The Role of Blockchain in Verifying E-Discovery Data

-
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Blockchain Technology: A Game Changer for E-Discovery
- Enhancing Data Integrity in E-Discovery with Blockchain
- The Impact of Blockchain on E-Discovery Workflows
- Smart Contracts and Their Role in E-Discovery Verification
- Challenges and Solutions of Implementing Blockchain in E-Discovery
- Future Trends: Blockchain’s Evolving Role in Legal Data Verification
- Conclusion
Introduction
The role of blockchain in verifying e-discovery data is increasingly significant in the realm of legal technology. As organizations face growing volumes of electronic data, the need for reliable and tamper-proof methods of data verification has become paramount. Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and immutable nature, offers a robust solution for ensuring the integrity and authenticity of e-discovery materials. By providing a transparent and secure ledger for tracking data provenance, blockchain enhances the trustworthiness of evidence presented in legal proceedings. This introduction explores how blockchain can streamline the e-discovery process, mitigate risks of data manipulation, and ultimately support the legal industry’s demand for accuracy and accountability in digital evidence management.
Blockchain Technology: A Game Changer for E-Discovery
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital information management, the role of blockchain technology in verifying e-discovery data has emerged as a transformative force. E-discovery, the process of identifying, collecting, and producing electronically stored information for legal proceedings, has traditionally faced challenges related to data integrity, authenticity, and security. However, the introduction of blockchain offers a robust solution to these issues, fundamentally changing how legal professionals approach the verification of digital evidence.
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger technology that records transactions across multiple computers in a way that ensures the data cannot be altered retroactively without the consensus of the network. This inherent characteristic of immutability is particularly advantageous in the context of e-discovery, where the authenticity of data is paramount. By utilizing blockchain, legal teams can create a verifiable chain of custody for digital evidence, ensuring that every piece of information is traceable and has not been tampered with. This capability not only enhances the credibility of the evidence presented in court but also streamlines the process of data verification, reducing the time and resources typically required for thorough audits.
Moreover, the transparency offered by blockchain technology fosters trust among all parties involved in the e-discovery process. When data is recorded on a blockchain, it becomes accessible to authorized users, allowing them to verify the integrity of the information independently. This transparency can mitigate disputes over the authenticity of evidence, as all stakeholders can confirm the data’s provenance and any changes made to it. Consequently, this level of trust can lead to more efficient negotiations and settlements, as parties are less likely to contest the validity of the evidence presented.
In addition to enhancing data integrity and transparency, blockchain technology also addresses concerns related to data security. In an era where cyber threats are increasingly sophisticated, protecting sensitive information is crucial. Blockchain employs advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data, making it significantly more difficult for unauthorized parties to access or alter the information. This heightened level of security is particularly important in legal contexts, where the confidentiality of client information and the integrity of evidence are paramount. By leveraging blockchain, legal professionals can ensure that their e-discovery data remains protected against potential breaches, thereby safeguarding their clients’ interests.
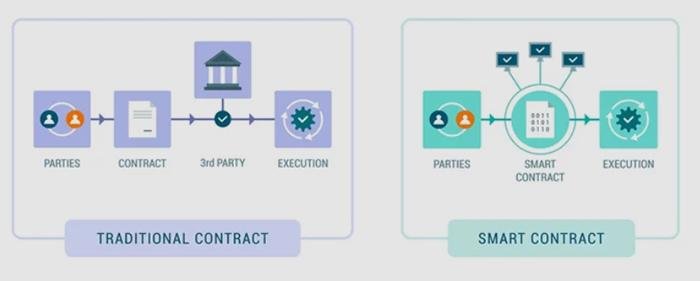
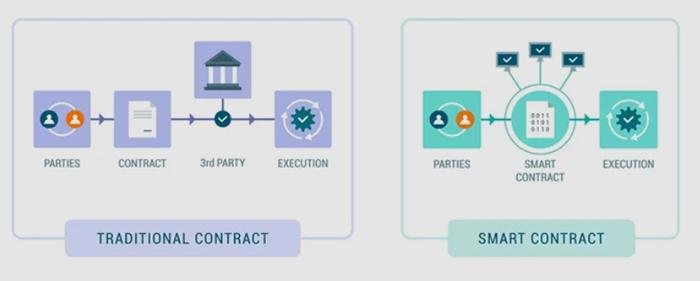
Furthermore, the integration of smart contracts within blockchain systems can automate various aspects of the e-discovery process. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. By automating routine tasks such as data collection and verification, legal teams can focus their efforts on more complex issues that require human judgment and expertise. This not only increases efficiency but also reduces the likelihood of human error, further enhancing the reliability of the e-discovery process.
As the legal industry continues to adapt to the digital age, the adoption of blockchain technology in e-discovery represents a significant advancement. By providing a secure, transparent, and efficient means of verifying digital evidence, blockchain is poised to revolutionize how legal professionals handle e-discovery. As organizations increasingly recognize the benefits of this technology, it is likely that blockchain will become a standard tool in the legal toolkit, paving the way for a more trustworthy and streamlined approach to managing electronic evidence. In conclusion, the intersection of blockchain and e-discovery not only addresses existing challenges but also sets the stage for a more secure and efficient future in legal proceedings.
Enhancing Data Integrity in E-Discovery with Blockchain
In the realm of e-discovery, where the integrity and authenticity of data are paramount, blockchain technology emerges as a transformative force. As legal professionals navigate the complexities of digital evidence, the need for reliable verification methods becomes increasingly critical. Blockchain, with its decentralized and immutable nature, offers a robust solution to enhance data integrity in e-discovery processes. By leveraging this innovative technology, organizations can ensure that the data they collect, store, and present in legal proceedings remains unaltered and trustworthy.
At its core, blockchain operates as a distributed ledger that records transactions across multiple nodes in a network. This decentralized approach eliminates the risk of a single point of failure, making it exceedingly difficult for malicious actors to tamper with the data. In the context of e-discovery, this means that once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be modified or deleted without consensus from the network participants. Consequently, legal teams can confidently assert the authenticity of their evidence, knowing that any alterations would be immediately detectable.
Moreover, the transparency inherent in blockchain technology further bolsters the credibility of e-discovery data. Each transaction is time-stamped and linked to previous entries, creating a chronological chain of custody that is easily traceable. This feature is particularly advantageous in legal scenarios where the provenance of data is scrutinized. By providing a clear and verifiable history of how data was collected and handled, blockchain enables legal professionals to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and best practices, thereby reinforcing the integrity of their findings.
In addition to enhancing data integrity, blockchain can streamline the e-discovery process itself. Traditional methods of data collection and verification often involve cumbersome manual processes that are prone to human error. By automating these tasks through smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code—organizations can reduce the time and resources spent on e-discovery. Smart contracts can facilitate automatic verification of data integrity, ensuring that only authentic and unaltered information is considered during legal proceedings. This not only accelerates the e-discovery timeline but also minimizes the risk of disputes over data authenticity.
Furthermore, the integration of blockchain in e-discovery can foster greater collaboration among stakeholders. In many cases, multiple parties are involved in the discovery process, including legal teams, clients, and third-party vendors. Blockchain’s shared ledger allows all participants to access the same information in real-time, promoting transparency and reducing the likelihood of miscommunication. This collaborative environment can lead to more efficient data sharing and a more cohesive approach to managing e-discovery tasks.
As organizations increasingly recognize the value of blockchain in enhancing data integrity, the legal industry is poised to undergo a significant transformation. The adoption of this technology not only addresses the pressing challenges of data authenticity and verification but also aligns with the growing demand for innovative solutions in legal practice. By embracing blockchain, legal professionals can ensure that their e-discovery processes are not only efficient but also secure and reliable.
In conclusion, the role of blockchain in verifying e-discovery data cannot be overstated. Its ability to provide an immutable record of transactions, enhance transparency, streamline processes, and foster collaboration positions it as a vital tool in the legal landscape. As the complexities of digital evidence continue to evolve, the integration of blockchain technology will undoubtedly play a crucial role in safeguarding the integrity of e-discovery data, ultimately leading to more just and equitable legal outcomes.
The Impact of Blockchain on E-Discovery Workflows

The advent of blockchain technology has ushered in a new era for various industries, and the field of e-discovery is no exception. E-discovery, the process of identifying, collecting, and producing electronically stored information (ESI) for legal proceedings, has traditionally faced challenges related to data integrity, security, and transparency. However, the integration of blockchain into e-discovery workflows promises to address these issues effectively, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency and reliability of the process.
To begin with, one of the most significant impacts of blockchain on e-discovery workflows is its ability to ensure data integrity. In legal contexts, the authenticity of evidence is paramount. Blockchain operates on a decentralized ledger system that records transactions in a manner that is immutable and tamper-proof. Each piece of data added to the blockchain is time-stamped and linked to previous entries, creating a chronological chain of custody that is easily verifiable. This feature is particularly beneficial in e-discovery, where maintaining the integrity of digital evidence is crucial. By utilizing blockchain, legal teams can confidently assert that the data has not been altered or manipulated, thereby bolstering the credibility of their findings.
Moreover, the transparency offered by blockchain technology enhances the trustworthiness of e-discovery processes. In traditional workflows, the potential for human error or intentional misconduct can lead to disputes over the authenticity of evidence. However, with blockchain, all participants in the e-discovery process can access a shared, immutable record of transactions. This transparency not only fosters trust among parties involved but also simplifies the auditing process. Legal professionals can easily trace the history of data, ensuring that all actions taken during the e-discovery process are documented and verifiable. Consequently, this level of transparency can significantly reduce the likelihood of disputes and enhance the overall efficiency of legal proceedings.
In addition to integrity and transparency, blockchain technology also streamlines the e-discovery workflow by automating various processes. Smart contracts, a feature of blockchain, can be programmed to execute specific actions when predetermined conditions are met. For instance, a smart contract could automatically trigger the collection of relevant data once a legal hold is issued. This automation not only saves time but also minimizes the risk of human error, allowing legal teams to focus on more strategic tasks rather than getting bogged down in administrative details. As a result, the integration of blockchain can lead to faster turnaround times in e-discovery, ultimately benefiting clients and legal practitioners alike.
Furthermore, the security features inherent in blockchain technology cannot be overlooked. In an era where data breaches and cyber threats are increasingly common, the need for robust security measures is paramount. Blockchain employs advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data, making it significantly more difficult for unauthorized parties to access or alter sensitive information. This heightened level of security is particularly important in e-discovery, where the stakes are high, and the confidentiality of data must be preserved. By leveraging blockchain, legal teams can ensure that their e-discovery processes are not only efficient but also secure.
In conclusion, the impact of blockchain on e-discovery workflows is profound and multifaceted. By enhancing data integrity, promoting transparency, automating processes, and bolstering security, blockchain technology is poised to revolutionize the way legal professionals approach e-discovery. As the legal landscape continues to evolve, embracing these technological advancements will be essential for maintaining a competitive edge and ensuring the integrity of the judicial process. The future of e-discovery, therefore, appears to be intricately linked to the capabilities offered by blockchain, paving the way for more efficient and reliable legal practices.
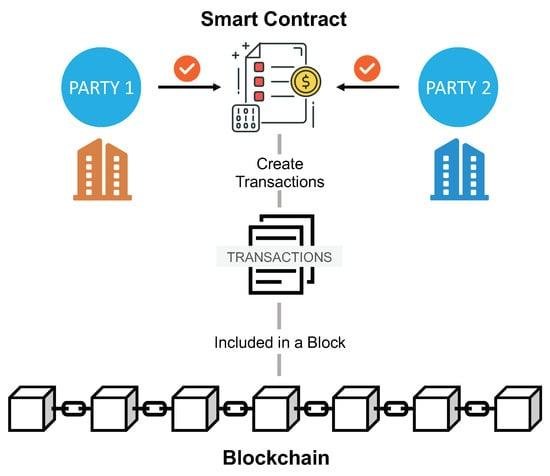
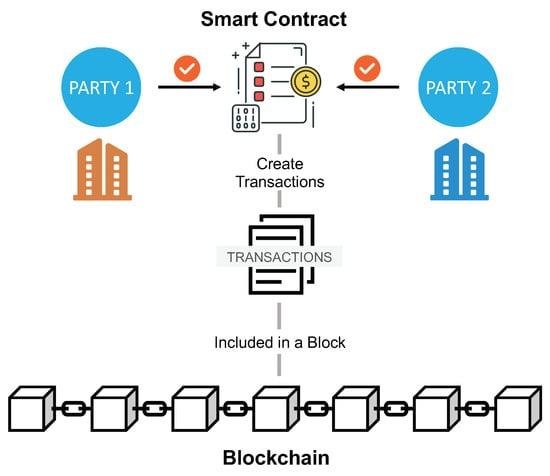
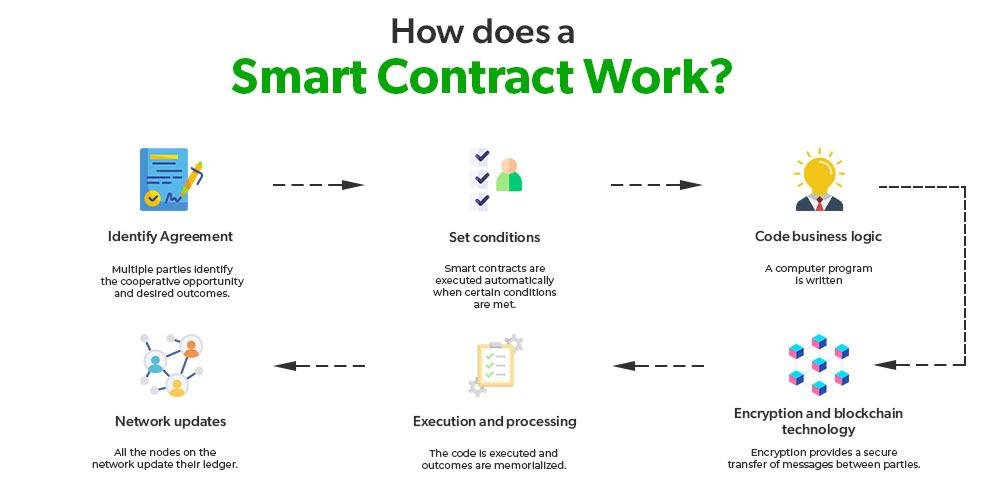
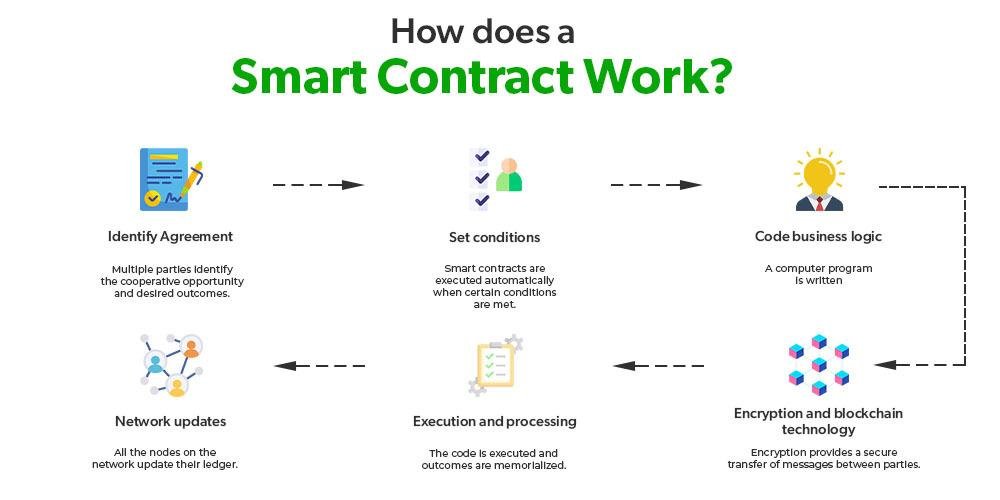
Smart Contracts and Their Role in E-Discovery Verification
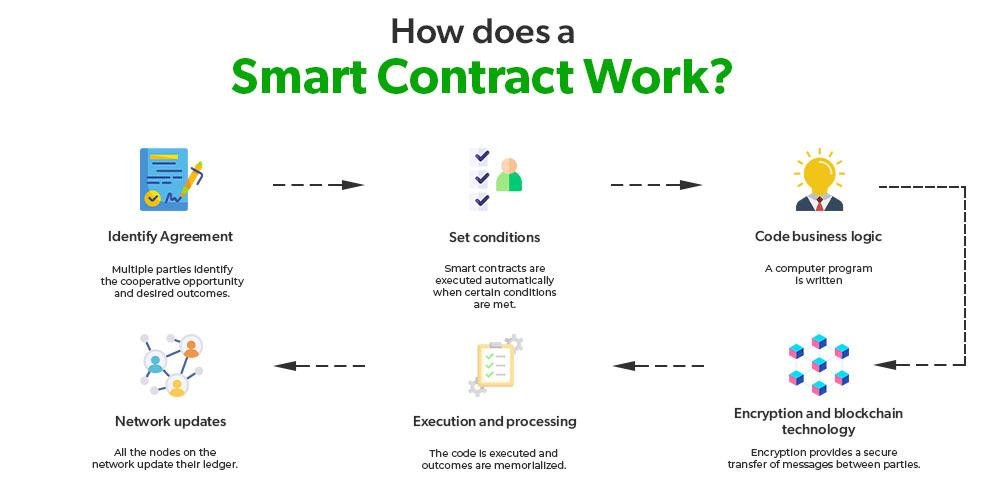
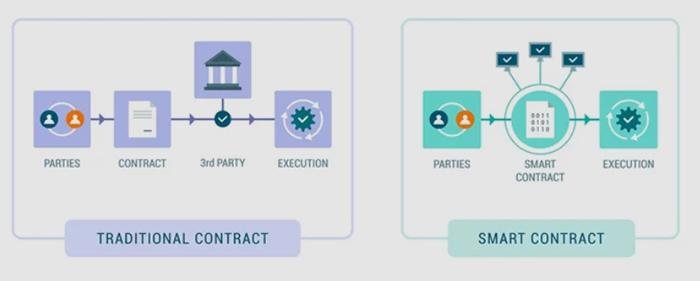
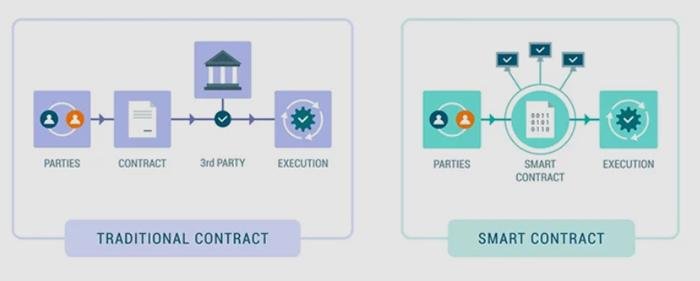
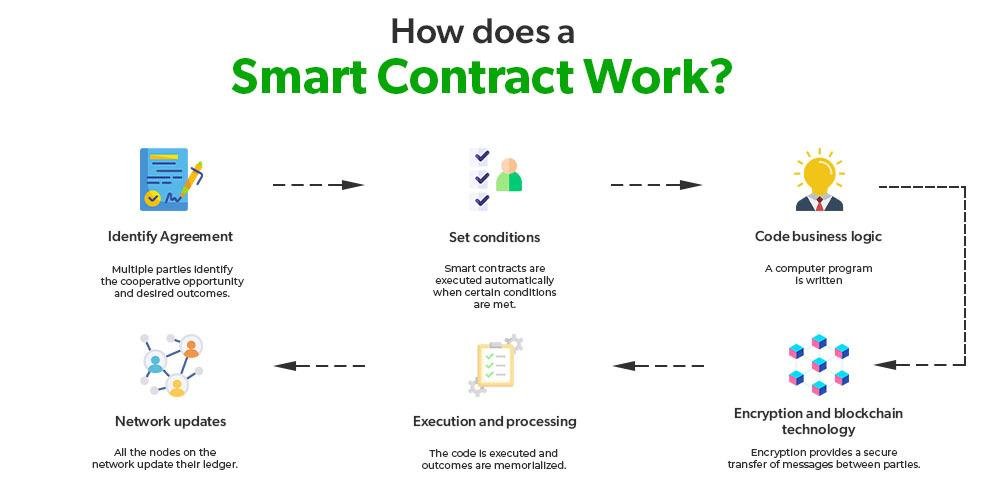
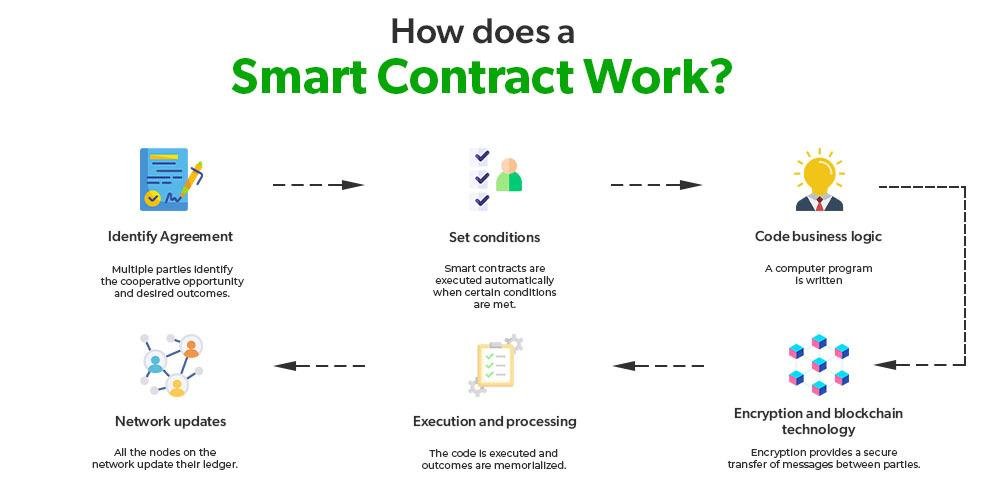
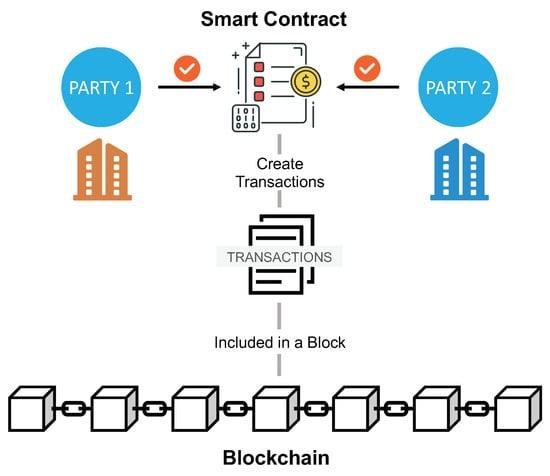
In the realm of e-discovery, where the integrity and authenticity of data are paramount, smart contracts emerge as a transformative tool that enhances the verification process. Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, operate on blockchain technology. This innovative approach not only streamlines the e-discovery process but also ensures that the data remains tamper-proof and verifiable throughout its lifecycle.
To understand the significance of smart contracts in e-discovery, it is essential to recognize the challenges that traditional methods face. In conventional e-discovery, the verification of data authenticity often relies on manual processes, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error. Moreover, the potential for data manipulation during transfer or storage raises concerns about the reliability of the evidence presented in legal proceedings. Here, smart contracts offer a solution by automating the verification process, thereby reducing the risk of human error and enhancing the overall efficiency of e-discovery.
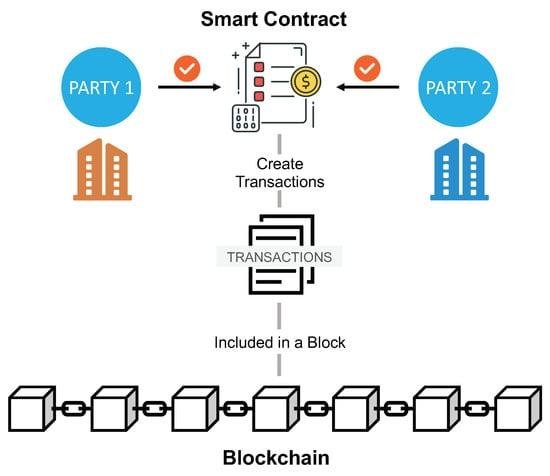
When a smart contract is deployed, it operates on a decentralized blockchain network, which means that all transactions and data exchanges are recorded in a transparent and immutable manner. This characteristic is particularly beneficial for e-discovery, as it allows all parties involved to access a single source of truth. As data is collected, processed, and shared, the smart contract can automatically log each action, creating a comprehensive audit trail. This audit trail serves as a reliable record that can be referenced during legal proceedings, ensuring that the data’s integrity is maintained and easily verifiable.
Furthermore, the automation provided by smart contracts significantly accelerates the e-discovery process. By eliminating the need for manual verification steps, legal teams can focus their efforts on analyzing the data rather than spending excessive time on confirming its authenticity. For instance, when a document is uploaded to the blockchain, the smart contract can automatically verify its origin and confirm that it has not been altered since its initial creation. This instantaneous verification not only saves time but also enhances the overall accuracy of the e-discovery process.
In addition to improving efficiency and accuracy, smart contracts also enhance security in e-discovery. The decentralized nature of blockchain technology means that data is not stored in a single location, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. Each participant in the network has a unique cryptographic key, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access or modify the data. This level of security is crucial in legal contexts, where the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information must be preserved.
Moreover, the use of smart contracts in e-discovery fosters greater collaboration among legal teams, clients, and other stakeholders. By providing a transparent and immutable record of all transactions, smart contracts facilitate trust among parties involved in the legal process. This trust is essential, as it allows for more open communication and collaboration, ultimately leading to more effective legal strategies and outcomes.
In conclusion, smart contracts play a pivotal role in enhancing the verification of e-discovery data. By automating processes, providing a transparent audit trail, and ensuring data security, they address many of the challenges faced by traditional e-discovery methods. As the legal landscape continues to evolve, the integration of smart contracts into e-discovery practices will likely become increasingly prevalent, paving the way for a more efficient, secure, and trustworthy legal process.
Challenges and Solutions of Implementing Blockchain in E-Discovery
The integration of blockchain technology into the realm of e-discovery presents a myriad of challenges that must be navigated to harness its full potential. One of the primary hurdles is the complexity of the technology itself. Blockchain operates on a decentralized ledger system, which, while offering enhanced security and transparency, can be difficult for legal professionals who may not have a technical background to fully understand. This gap in knowledge can lead to resistance in adoption, as stakeholders may be hesitant to embrace a system that they do not comprehend. To address this issue, comprehensive training programs and workshops can be developed, aimed at educating legal teams about the fundamentals of blockchain and its specific applications in e-discovery. By fostering a better understanding of the technology, legal professionals can become more comfortable with its implementation, ultimately leading to a smoother transition.
Another significant challenge lies in the integration of blockchain with existing e-discovery tools and processes. Many organizations have established workflows and systems that may not be compatible with blockchain technology. This lack of interoperability can create friction, as firms may be reluctant to overhaul their entire e-discovery infrastructure. To mitigate this challenge, developers can focus on creating hybrid solutions that allow for the seamless integration of blockchain with traditional e-discovery platforms. By ensuring that these systems can work in tandem, organizations can gradually adopt blockchain without the need for a complete overhaul, thus minimizing disruption and resistance.
Moreover, the legal landscape itself poses challenges to the implementation of blockchain in e-discovery. The regulatory environment surrounding data management and privacy is constantly evolving, and organizations must navigate a complex web of laws and regulations. This uncertainty can create apprehension among legal teams, as they may fear that adopting blockchain could expose them to compliance risks. To counter this concern, it is essential for stakeholders to engage with regulatory bodies and legal experts to develop clear guidelines for the use of blockchain in e-discovery. By establishing a framework that addresses compliance issues, organizations can confidently move forward with blockchain implementation, knowing that they are adhering to legal standards.
In addition to these challenges, there is also the issue of data immutability inherent in blockchain technology. While the ability to create an unalterable record of data is one of blockchain’s most significant advantages, it can also pose problems in the context of e-discovery. For instance, if erroneous or irrelevant data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be easily modified or deleted. This raises concerns about the potential for including inadmissible evidence in legal proceedings. To address this issue, organizations can implement robust data governance policies that dictate what information is recorded on the blockchain. By establishing clear criteria for data inclusion, firms can ensure that only relevant and accurate information is captured, thereby maintaining the integrity of the e-discovery process.
Finally, the cost of implementing blockchain technology can be a barrier for many organizations. The initial investment required for infrastructure, training, and ongoing maintenance can be daunting, particularly for smaller firms. However, as the technology matures and becomes more widely adopted, costs are likely to decrease. In the meantime, organizations can explore partnerships with technology providers or consider phased implementations that spread costs over time. By taking a strategic approach to investment, firms can gradually realize the benefits of blockchain in e-discovery without overwhelming their budgets.
In conclusion, while the challenges of implementing blockchain in e-discovery are significant, they are not insurmountable. Through education, integration strategies, regulatory engagement, data governance, and strategic investment, organizations can successfully navigate these obstacles and unlock the transformative potential of blockchain technology in the legal field.
Future Trends: Blockchain’s Evolving Role in Legal Data Verification
As the legal landscape continues to evolve, the integration of technology into traditional practices has become increasingly vital. Among the myriad of technological advancements, blockchain stands out as a transformative force, particularly in the realm of e-discovery data verification. The future trends surrounding blockchain’s role in this area suggest a paradigm shift that could enhance the integrity, efficiency, and transparency of legal processes.
To begin with, the inherent characteristics of blockchain technology—decentralization, immutability, and transparency—position it as an ideal solution for addressing the challenges associated with e-discovery. In a world where data breaches and manipulation are prevalent, the ability to create a tamper-proof record of digital evidence is invaluable. As legal professionals seek to ensure the authenticity of documents and communications, blockchain can provide a secure framework for verifying the provenance of data. This capability not only bolsters the credibility of evidence presented in court but also fosters trust among all parties involved in legal proceedings.
Moreover, as organizations increasingly rely on digital communication and storage, the volume of data generated has skyrocketed. This surge presents significant challenges for legal teams tasked with sifting through vast amounts of information during e-discovery. Here, blockchain can streamline the process by enabling automated data verification. Smart contracts, a feature of blockchain technology, can facilitate the automatic execution of agreements when predefined conditions are met. This automation can significantly reduce the time and resources required for data verification, allowing legal professionals to focus on more strategic aspects of their cases.
In addition to enhancing efficiency, blockchain’s role in e-discovery data verification is likely to evolve in response to regulatory changes and compliance requirements. As governments and regulatory bodies increasingly recognize the importance of data integrity, the demand for robust verification mechanisms will grow. Blockchain’s ability to provide an auditable trail of data transactions aligns seamlessly with these regulatory needs. Consequently, legal practitioners who adopt blockchain solutions may find themselves better equipped to navigate the complexities of compliance, thereby reducing the risk of penalties associated with data mishandling.
Furthermore, the collaborative nature of blockchain technology can foster greater cooperation among legal teams, clients, and third-party vendors. By creating a shared, immutable ledger of e-discovery data, all stakeholders can access the same information in real-time, minimizing disputes over data authenticity. This collaborative approach not only enhances communication but also promotes a more efficient resolution of legal matters. As the legal industry continues to embrace innovation, the potential for blockchain to facilitate collaboration will likely become a focal point in the future of e-discovery.
Looking ahead, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with blockchain technology may further revolutionize the verification of e-discovery data. AI can analyze patterns and identify anomalies within large datasets, while blockchain can ensure that the data remains unaltered throughout the process. This synergy could lead to more sophisticated verification methods, enabling legal professionals to detect fraudulent activities or discrepancies with greater accuracy. As these technologies converge, the legal field may witness a new era of data verification that is not only more reliable but also more adaptive to the ever-changing digital landscape.
In conclusion, the future trends surrounding blockchain’s evolving role in legal data verification are promising. As the technology matures, its potential to enhance the integrity, efficiency, and transparency of e-discovery processes will likely become increasingly recognized. Legal professionals who embrace these advancements will not only improve their practice but also contribute to a more trustworthy legal system, ultimately benefiting all stakeholders involved.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology plays a crucial role in enhancing the integrity and reliability of e-discovery data by providing a secure, immutable ledger for recording transactions and changes. Its decentralized nature ensures that data cannot be altered or tampered with, thereby increasing trust in the authenticity of the evidence presented in legal proceedings. By enabling transparent tracking of data provenance and access, blockchain facilitates compliance with legal standards and improves the overall efficiency of the e-discovery process. Consequently, the integration of blockchain in e-discovery not only strengthens the legal framework but also fosters greater confidence among stakeholders in the accuracy and validity of digital evidence.