Understanding the Power of DAOs: What They Can Achieve and Why

Introduction to Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
In a groundbreaking real estate deal in November 2021, a group of roughly 6,000 individuals joined forces online, using platforms like Discord, to acquire 40 acres of land in Wyoming. This transaction, devoid of a centralized governing body, operates through collective voting but without human intervention, epitomizing the essence of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs).
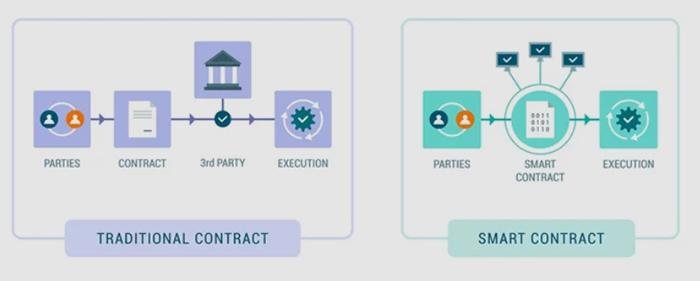
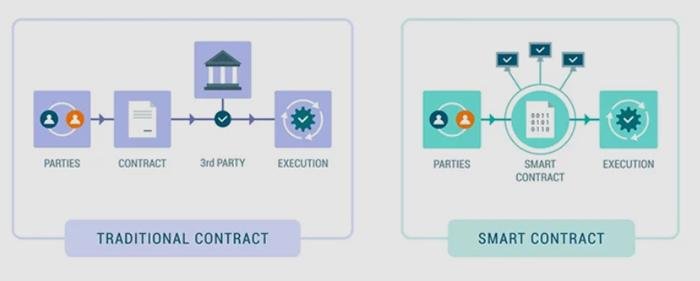
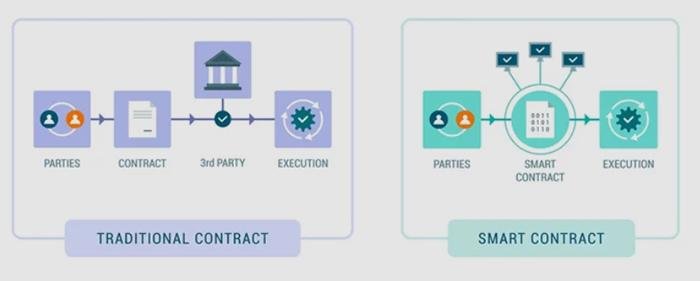
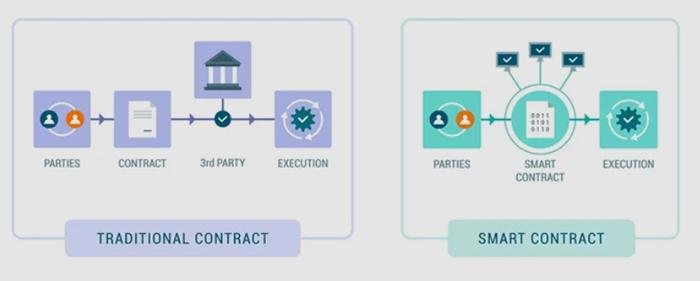
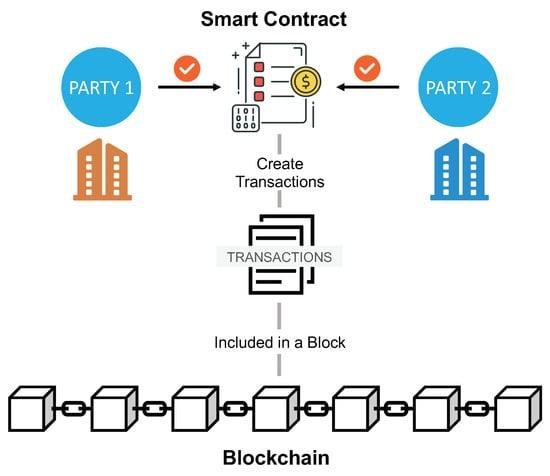
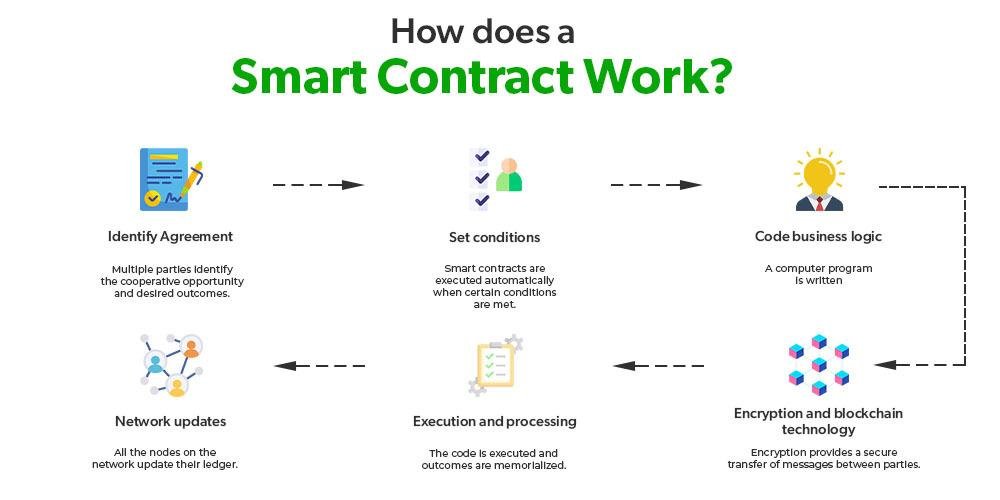
Deciphering DAOs DAOs, short for decentralized autonomous organizations, represent a novel class of digital entities. While bearing some resemblance to traditional company structures, DAOs distinguish themselves through the automated enforcement of operating rules via smart contracts. These unique features—central to their operations—facilitate democratic decision-making among members, eliminating the need for a single controlling authority.
Emergence and Experimentation
DAOs are in an exploratory phase, boasting fewer than 5,000 globally and only a handful exceeding $1 million in assets. Despite their nascent status, DAOs have ventured into diverse domains, from investing to supporting cultural assets and philanthropy. This experimental nature highlights their potential to revolutionize established organizational models.
Building DAO Frameworks
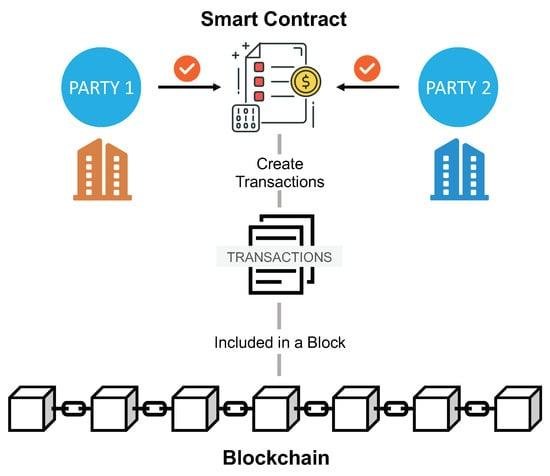
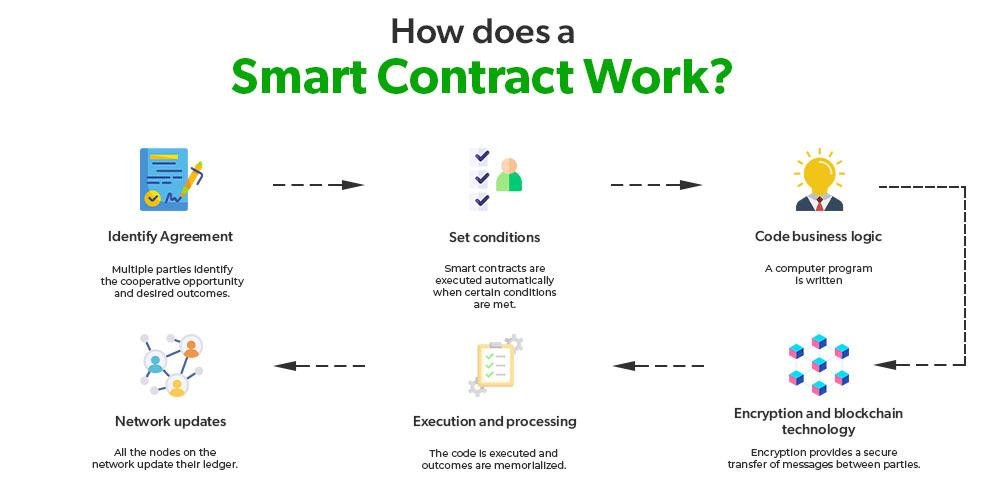
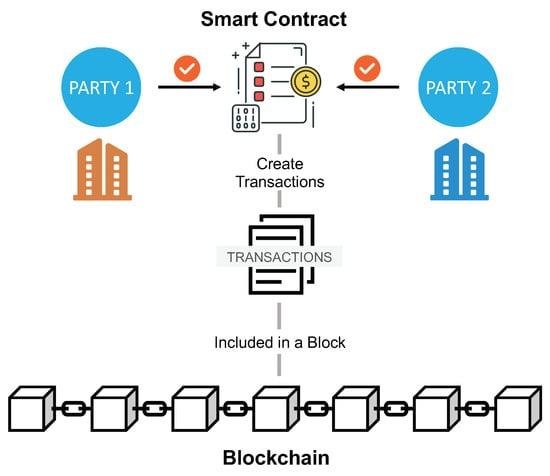
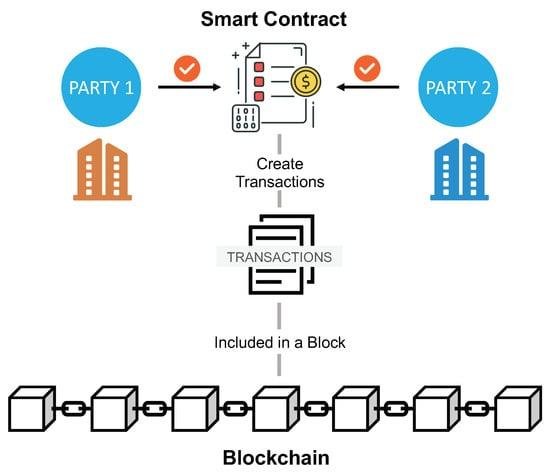
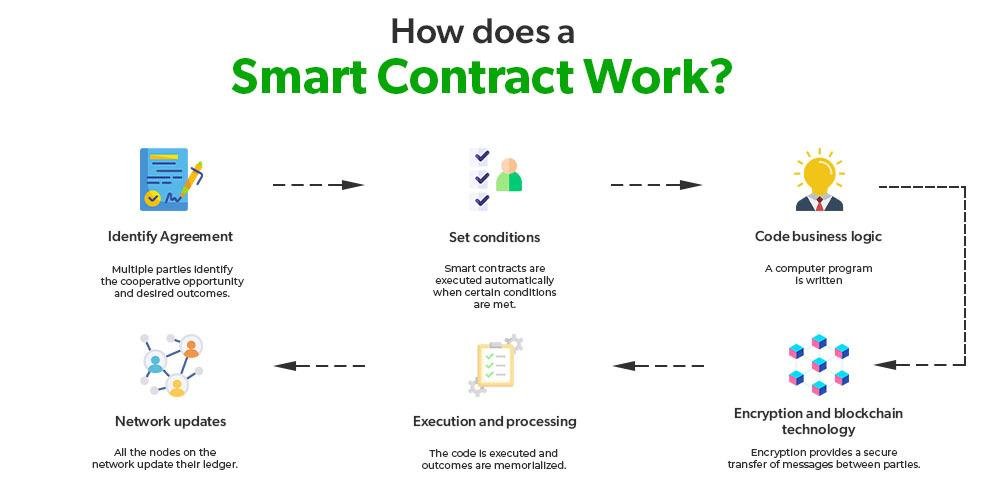
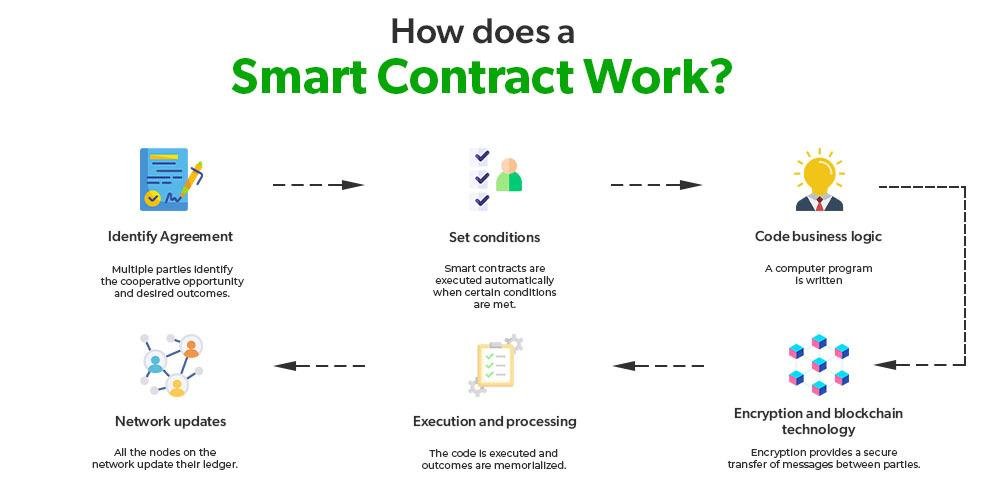
Originating from globally dispersed individuals rallying around a shared goal, DAO creation often stems from online platforms like Twitter or Discord. Transforming an idea into a functioning DAO involves developers crafting smart contracts forming the DAO’s core operating system. These self-executing programs autonomously execute decisions but are susceptible to security vulnerabilities due to their reliance on precise coding.
Funding and Operations
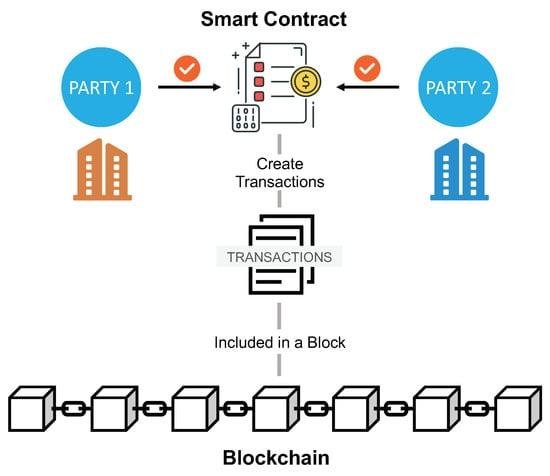
DAOs raise capital by issuing tokens tied to the smart contract, signifying ownership and governance rights. Once operational, decision-making shifts from creators to all members, requiring consensus on proposals through transparent voting mechanisms. However, the rigid smart contract-driven decision-making limits DAOs in adapting to rapidly evolving market dynamics.
Challenges and Legal Frontiers
Legally, DAOs navigate uncharted territory, facing uncertainties in taxation, contract legality, and jurisdictional complexities. Lacking identifiable attributes of traditional corporations poses challenges in legal recognition and formal business interaction. Nonetheless, Wyoming’s legislation, categorizing DAOs as a distinct form of LLC, suggests a potential path for legitimizing DAOs within legal frameworks.
Case Study:
CityDAO CityDAO, born from a tweet idea, aims to build a futuristic city on the Ethereum blockchain. Despite legal uncertainties, it succeeded in acquiring land in Wyoming, pioneering governance through NFT-based rights. The complexities of securities laws pose challenges, demanding careful navigation in unexplored territories.
Conclusion:
Shaping the Future DAOs won’t supplant traditional organizations but offer innovative prospects. Imagining hybrid models, and integrating smart contracts into conventional structures, remains promising. As Web3 unfolds, DAOs hold the potential to reshape group-level activities, sparking imagination about their role in the evolving business landscape.
FAQs
What is a DAO?
A decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) is an innovative concept that combines the power of blockchain technology with collective decision-making. Essentially, it is a self-governing entity that operates on a set of predetermined rules encoded in smart contracts.
How does a DAO work?
DAOs operate through consensus mechanisms, where token holders have voting rights to decide on various proposals and actions within the organization. These decisions are executed automatically based on the predefined rules embedded in the smart contract code.
Can anyone participate in a DAO?
Yes! One of the defining features of DAOs is their openness and inclusivity. Anyone with access to the internet can become a member or token holder in a DAO, allowing them to contribute ideas, vote on proposals, and even earn rewards for their participation.
Are DAOs secure?
While no system is entirely immune to security risks, DAOs leverage blockchain technology’s inherent transparency and immutability to enhance security measures. The use of smart contracts helps ensure that all transactions and governance actions within the organization are executed as intended without any possibility of external manipulation.
What can DAOs achieve?
DAOs have limitless potential across various industries and sectors. They can be used for decentralized crowdfunding campaigns (ICO), collaborative decision-making processes, managing digital assets collectively, creating decentralized applications (dApps), or even governing entire communities autonomously.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are revolutionizing how we think about organizational structures by enabling transparent decision-making processes powered by blockchain technology. With their open participation model and potential applications across diverse sectors, it’s clear that we’re only beginning to scratch the surface of what they can achieve.