harmoniously for the benefit of all.