Understanding Smart Contracts: What They Mean for the Legal Industry

-
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Introduction To Smart Contracts: Revolutionizing The Legal Landscape
- How Smart Contracts Enhance Efficiency In Legal Transactions
- The Role Of Smart Contracts In Reducing Legal Disputes
- Smart Contracts And Their Impact On Contract Law
- Legal Challenges And Considerations In Implementing Smart Contracts
- Future Prospects: Smart Contracts And The Evolution Of The Legal Industry
- Conclusion
Introduction
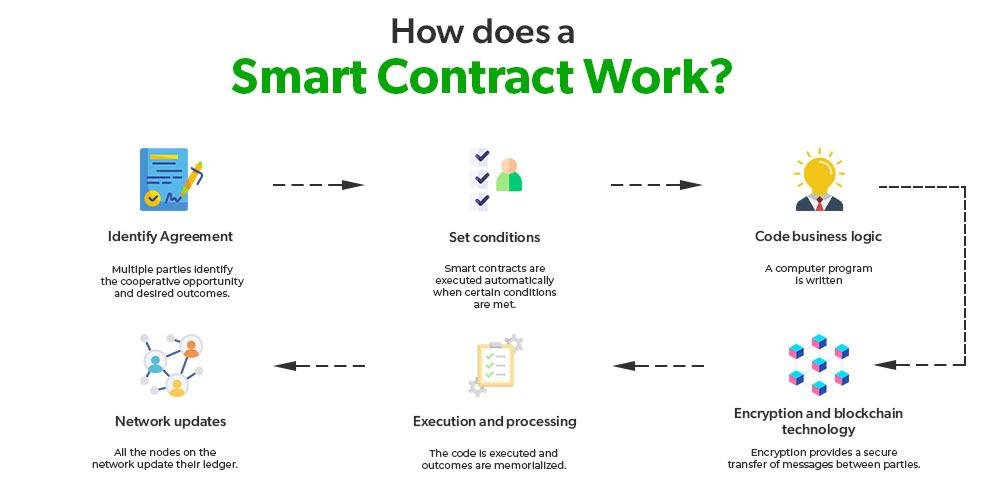
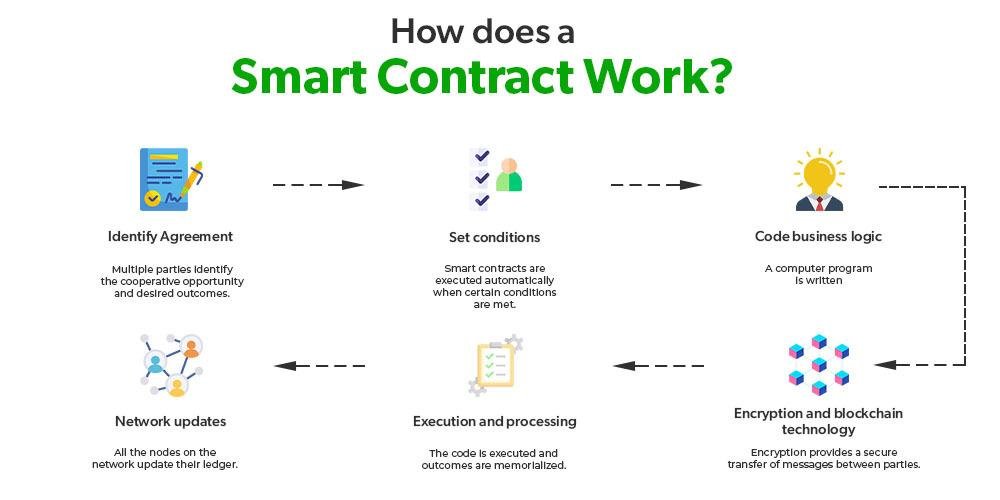
The advent of blockchain technology has ushered in a new era of digital innovation, with smart contracts emerging as one of its most transformative applications. These self-executing contracts, encoded with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code, promise to revolutionize the legal industry by automating and streamlining processes traditionally handled by legal professionals. As the legal sector grapples with the implications of this technology, understanding smart contracts becomes crucial. They offer the potential to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize human error, while also posing challenges related to legal enforceability, jurisdiction, and the need for new regulatory frameworks. This exploration delves into the essence of smart contracts, their operational mechanics, and the profound impact they are poised to have on the legal landscape, reshaping how agreements are crafted, executed, and enforced in the digital age.
Introduction To Smart Contracts: Revolutionizing The Legal Landscape
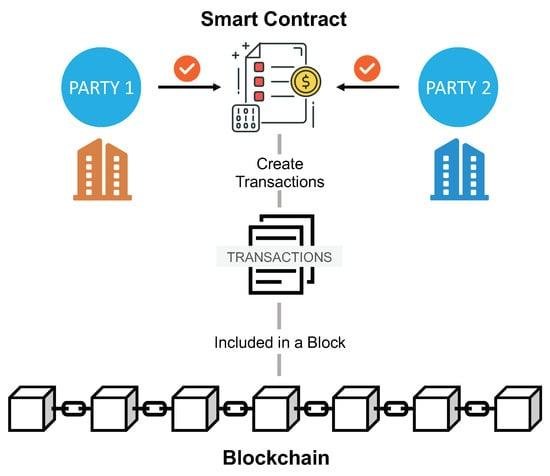
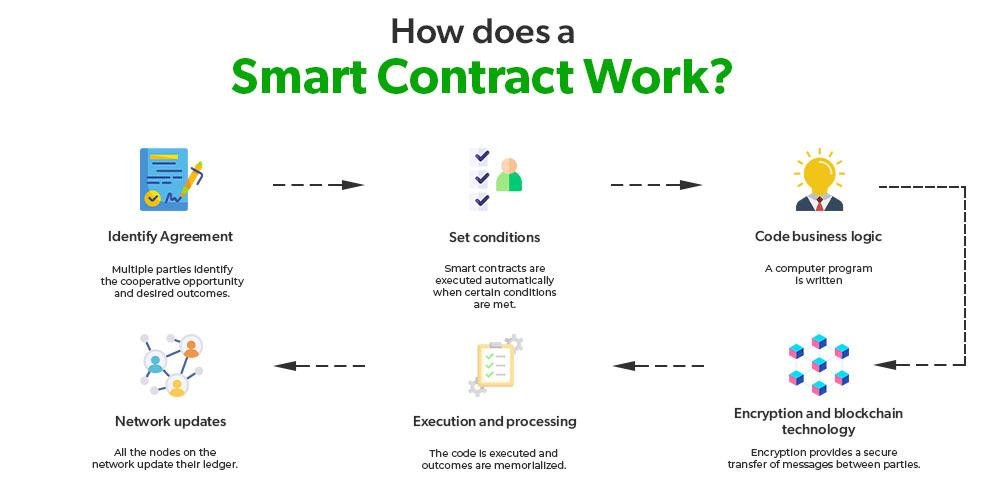
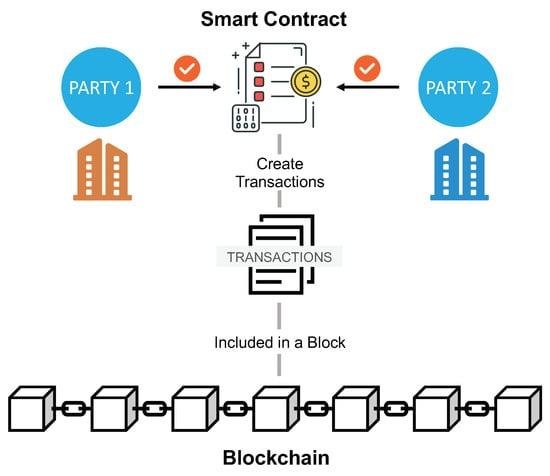
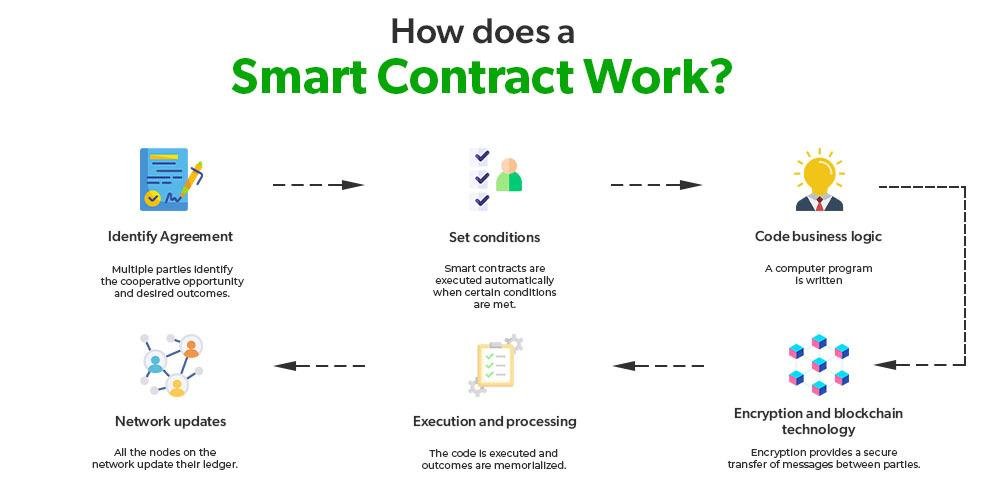
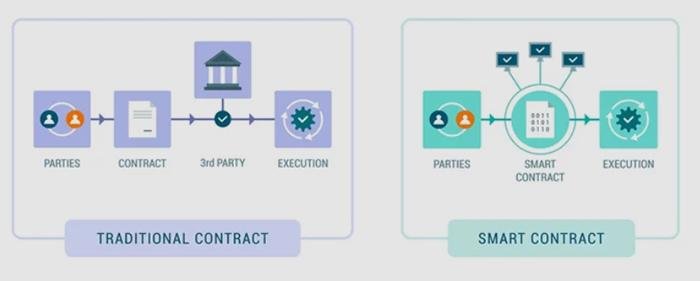
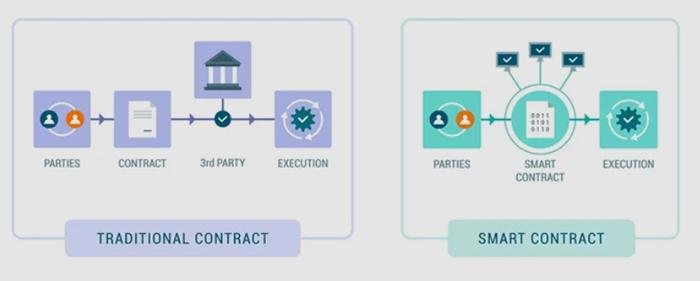
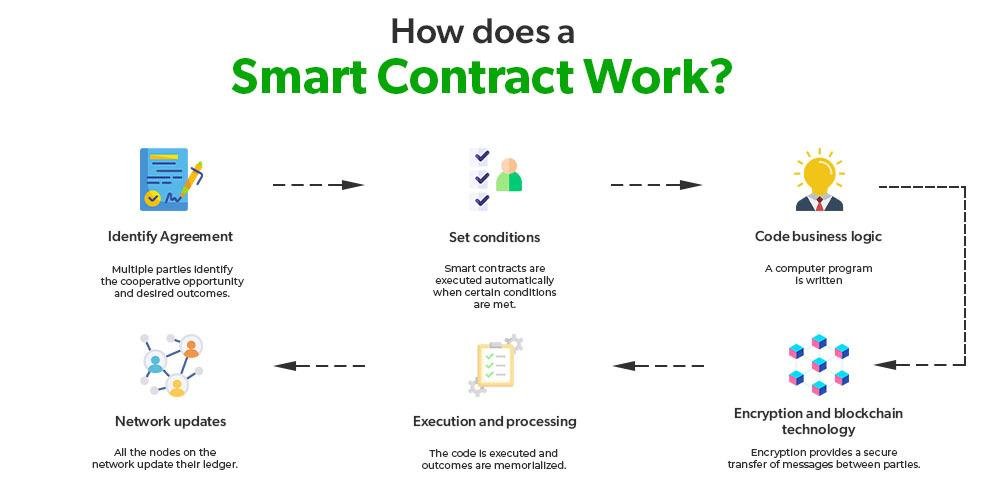
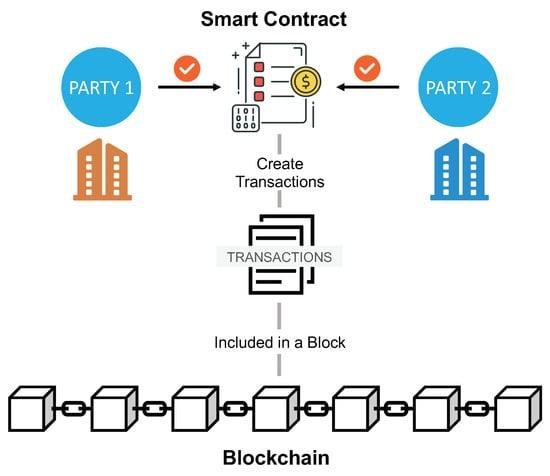
Smart contracts, a term that has gained significant traction in recent years, are poised to revolutionize the legal landscape by introducing a new paradigm in how agreements are executed and enforced. At their core, smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. These contracts operate on blockchain technology, which ensures that once the conditions are met, the contract is automatically executed without the need for intermediaries. This innovative approach promises to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize the potential for human error, thereby offering a transformative impact on the legal industry.
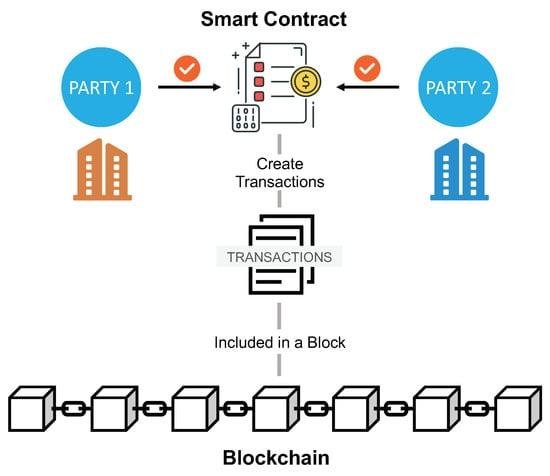
To fully appreciate the potential of smart contracts, it is essential to understand their underlying technology. Blockchain, the foundation upon which smart contracts are built, is a decentralized and distributed ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. This decentralization ensures that the data is secure, transparent, and immutable, making it an ideal platform for executing contracts. By leveraging blockchain technology, smart contracts can provide a level of trust and security that traditional contracts often lack, as they eliminate the need for a central authority to verify and enforce the terms of the agreement.
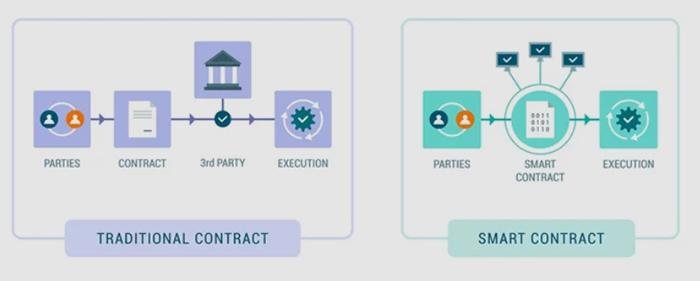
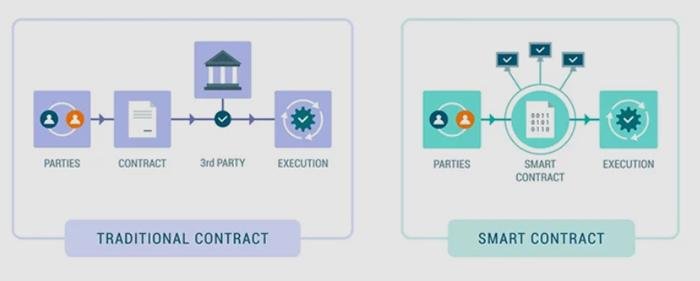
The implications of smart contracts for the legal industry are profound. Traditionally, legal contracts require extensive negotiation, documentation, and oversight, often involving multiple parties such as lawyers, notaries, and financial institutions. This process can be time-consuming and costly, with the potential for disputes arising from misinterpretations or breaches of contract. Smart contracts, however, streamline this process by automating the execution of contract terms, thereby reducing the need for intermediaries and minimizing the risk of disputes. As a result, legal professionals can focus on more complex and strategic aspects of their work, rather than being bogged down by routine contract management tasks.
Moreover, smart contracts offer the potential to enhance transparency and accountability in contractual relationships. Since the terms of a smart contract are encoded on the blockchain, all parties involved have access to the same information, reducing the likelihood of misunderstandings or misrepresentations. This transparency can foster greater trust between parties, as they can be confident that the contract will be executed exactly as agreed upon. Additionally, the immutable nature of blockchain records ensures that once a contract is executed, it cannot be altered or tampered with, providing an additional layer of security and reliability.
Despite these advantages, the adoption of smart contracts in the legal industry is not without challenges. One of the primary concerns is the need for a legal framework that recognizes and enforces smart contracts. As this technology is still relatively new, many jurisdictions have yet to establish clear regulations governing their use. Furthermore, the complexity of coding contract terms into a digital format requires a level of technical expertise that may be beyond the reach of some legal professionals. As such, there is a growing need for collaboration between legal experts and technologists to develop standardized protocols and best practices for implementing smart contracts.
In conclusion, smart contracts represent a significant advancement in the way legal agreements are executed and enforced. By harnessing the power of blockchain technology, they offer the potential to streamline processes, reduce costs, and enhance transparency in the legal industry. However, realizing this potential will require overcoming regulatory and technical challenges, as well as fostering collaboration between legal and technological experts. As the legal landscape continues to evolve, smart contracts are likely to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of legal practice.
How Smart Contracts Enhance Efficiency In Legal Transactions
Smart contracts, a revolutionary development in the realm of blockchain technology, are poised to transform the legal industry by enhancing efficiency in legal transactions. These self-executing contracts, with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code, offer a new level of automation and reliability that traditional contracts cannot match. As the legal industry grapples with the complexities of modern transactions, smart contracts present a promising solution to streamline processes, reduce costs, and minimize human error.
To begin with, smart contracts operate on blockchain platforms, which are decentralized and immutable. This means that once a smart contract is deployed, it cannot be altered, ensuring the integrity and security of the agreement. This feature is particularly beneficial in legal transactions, where trust and transparency are paramount. By eliminating the need for intermediaries, such as lawyers or notaries, smart contracts reduce the time and expense associated with contract execution. Consequently, parties involved in a transaction can focus on the substantive aspects of their agreement rather than procedural formalities.
Moreover, the automation inherent in smart contracts significantly enhances efficiency. Traditional contracts often require manual oversight to ensure compliance with the agreed terms, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error. In contrast, smart contracts automatically execute actions when predefined conditions are met. For instance, in a real estate transaction, a smart contract could automatically transfer ownership of a property once payment is received, without the need for manual intervention. This not only accelerates the transaction process but also reduces the risk of disputes arising from non-compliance.
In addition to automation, smart contracts offer unparalleled accuracy. The precise nature of coding ensures that the terms of the contract are clear and unambiguous, leaving little room for interpretation. This clarity is crucial in legal transactions, where misunderstandings can lead to costly litigation. By providing a clear framework for execution, smart contracts help prevent disputes and foster a more harmonious business environment.
Furthermore, the use of smart contracts can lead to significant cost savings. Traditional legal processes often involve substantial fees for drafting, reviewing, and enforcing contracts. Smart contracts, by contrast, can be created and executed with minimal human intervention, reducing the need for expensive legal services. This democratization of contract management allows smaller businesses and individuals to engage in complex transactions that were previously out of reach due to prohibitive costs.
Despite these advantages, it is important to acknowledge the challenges that smart contracts present. The legal industry must adapt to this new technology by developing expertise in blockchain and coding. Additionally, the rigidity of smart contracts, while beneficial for security, can be a drawback if unforeseen circumstances arise that require contract modification. Therefore, it is essential for legal professionals to carefully consider the design and implementation of smart contracts to ensure they meet the needs of all parties involved.
In conclusion, smart contracts hold immense potential to enhance efficiency in legal transactions by providing a secure, automated, and cost-effective alternative to traditional contracts. As the legal industry continues to evolve, embracing this technology could lead to more streamlined processes and improved access to justice. However, it is crucial for legal professionals to remain vigilant and adaptable, ensuring that smart contracts are used effectively and ethically to benefit all stakeholders.
The Role Of Smart Contracts In Reducing Legal Disputes

Smart contracts, a revolutionary application of blockchain technology, are poised to transform the legal industry by significantly reducing the incidence of legal disputes. These self-executing contracts, with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code, offer a level of precision and automation that traditional contracts cannot match. As the legal industry grapples with the complexities of modern transactions, smart contracts present a promising solution to streamline processes and minimize misunderstandings.
To begin with, smart contracts operate on a decentralized blockchain network, ensuring that all parties involved have access to the same information. This transparency is crucial in reducing disputes, as it eliminates the possibility of one party altering the terms without the knowledge of others. Moreover, the immutable nature of blockchain means that once a smart contract is deployed, it cannot be changed. This permanence provides a level of security and trust that is often lacking in traditional contracts, where terms can be subject to interpretation and manipulation.
Furthermore, the automation inherent in smart contracts plays a significant role in minimizing disputes. By automatically executing actions when predefined conditions are met, smart contracts remove the need for intermediaries, such as lawyers or notaries, to enforce the terms. This not only reduces the potential for human error but also decreases the time and cost associated with contract enforcement. For instance, in a real estate transaction, a smart contract could automatically transfer ownership of a property once payment is received, without the need for manual intervention. This efficiency can prevent delays and disagreements that often arise from human oversight or miscommunication.
In addition to automation, smart contracts offer a level of precision that is unparalleled in traditional legal agreements. The code-based nature of these contracts requires that terms be explicitly defined, leaving little room for ambiguity. This clarity is essential in preventing disputes, as it ensures that all parties have a mutual understanding of their obligations and rights. In contrast, traditional contracts often rely on legal jargon and complex language, which can lead to differing interpretations and, consequently, disputes.
Moreover, the use of smart contracts can facilitate cross-border transactions, which are often fraught with legal challenges due to differing jurisdictions and regulations. By providing a standardized framework that is not bound by geographical limitations, smart contracts can simplify international agreements and reduce the likelihood of disputes arising from jurisdictional conflicts. This global applicability is particularly beneficial in an increasingly interconnected world, where businesses and individuals frequently engage in transactions across borders.
However, it is important to acknowledge that while smart contracts hold great potential in reducing legal disputes, they are not without challenges. The reliance on code means that any errors or bugs can have significant consequences, and the lack of legal recourse in such situations can be problematic. Additionally, the current legal framework in many jurisdictions does not fully recognize smart contracts, which can complicate their enforceability. Despite these challenges, the legal industry is gradually adapting to accommodate this innovative technology, with some jurisdictions already taking steps to integrate smart contracts into their legal systems.
In conclusion, smart contracts represent a significant advancement in the legal industry, offering a means to reduce disputes through transparency, automation, and precision. While challenges remain, the potential benefits of smart contracts in streamlining processes and minimizing misunderstandings are undeniable. As the technology continues to evolve, it is likely that smart contracts will become an integral part of the legal landscape, transforming the way agreements are made and enforced.
Smart Contracts And Their Impact On Contract Law
Smart contracts, a revolutionary development in the realm of blockchain technology, are poised to transform the legal industry by redefining how contracts are created, executed, and enforced. These self-executing contracts, with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code, offer a new level of efficiency and security that traditional contracts struggle to match. As the legal industry grapples with the implications of this technology, it is essential to understand how smart contracts function and what they mean for contract law.
At their core, smart contracts are designed to automatically execute and enforce the terms of an agreement when predetermined conditions are met. This automation reduces the need for intermediaries, such as lawyers or notaries, thereby streamlining processes and reducing costs. For instance, in a real estate transaction, a smart contract could automatically transfer ownership of a property once payment is received, eliminating the need for manual verification and paperwork. This not only accelerates the transaction process but also minimizes the risk of human error or fraud.
Moreover, the immutable nature of blockchain technology ensures that once a smart contract is deployed, it cannot be altered. This feature provides a level of security and trust that is difficult to achieve with traditional contracts, where terms can be disputed or manipulated. However, this immutability also presents challenges, particularly when it comes to addressing unforeseen circumstances or errors in the contract code. Unlike traditional contracts, which can be amended through negotiation or legal intervention, smart contracts require careful planning and coding to ensure all potential scenarios are accounted for.
The rise of smart contracts also raises important questions about the role of contract law in this new digital landscape. Traditional contract law is built on principles such as offer, acceptance, and consideration, which may not neatly apply to smart contracts. For example, the concept of “meeting of the minds,” a fundamental element of contract formation, becomes more complex when agreements are executed by code rather than human intent. Legal professionals must therefore adapt and develop new frameworks to address these challenges, ensuring that smart contracts are legally enforceable and that parties’ rights are protected.
Furthermore, the cross-border nature of blockchain technology complicates jurisdictional issues, as smart contracts can be executed globally without regard to national boundaries. This raises questions about which legal system governs a smart contract and how disputes are resolved. As a result, there is a growing need for international cooperation and standardization to create a cohesive legal framework that can accommodate the unique characteristics of smart contracts.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of smart contracts for the legal industry are significant. By reducing reliance on intermediaries, increasing transparency, and enhancing security, smart contracts can lead to more efficient and cost-effective legal processes. Legal professionals who embrace this technology and adapt to its nuances will be well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly digital world.
In conclusion, while smart contracts present both opportunities and challenges for the legal industry, their impact on contract law is undeniable. As this technology continues to evolve, it will be crucial for legal professionals to stay informed and engaged, ensuring that they can effectively navigate the complexities of smart contracts and harness their potential to transform the practice of law.
Legal Challenges And Considerations In Implementing Smart Contracts
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the legal industry finds itself at the forefront of technological innovation, particularly with the advent of smart contracts. These self-executing contracts, encoded on blockchain technology, promise to revolutionize the way agreements are made and enforced. However, while the potential benefits are significant, the implementation of smart contracts also presents a myriad of legal challenges and considerations that must be addressed to ensure their effective integration into the legal framework.
To begin with, one of the primary legal challenges associated with smart contracts is the question of enforceability. Traditional contracts are governed by established legal principles that ensure their validity and enforceability in a court of law. Smart contracts, on the other hand, operate on code and execute automatically when predefined conditions are met. This raises the question of whether these digital agreements can be recognized as legally binding. Jurisdictions around the world are grappling with this issue, as the lack of a clear legal framework for smart contracts can lead to uncertainty and disputes.
Moreover, the immutable nature of blockchain technology, while often touted as a strength, also poses significant legal considerations. Once a smart contract is deployed on a blockchain, it cannot be altered. This immutability can be problematic if errors are discovered in the contract code or if unforeseen circumstances arise that necessitate changes to the agreement. Traditional contracts allow for amendments and renegotiations, but smart contracts lack this flexibility. Legal professionals must therefore consider how to incorporate mechanisms for dispute resolution and contract modification within the framework of smart contracts.
In addition to enforceability and immutability, the issue of jurisdiction presents another legal challenge. Smart contracts operate on decentralized networks that transcend national borders, making it difficult to determine which jurisdiction’s laws apply in the event of a dispute. This lack of a clear legal jurisdiction can complicate the resolution of disputes and create additional legal hurdles. Legal practitioners must navigate these complexities by developing strategies to address jurisdictional issues, such as incorporating choice of law clauses within smart contracts.
Furthermore, the implementation of smart contracts raises concerns about data privacy and security. Smart contracts often require access to sensitive data to execute their terms, and the decentralized nature of blockchain technology can make it challenging to protect this information. Legal professionals must ensure that smart contracts comply with data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, to safeguard personal information and maintain the trust of parties involved.
Finally, the integration of smart contracts into the legal industry necessitates a reevaluation of the role of legal professionals. While smart contracts can automate many aspects of contract execution, they cannot replace the nuanced understanding and judgment that legal professionals bring to the table. Lawyers will need to adapt by developing new skills in coding and blockchain technology to effectively draft, interpret, and manage smart contracts. This shift in skill sets presents both a challenge and an opportunity for the legal profession to evolve alongside technological advancements.
In conclusion, while smart contracts hold the promise of transforming the legal industry by streamlining processes and reducing costs, their implementation is not without significant legal challenges and considerations. Issues of enforceability, immutability, jurisdiction, data privacy, and the evolving role of legal professionals must be carefully addressed to harness the full potential of smart contracts. As the legal industry continues to adapt to these technological innovations, it is crucial for legal professionals to engage with these challenges proactively, ensuring that smart contracts are integrated into the legal framework in a manner that upholds the principles of justice and fairness.
Future Prospects: Smart Contracts And The Evolution Of The Legal Industry
The advent of smart contracts is poised to revolutionize the legal industry, offering a glimpse into a future where traditional legal processes are streamlined through technology. At their core, smart contracts are self-executing agreements with the terms of the contract directly written into lines of code. These contracts operate on blockchain technology, ensuring that once predetermined conditions are met, the contract is automatically executed. This innovation promises to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize the potential for human error, thereby transforming the way legal professionals approach contract management.
As we delve deeper into the implications of smart contracts for the legal industry, it becomes evident that their potential extends far beyond mere automation. One of the most significant advantages is the reduction in the need for intermediaries. Traditionally, legal contracts require the involvement of lawyers, notaries, and other third parties to ensure compliance and enforceability. Smart contracts, however, eliminate the necessity for such intermediaries by embedding trust and transparency directly into the code. This shift not only accelerates the contract execution process but also reduces the associated costs, making legal services more accessible to a broader audience.
Moreover, the immutable nature of blockchain technology ensures that once a smart contract is deployed, it cannot be altered. This feature provides an unprecedented level of security and reliability, as parties involved can be confident that the terms agreed upon will be executed without interference. Consequently, this could lead to a reduction in disputes and litigation, as the clarity and precision of smart contracts leave little room for misinterpretation. However, it is essential to recognize that while smart contracts offer numerous benefits, they also present new challenges for the legal industry.
One such challenge is the need for legal professionals to adapt to this technological shift. Lawyers will need to acquire a new set of skills, including a basic understanding of coding and blockchain technology, to effectively draft and interpret smart contracts. This requirement may initially pose a barrier to entry for some practitioners, but it also presents an opportunity for the legal industry to evolve and embrace innovation. By integrating technology into their practice, legal professionals can offer more efficient and cost-effective services, ultimately benefiting their clients.
Furthermore, the widespread adoption of smart contracts will necessitate changes in the regulatory landscape. As these contracts operate across borders and jurisdictions, there will be a need for standardized legal frameworks to govern their use. Policymakers and legal experts must collaborate to develop regulations that address issues such as data privacy, security, and enforceability, ensuring that smart contracts are used responsibly and ethically.
In conclusion, the future prospects of smart contracts in the legal industry are both promising and complex. While they offer the potential to streamline processes, reduce costs, and enhance security, they also require legal professionals to adapt and embrace new technologies. As the industry evolves, it will be crucial for stakeholders to work together to address the challenges and opportunities presented by smart contracts. By doing so, the legal industry can harness the power of technology to better serve its clients and meet the demands of an increasingly digital world.
Conclusion
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, are revolutionizing the legal industry by offering increased efficiency, transparency, and security. They reduce the need for intermediaries, minimize the risk of human error, and ensure automatic enforcement of contractual terms. However, their integration into the legal framework poses challenges, such as the need for new legal standards, addressing jurisdictional issues, and ensuring the code’s accuracy and fairness. As the legal industry adapts to these technological advancements, professionals must balance the benefits of automation with the complexities of legal interpretation and enforcement, ultimately reshaping the landscape of contract law.