The Legal Implications of Adopting Smart Contracts
In an age where technology intertwines seamlessly with everyday life, the emergence of smart contracts stands as a beacon of innovation within the realm of digital transactions. These self-executing agreements, powered by blockchain technology, promise to revolutionize the way parties engage in contractual relationships. However, as organizations and individuals warm to the idea of automating agreements, a pressing question looms: what are the legal implications of adopting smart contracts? This article delves into the intricate legal landscape surrounding these digital constructs, exploring their potential benefits, challenges, and the evolving jurisprudence that accompanies this unprecedented technological shift. As we unravel the complexities of smart contracts, we invite readers to consider not just their efficiency and transparency, but also the fundamental legal principles that govern this brave new world of automated agreements.
Understanding Smart Contracts and Their Legal Framework
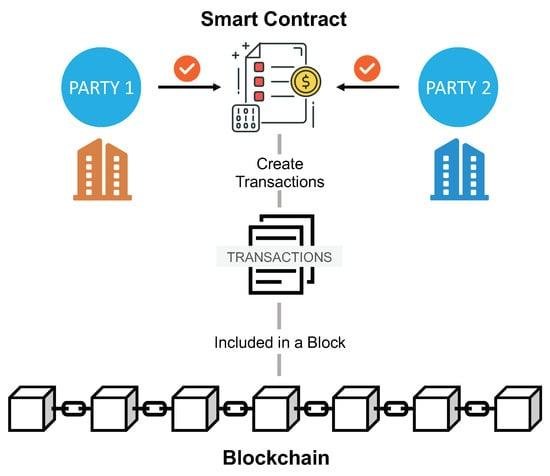
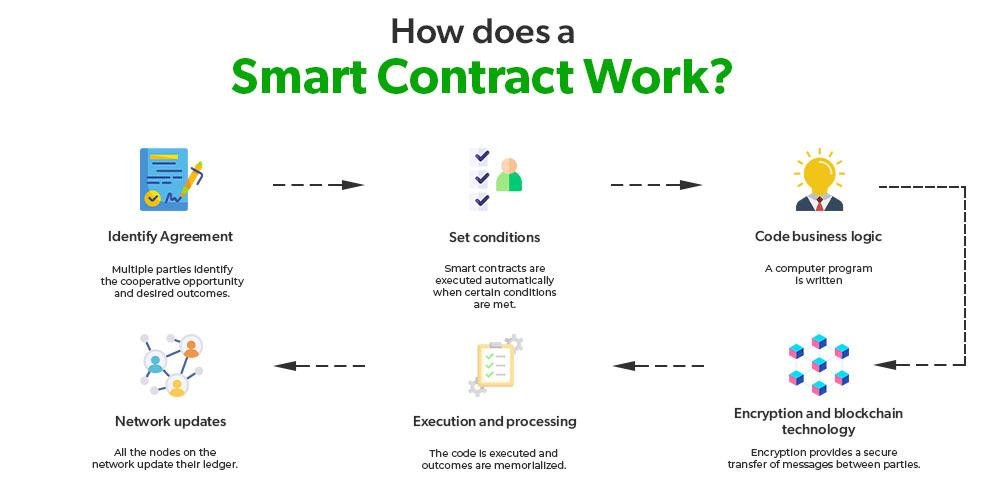
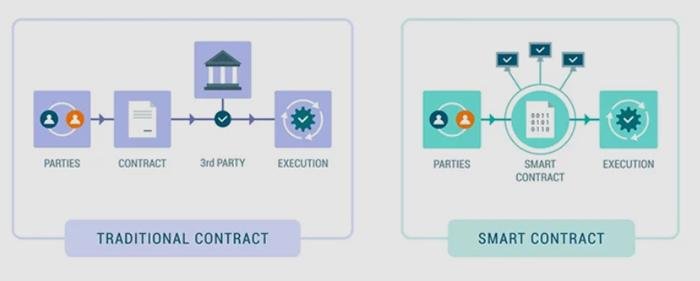
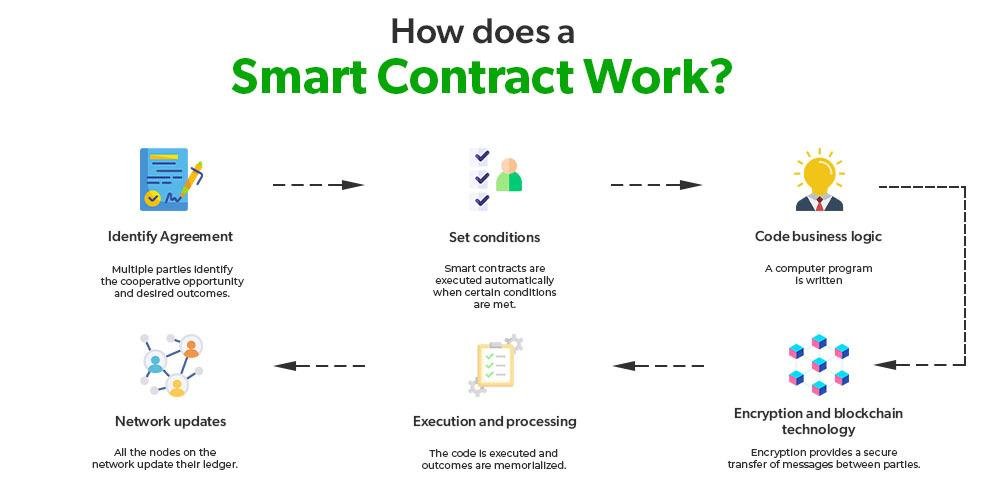
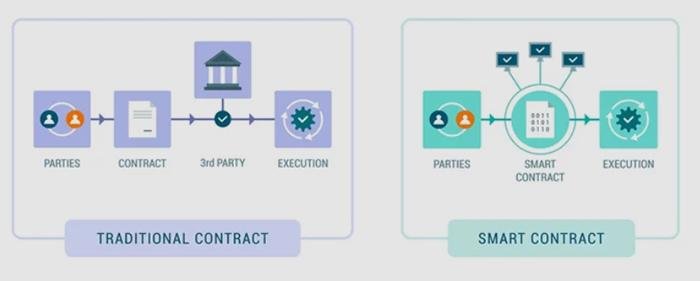
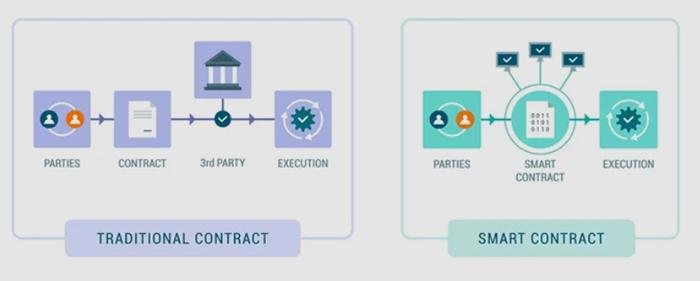
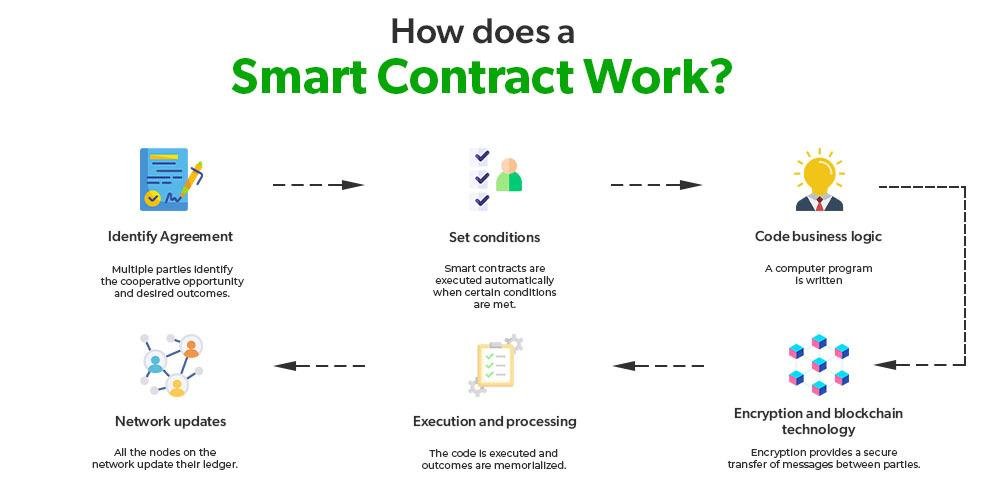
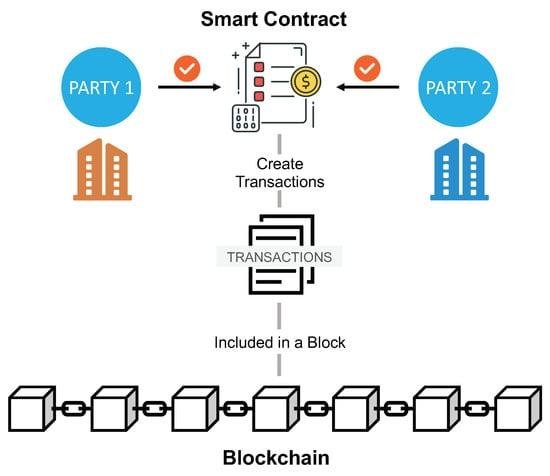
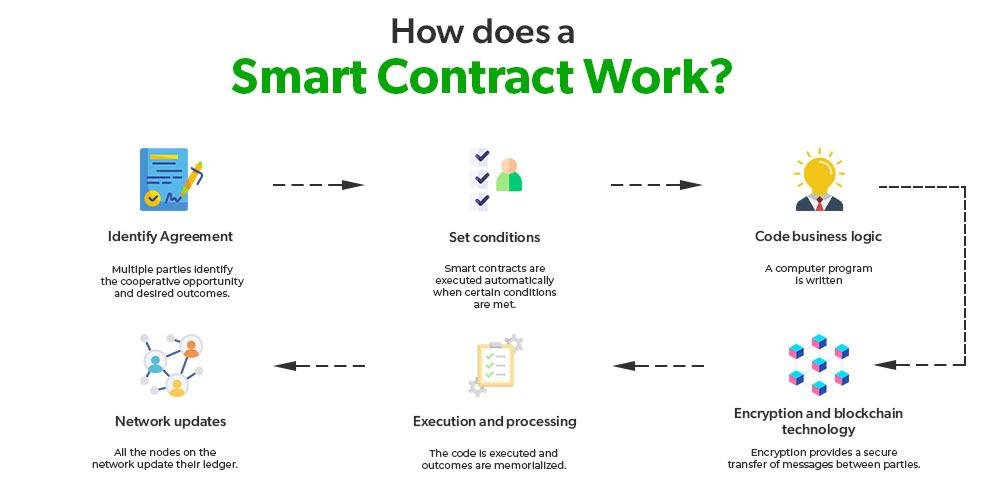
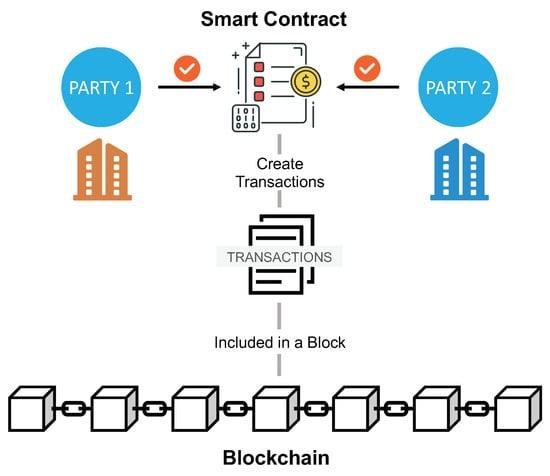
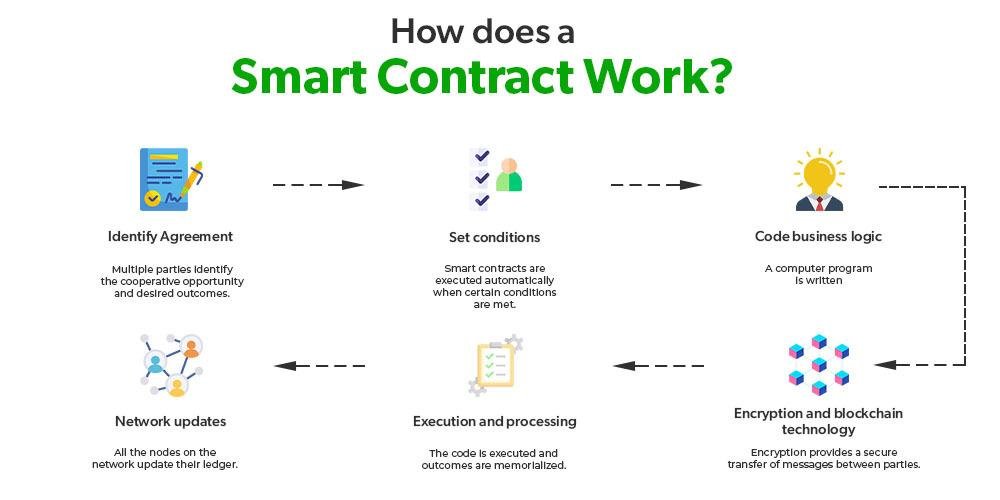
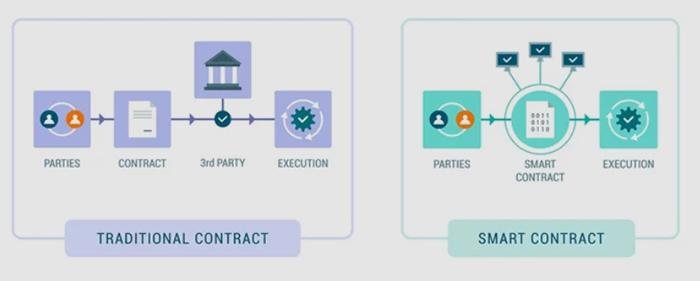
Smart contracts, self-executing agreements with the terms of the contract directly written into code, represent a significant evolution in the realm of contractual relationships. They automate transactions and enforce terms without the need for intermediaries, potentially streamlining processes and reducing costs. However, the legality of smart contracts hinges on several factors:
- Jurisdiction: The applicability of local laws concerning digital agreements varies widely, impacting enforceability.
- Intent: Determining the parties’ intent can be challenging, as the code itself may not explicitly reflect their agreement.
- Regulatory Compliance: Smart contracts must align with existing regulations, particularly in sectors like finance and healthcare.
The intersection of technology and law raises questions about the adequacy of traditional legal frameworks to govern these innovative tools. While some jurisdictions are actively crafting legislation to address smart contracts, a universal legal structure remains elusive. This gap introduces potential risks, including:
- Liability Issues: In the event of a failure, pinpointing liability may be complex.
- Dispute Resolution: Traditional litigation may not effectively resolve conflicts arising from transactions facilitated by smart contracts.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Given their public nature on blockchains, managing sensitive information becomes critical.
| Aspect | Traditional Contracts | Smart Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | Manual intervention | Automatic execution |
| Enforcement | Legal intervention | Code-based |
| Modification | Requires consent | Code changes required |

Navigating Jurisdictional Challenges in Smart Contract Implementation
As organizations venture into the realm of smart contracts, they inevitably encounter a labyrinth of jurisdictional challenges that can complicate their implementation. Given that smart contracts operate on decentralized networks, determining which legal framework applies can be ambiguous. Key considerations include:
- Territoriality: Different jurisdictions have varying regulations concerning digital contracts and blockchain technology.
- Contract Validity: The enforceability of smart contracts depends on the recognition of their existence in each jurisdiction.
- Data Protection Laws: Compliance with laws such as GDPR can pose significant challenges, especially when personal data is involved.
Moreover, cross-border transactions exacerbate these challenges. Companies may find themselves navigating a patchwork of legal systems that each has its own stance on blockchain technology. To address these obstacles, businesses can consider developing a jurisdictional strategy by analyzing the legal landscape and establishing clear terms within the smart contract that specify dispute resolution mechanisms and applicable laws. The following table summarizes potential strategies:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Jurisdiction Clause | Specifying the governing law within the smart contract. |
| Arbitration Agreement | Choosing arbitration as a preferred method for resolving disputes. |
| Legal Compliance Audit | Regularly reviewing compliance with local regulations. |

Mitigating Risks through Proper Legal Drafting and Compliance
Engaging in smart contracts presents a dynamic approach to business transactions, but it also necessitates rigorous legal drafting and adherence to compliance standards to safeguard against potential risks. One of the critical steps in this process is ensuring that the terms embedded in the smart contract are comprehensive and unambiguous. A well-crafted contract not only clarifies the obligations and expectations of all parties involved but also incorporates provisions for dispute resolution, liability limitations, and termination rights. This proactive drafting can mitigate financial exposure, reputational harm, and legal disputes altogether. It is essential for organizations to collaborate closely with legal experts to assess the implications of applicable laws and regulations while tailoring the contract to meet specific business needs.
In addition to thoughtful drafting, compliance with regulatory frameworks is paramount to securing the enforceability of smart contracts. Organizations must stay informed of relevant legislative updates and industry trends, ensuring that their smart contracts are compliant with regulations such as data protection laws, consumer protection statutes, and blockchain-specific regulations. A diligent compliance strategy may include:
- Regular audits of contract terms against the latest legal developments
- Risk assessment to identify vulnerabilities in contract execution
- Training programs for stakeholders to understand legal implications and best practices
By implementing these measures, businesses can confidently navigate the complexities of smart contracts and align with both legal and ethical standards, fostering trust and stability in automated transactions.

Future-Proofing Your Business: Recommendations for Smart Contract Adoption
Embracing smart contracts is not just a trend; it’s a strategic move toward enhancing efficiency and reliability in business operations. As you consider the integration of smart contracts, it is crucial to conduct a thorough risk assessment. This involves analyzing potential legal exposures that can arise from automated transactions. By reviewing existing contracts and identifying areas where automation can streamline processes, you can build a robust framework that ensures compliance with jurisdictional regulations. Engaging with legal experts familiar with blockchain technology will also provide insights into how existing laws may impact the operation of smart contracts in your sector.
Additionally, it’s essential to establish clear protocols for dispute resolution and governance within the smart contract framework. This can be achieved by defining the roles and responsibilities of all parties involved in the contract. Key considerations should include:
- Audit Trails: Ensure all transactions are traceable and verifiable.
- Amendment Procedures: Outline how changes to the contract will be handled.
- Termination Clauses: Specify conditions under which contracts can be revoked.
- Governance Structures: Decide on mechanisms for managing and enforcing the contract.
By addressing these aspects, businesses can create a resilient system that safeguards against potential future disputes and legal complications, ultimately leading to a more secure and efficient transactional environment.
To Conclude
as we stand on the precipice of a digital contract revolution, understanding the legal implications of adopting smart contracts is essential for stakeholders across all sectors. While the promise of automation and efficiency beckons, it is crucial to navigate the intricate landscape of regulatory compliance, liability, and enforceability. As technology evolves, so too must our legal frameworks, adapting to the nuances of this innovative approach to agreements. Whether you are a business leader, a policymaker, or an individual looking to harness the power of smart contracts, staying informed and engaged with these developments will empower you to make strategic decisions that align with an increasingly connected world. The fusion of law and technology presents both challenges and opportunities, and it is through proactive dialogue and collaboration that we can shape a future where smart contracts operate seamlessly within the legal ecosystem. As we move forward, let us embrace the potential of smart contracts with a discerning eye, ensuring that our legal structures not only accommodate innovation but also safeguard the principles of justice and fairness that underpin them.